Creatine
links: Amino Acid reference:
-
https://men-elite.com/2020/12/04/the-dopamine-dream-team-stack-try-this-for-laser-sharp-focus-and-euphoria/
- Increases mitochondrial membrane potential, reducecs intra-mitochondrial levels of reactive oxygen species amd calcium and maintained ATP levels.
- Reduces Homocysteine. 5-1-2021
Creatine
 #
#
-
Serum creatinine is an important indicator of kidney health.
-
Helps make Stomach Acid.
-
From Chris Masterjohn: “45% of your methylation demand is to synthesize creatine… there is at least one case study suggesting that someone with MTHFR mutation and really high homocysteine was able to cut the homocysteine in half using 5 grams of creatine per day.”
- Over 50% of SAM-derived methyl groups go to creatine.
-
Creatine supplementation reduces sleep need and homeostatic sleep pressure in rats
- NREM shows a 44% reduction in cerebral metabolic rate of glucose and a 25% reduction in the CMR of oxygen, while glucose and ATP concentrations increase.
-
A weak base with a pKa of 2.98, it needs strong acids.
-
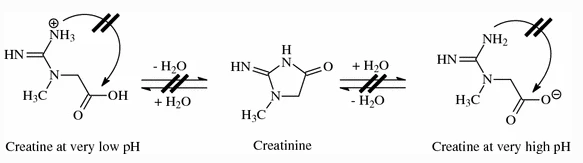 as you can see, it cyclicizes itself into Creatinine in solutions only when not too acidic (2.5) or not too alkaline. The monohydrate group, assuming it brings it to. Even though it shows a loss of H2O, this is indeed what happens in aqeuous solution.
as you can see, it cyclicizes itself into Creatinine in solutions only when not too acidic (2.5) or not too alkaline. The monohydrate group, assuming it brings it to. Even though it shows a loss of H2O, this is indeed what happens in aqeuous solution.
Metabolism #
- The creatine transporter transports it to all the organs.
- Degraded into creatinine at a constant rate depending on muscle mass.
- Or, it is converted to the active phosphocreatine via Creatine Kinase, using ATP. This essentially buffers phosphates such that ATP is less involved in inhibiting its own production via TCA.
Supplementation #
20g for 6 days = 18 $\pm$ 5 increase in muscle glycogen. R
Intranasal #
-
Creatine gluconate has the strongest neuroprotection. It bypasses the creatine transporter and promotes 3x an increase compared to monohydrate, or ~4x control.
- Nonetheless, insulin improves activity GLUT and creatine transporter.
-
Monohydrate is stable for a few days in water. Gluconate breaks down in <3 hours.
-
Creatine transporter deficiency impairs stress adaptation and brain energetics homeostasis
- Intranasal administration of Cr after cerebral ischemia increased the brain Cr/N-acetylaspartate ratio, partially averted the signaling imbalance, and reduced infarct size more potently than intraperitoneal Cr injection. (… a whopping 184mg/kg in mice.)
-
Creatine salts provide neuroprotection even after partial impairment of the creatine transporter