ABT-089
2023-10-10:
ABT-089 (Pozanicline) #
- α4β2 partial agonist.
- 16.7 nM for α4β2α5 nAChR vs 16.0 nM for α4β2 nAChR in rats.
- Weak α6β2β3 partial agonist, and even weaker α7 partial agonist / α3β4 nAChR antagonist.
- it’s unclear if a ligand with affinity towards a4b2 and not a6b2-types has been made yet
- α4α5β2
- a4b2 in adrenal glands should stimulate catecholamines
- Some studies on ADHD were shown to be ineffective. Stopped at phase 2. BUT, sirsad is still interested for other ‘cognitive benefit’. Improved visual working memory in nonhuman primates (delayed matching test) etc.
- Administration of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists ABT-089 and ABT-107 attenuates the reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior in rats
- See also other studies on α4β2 partial agonists, like Ispronicline (TC1734, AZD-3480):
-
Effects of TC-1734 (AZD3480), a selective neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist, on cognitive performance and the EEG of young healthy male volunteers
- Substantial cognitive benefit. U-shaped increase in performance with the word recall task, linear increase in digit vigilance (speed), picture recognition (sensitivity index), power of attention (speed), and quality of episodic memory.
- Pretty much linear increase in alpha ‘centroid’ and alpha peaks. Decrease in absolute delta and theta power.
-
Effects of TC-1734 (AZD3480), a selective neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist, on cognitive performance and the EEG of young healthy male volunteers
- [ABT-089: Pharmacological Properties of a Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist for the Potential Treatment of Cognitive Disorders]
- Administration of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists ABT-089 and ABT-107 attenuates the reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior in rats
- ABT-089, but not ABT-107, ameliorates nicotine withdrawal-induced cognitive deficits in C57BL6/J mice
- Central nicotinic receptor agonists ABT-418, ABT-089, and (–)-nicotine reduce distractibility in adult monkeys
-
Selectivity of ABT-089 for α4β2* and α6β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain
- ABT-089 had partial agonist activity (7-23% of nicotine) and high selectivity for α4α5β2 nAChR as evidenced by loss of activity in thalamus of α5-/- mice. ABT-089 stimulated [3H]-dopamine release (57%) exceeded the activity at α4β2 nAChR, that could be explained by the activity at α6β2* nAChR*
- Sirsad:A4b2 desensitization does occur but it’s at a much slower rate vs. nicotine, and additionally there is evidence showing benefit in chronic administration/ long lasting effect which may or may not be due to accumulation and downstream events as it occurs with all a4b2 ligands.
- visual memory improvement, as well as aspects of information processing speed being improved in primates and normal healthy people, respectively.
-
NEURONAL NICOTINIC RECEPTOR AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER: FOCUS ON COGNITION
-
ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys
- These relatively modest effects of ABT-089 under standard conditions can be increased dramatically when the monkeys perform the task in the presence of a visual distractor stimulus introduced during delay intervals. Under these conditions, ABT-089 completely reinstated normal performance: Central nicotinic receptor agonists ABT-418, ABT-089, and (-)-nicotine reduce distractibility in adult monkeys Methylphenidate is also active in the distractor model, although its effects are not as impressive as those obtained with ABT-089:
- Administered acutely, ABT-089 only marginally improved the spatial discrimination water maze performance of septal-lesioned rats. However, more robust improvement (45% error reduction on the last training day) was observed when ABT-089 was administered continuously
- Continuous infusion of (-)-nicotine produced comparable improvement in the spatial discrimination water maze performance of septal-lesioned rats, but a 40-fold higher dose of (-)-nicotine was required
- ABT-089 was efficacious at 1.3 – 4.0 μmol/kg/day (in rats) but not at a higher dose of 13 μmol/kg/day, resulting in a U-shaped dose response curve
-
ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine]: I. A potent and selective cholinergic channel modulator with neuroprotective properties
- ABT-089 has efficacy comparable to nicotine in evoking ACh release from rat hippocampal synaptosomes:
- ABT-089 is only about 70% as efficacious and 25-fold less potent than nicotine in inducing release of dopamine from striatal slices
- In contrast to nicotine and ABT-418, which activate dopaminergic neurons in ventral tegmental area (VTA) slices, ABT-089 was inactive in this assay at concentrations up to 10 μM
- Agonists at neuronal nAChRs can act postsynaptically to improve cognitive function but can also increase the release of a number of neurotransmitters involved in cognitive function The role of interactions between the cholinergic system and other neuromodulatory systems in learning and memory
- Was as efficacious as nicotine and slightly more potent than nicotine in inducing ACh release from prefrontal cortex in rats after local application: [Differential cholinergic “footprints” evoked by nicotine- and the a4β2*-selective partial agonist ABT-089 in prefrontal cortex]
-
ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys
-
ABT-089, a neuronal nicotinic receptor partial agonist, for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: results of a pilot study
- Improved spatial working memory, numeric working memory, and selective attention (reducing commission errors).
-
Double Dissociation of Nicotinic α7 and α4/β2 Sub-receptor Agonists for Enhancing Learning and Attentional Filtering of Distraction
- The alpha-7 nAChR agonist PHA-543613 selectively enhanced the learning speed of feature values but did not modulate how salient distracting information was filtered from ongoing choice processes. In contrast, the selective alpha-4/beta-2 nAChR agonist ABT-089 did not affect learning speed but reduced distractibility
- Prefrontal α7 and α4β2 receptors show a layer-specific expression profile with stronger α4β2 expression in thalamic recipient layer VI and α7 more prominent expression in layer V, which is rich in striatal projection neurons:
Layer-specific modulation of the prefrontal cortex by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
-
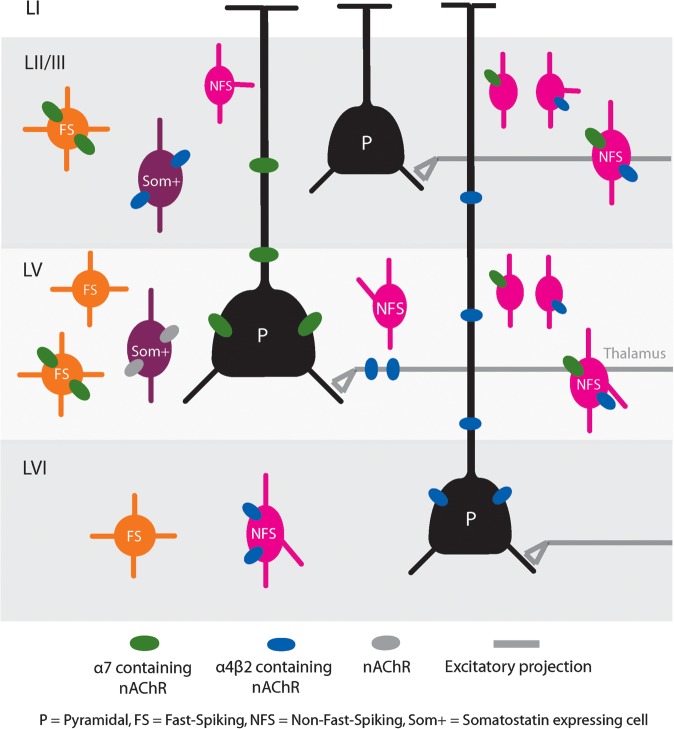
- In LII/III, only interneurons were activated. (and yet I see both nAChRs on the pyramidal spines?) Together, these results suggest that in the PFC nAChR activation results in inhibition of LII/III pyramidal neurons.
-
Dose #
- 2-4mg. Apparently 20 mg also works
- 77% bioavailability in monkeys. 32% in rats.
- Swiss says intranasal is tolerable, and that 2mg is comparable to the 20mg oral that he takes. At 8mg it also has focus improvements just like at 20mg (although be it mild), at 20mg it’s memory augmenting effects are acutely just much more noticeable
- U-shaped repsonse curve; any higher isn’t really any more efficacious?
- Half life of 1.7 hours, but sirsad says 24+ hour cognition enhancement for multiple of the α4β2 partial agonists:
- Long-lasting cognitive improvement with nicotinic receptor agonists: mechanisms of pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic discordance
- Machiney said it can last even for weeks.
- Anecdotes:
- The ABT dreams are really something else. Quite a bit stronger than TAK, and you remember them way longer… Judging by the dreams, there’s been no significant tolerance so far in 2 weeks of use
- Brendan: *better focus during the day and vivid dreams every night since I started it. Last night I travelled to and explored entire cities in foreign countries. 2mg in the morning works good. 4mg wasn’t noticeably better. *
- TreeSlayer: makes him more forgetful/absentminded like an absent-minded professor
- JC Denton: made him astral project one night.
- Reduces distractibility; confirmed by the literature.
- ‘Get shit done’ aggression