Nucleic Acid
2022-02-25: reference:
Nucleic Acid #
Just RNA (and its various types) and DNA.
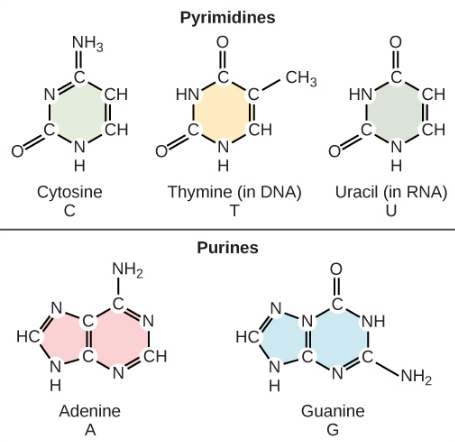
- The nucleobases are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and then DNA uses thymine, while RNA uses uracil.
-
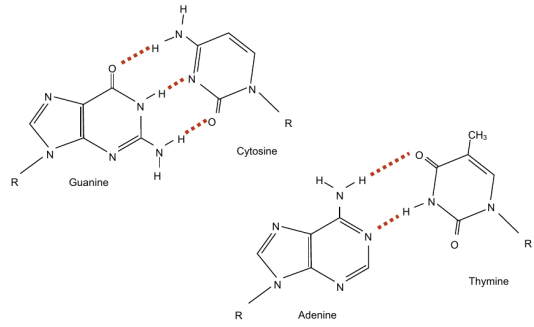
- Since G-C has 3 bonds instead of 2, it has a higher melting temperature than A-T. The stability is mainly due to molecular interactions of base stacking:
Base-stacking and base-pairing contributions into thermal stability of the DNA double helix
- Sometimes GC-content (proportion to AT/AU) of a nucleic acid molecule/gene/whatever is measured to do stuff like this being relevant.
- Some bacterial species with high GC undergo autolysis more readily in spite of the higher thermostability.
- Since G-C has 3 bonds instead of 2, it has a higher melting temperature than A-T. The stability is mainly due to molecular interactions of base stacking:
Base-stacking and base-pairing contributions into thermal stability of the DNA double helix
- Vertically, they consist of a (deoxy)ribose-phosphate backbone:
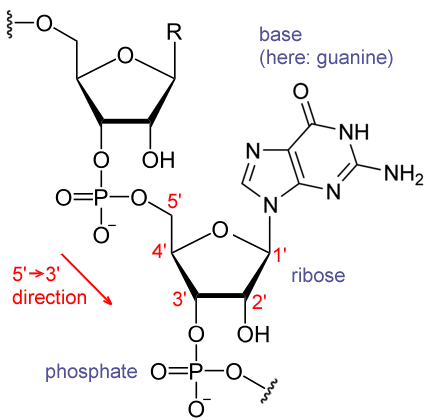 (DNA lacks the 2’ -OH groups)
(DNA lacks the 2’ -OH groups)
- The complementary strand goes in the 3’->5’ direction.
- In the context of transcription, the 5’->3’ is the template strand, the other the coding strand.
- Notice the negative charge on each phosphate. Because of this, gene delivery vectors use cationic liposomes and things like that.
- I don’t know the point, but there are up to 3 phosphates at least at certain oints.
- The complementary strand goes in the 3’->5’ direction.