Anthocyanidin
2023-05-21:
Anthocyanidin #
- (Not Anthocyanins, which are pigments found in a lot of berries and purple sweet potatoes)
- Anthocyanins are readily excreted, and in vivo enhancement of Antioxidant capacity of blood may just be from increased Uric Acid by metabolizing flavonoids! (I think Nemo said this)
-
Proanthocyanidins in grape seeds: An updated review of their health benefits and potential uses in the food industry
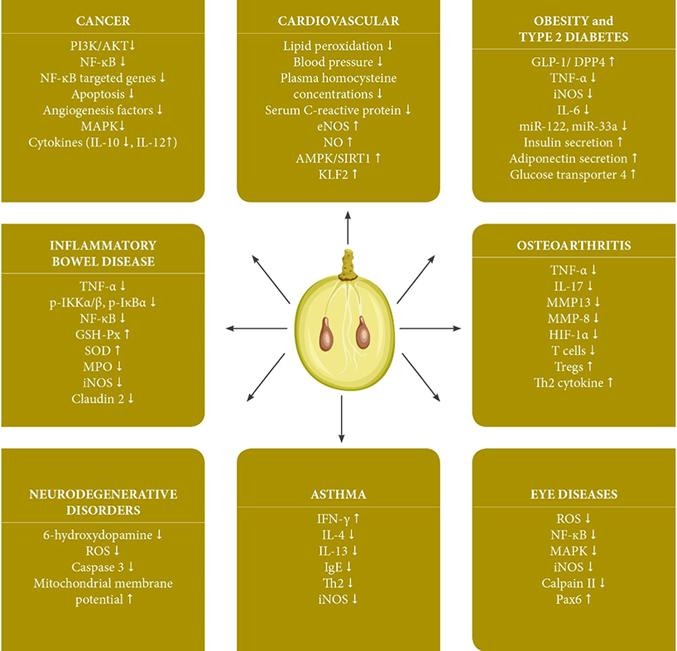 #Read
#Read - Grapes are among the richest sources of polyphenols.
- In grape skin and stems; the monomers are (+)-gallocatechin, (−)-epicatechin, (+)-catechin, and (−)-epicatechin 3-O-gallate. Whereas seeds are formed by (−)-epicatechin 3-O-gallate, (−)-catechin, and (+)-epicatechin. - The content of (+)-catechin and (−)-epicatechin is higher in the colored cultivars than in white grapes
- Can act as antinutrients by inhibiting digestive enzymes.
- [Epicatechin B-ring conjugates: First enantioselective synthesis and evidence for their occurrence in human biological fluids]
- Proanthocyanidin polymers might be able to transfer back into the small intestine via enterohepatic recirculation/bile excretion.
- bioavailability primarily relies on the degree of polymerization
- Increased Succinate Dehydrogenase activity
- The high number of hydroxyl groups in proanthocyanidins inhibits bacterial adhesion and coaggregation, reducing biofilm formation and decreasing inflammation