- Enter the nootroposphere:
- /r/NootropicsFrontline and the Rocketchat server
- /r/NooTopics and on Discord
- /r/Nootropics
- Bio_Tolerance on Discord
- See also:
- Nootropics · Gwern.net
- Biohacking Bible
- /r/prefrontal
- /r/remodeledbrain and https://remodeledbrain.com/
- http://www.scholarpedia.org/
- https://www.youtube.com/user/InquilineKea/playlists
- https://andrewtmckenzie.com/
- Fewer Lacunae | Distilled, Integrative Research
- Neruoskeptic
- The Brain From Top to Bottom
- NeuroLogos - YouTube
- MITCBMM - YouTube
- AJ Keefe - YouTube
- Some favorite foundational neuroscience resources:
- Principles of Neural Science (Kandel et al.)
- Psychopharmacology - Drugs, the Brain, and Behavior (Meyer et al.)
- Learning and Memory: A Comprehensive Reference, as well as Concise Learning and Memory (Byrne)
- The Prefrontal Cortex (Fuster)
- Tuning the Brain: Principles and Practice of Neurosomatic Medicine (Goldstein)
- Computational Cognitive Neuroscience (O’Reilly et al.)
- The Brain from Inside Out, as well as Rhythms of the Brain (Buzsáki)
- Principles of Brain Dynamics - Global State Interactions
- Unified Theories of Cognition (Newell)
- Mind and Tissue - Russian Research Perspectives on the Human Brain (Peat)
- Fundamentals to a Pharmacology of the Mind (Corneliu)
- The Cambridge Handbook of Intelligence and Cognitive Neuroscience
- Foundations of Neuroscience (Henley) - Medicine LibreTexts
- The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2013/14
- https://cosmicnootropic.com/blog/a-soviet-book-on-nootropics/
Pharmacopoeia
I’ll proceed to infodump all the relevant substances in the sphere. Read the wikipedia articles, some studies, and spend a bit of time reading anecdotes, and you’ll essentially be pretty caught up with the ‘canon’.
I’ve put personal ratings next to most of the noots I’ve personally taken, but bear in mind subjectivity yields ± a star or 2; no brain/organism is exactly alike and I won’t bother trying to be context-invariant. It’s also on a bit of a relative scale: by all means, I can’t wait for the day all the five-star things I’ve listed pale in comparison to certain future therapies.
I’ve also left out a fair bit of ‘supplements’; I want to focus on compounds with more brain-selective MOAs rather than improving general metabolism/health with cognition being downstream (not that that isn’t perfectly legitimate) as well as whatever pharmeceuticals such as antidepressants where incurring a net benefit is rather far from universal (the lack of side effects is a requirement for being a proper nootropic)
9-Me-BC
Controversy around potential toxicity.
ABT-089
-
α4β2 partial agonist.
- Weak α6β2β3 partial agonist, and even weaker α7 partial agonist / α3β4 antagonist (which further helps with nicotine cessation)
-
Some studies on ADHD were shown to be ineffective. Stopped at phase 2. Still may be promising for other cognitive benefits, like Improved visual working memory in nonhuman primates (delayed matching test) etc. It also significantly increases vivid/lucid dreaming.
-
See also other studies on α4β2 partial agonists, like Ispronicline (TC1734, AZD-3480):
- Effects of TC-1734 (AZD3480), a selective neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist, on cognitive performance and the EEG of young healthy male volunteers
- Substantial cognitive benefit. U-shaped increase in performance with the word recall task, linear increase in digit vigilance (speed), picture recognition (sensitivity index), power of attention (speed), and quality of episodic memory.
- Pretty much linear increase in alpha ‘centroid’ and alpha peaks. Decrease in absolute delta and theta power.
- Effects of TC-1734 (AZD3480), a selective neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist, on cognitive performance and the EEG of young healthy male volunteers
-
[ABT-089: Pharmacological Properties of a Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist for the Potential Treatment of Cognitive Disorders]
-
Selectivity of ABT-089 for α4β2* and α6β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain
- ABT-089 had partial agonist activity (7-23% of nicotine) and high selectivity for α4α5β2 nAChR as evidenced by loss of activity in thalamus of α5-/- mice. ABT-089 stimulated [3H]-dopamine release (57%) exceeded the activity at α4β2 nAChR, that could be explained by the activity at α6β2* nAChR*
-
- ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys
- These relatively modest effects of ABT-089 under standard conditions can be increased dramatically when the monkeys perform the task in the presence of a visual distractor stimulus introduced during delay intervals. Under these conditions, ABT-089 completely reinstated normal performance: Central nicotinic receptor agonists ABT-418, ABT-089, and (-)-nicotine reduce distractibility in adult monkeys Methylphenidate is also active in the distractor model, although its effects are not as impressive as those obtained with ABT-089:
- Administered acutely, ABT-089 only marginally improved the spatial discrimination water maze performance of septal-lesioned rats. However, more robust improvement (45% error reduction on the last training day) was observed when ABT-089 was administered continuously
- Continuous infusion of (-)-nicotine produced comparable improvement in the spatial discrimination water maze performance of septal-lesioned rats, but a 40-fold higher dose of (-)-nicotine was required
- ABT-089 was efficacious at 1.3 – 4.0 μmol/kg/day (in rats) but not at a higher dose of 13 μmol/kg/day, resulting in a U-shaped dose response curve
- ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine]: I. A potent and selective cholinergic channel modulator with neuroprotective properties
- ABT-089 has efficacy comparable to nicotine in evoking ACh release from rat hippocampal synaptosomes:
- ABT-089 is only about 70% as efficacious and 25-fold less potent than nicotine in inducing release of dopamine from striatal slices
- In contrast to nicotine and ABT-418, which activate dopaminergic neurons in ventral tegmental area (VTA) slices, ABT-089 was inactive in this assay at concentrations up to 10 μM
- Agonists at neuronal nAChRs can act postsynaptically to improve cognitive function but can also increase the release of a number of neurotransmitters involved in cognitive function The role of interactions between the cholinergic system and other neuromodulatory systems in learning and memory
- Was as efficacious as nicotine and slightly more potent than nicotine in inducing ACh release from prefrontal cortex in rats after local application: [Differential cholinergic “footprints” evoked by nicotine- and the a4β2-selective partial agonist ABT-089 in prefrontal cortex]
- ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys
-
- Improved spatial working memory, numeric working memory, and selective attention (reducing commission errors).
-
- The alpha-7 nAChR agonist PHA-543613 selectively enhanced the learning speed of feature values but did not modulate how salient distracting information was filtered from ongoing choice processes. In contrast, the selective alpha-4/beta-2 nAChR agonist ABT-089 did not affect learning speed but reduced distractibility.
- Prefrontal α7 and α4β2 receptors show a layer-specific expression profile with stronger α4β2 expression in thalamic recipient layer VI and α7 more prominent expression in layer V, which is rich in striatal projection neurons: Layer-specific modulation of the prefrontal cortex by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
-
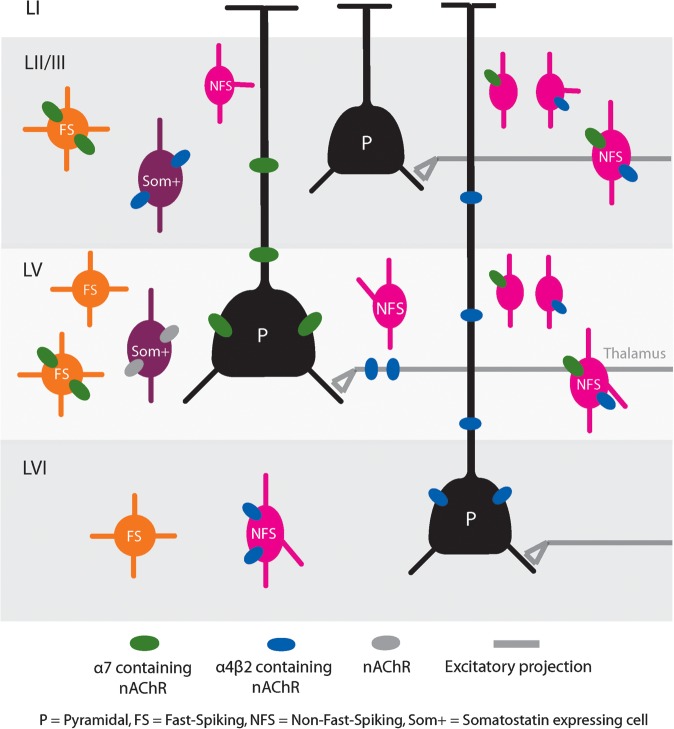
- In LII/III, only interneurons were activated. (and yet I see both nAChRs on the pyramidal spines?). Together, these results suggest that in the PFC nAChR activation results in inhibition of LII/III pyramidal neurons.*
-
-
Half life of 1.7 hours, but apparently 24+ hour cognition enhancement is seen for multiple of the α4β2 partial agonists:
Dose: ~2mg intranasal may be the best. It is orally bioavailable, but there are multiple anecdotes of similar oral doses not yielding comparable effects, instead needing ~8-20mg.
Random α4β2 notes
- Estradiol is a PAM. Zinc potentiates α4-containing somehow.
- Selective a4b2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists Target Epigenetic Mechanisms in Cortical GABAergic Neurons
- Stimulation is associated with Growth Hormone secretion.
- Association of a Nicotinic Receptor Mutation with Reduced Height and Blunted Physostigmine-Stimulated Growth Hormone Release
- People with the inactive CHRNA4 mutation Ser248Phe are an average of 10 cm (4 inches) shorter than average and predisposed to obesity
- Association of a Nicotinic Receptor Mutation with Reduced Height and Blunted Physostigmine-Stimulated Growth Hormone Release
- Stimulation of dopamine release by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands in rat brain slices correlates with the profile of high, but not low, sensitivity α4β2 subunit combination (i.e. stimulating α4₃β2₂)
Structure
- Can have 3 or 2 of each: α4₂β2₃$ has high sensitivity to Nicotine, lower sensitivity to acetylcholine, and a low Ca2+ permeability relative to $α4₃β2₂$ (which has another binding site)
- So what does that even tell us about the net effect of nicotine administration? No idea really.
- Two distinct allosteric binding sites at α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors revealed by NS206 and NS9283 give unique insights to binding activity-associated linkage at Cys-loop receptors
Subtypes
-
-
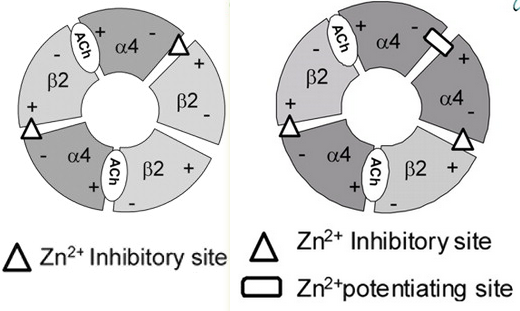
Additional Acetylcholine (ACh) Binding Site at α4/α4 Interface of (α4β2)2α4 Nicotinic Receptor Influences Agonist Sensitivity in other words, just $α4₃β2₂$.
- Notice the isoform-specific β2-β2 vs α4-α4 interfaces:
- Agonist occupation of the α4(+)-α4(-) interface leads to channel gating. α4-α4 contains a Zn2+ site that either inhibits or potentiates depending on its concentration, whereas the β2-α4 homology is only an inhibitory site.
- Previously: Non-Agonist-Binding Subunit Interfaces Confer Distinct Functional Signatures to the Alternate Stoichiometries of the α4β2 Nicotinic Receptor: An α4–α4 Interface Is Required for Zn2+ Potentiation
- Zn2+ inhibition is voltage-dependent on (α4)2(β2)3 but not on (α4)3(β2)2.
- Previously: Non-Agonist-Binding Subunit Interfaces Confer Distinct Functional Signatures to the Alternate Stoichiometries of the α4β2 Nicotinic Receptor: An α4–α4 Interface Is Required for Zn2+ Potentiation
- Agonist occupation of the α4(+)-α4(-) interface leads to channel gating. α4-α4 contains a Zn2+ site that either inhibits or potentiates depending on its concentration, whereas the β2-α4 homology is only an inhibitory site.
- Notice the isoform-specific β2-β2 vs α4-α4 interfaces:
Desensitization
- Regulation of α4β2 Nicotinic Receptor Desensitization by Calcium and Protein Kinase C
- After prolonged nicotine treatment, α4β2 nAChRs accumulate in a “deep” desensitized state, from which recovery is very slow. We suggest that PKC-dependent phosphorylation of α4 subunits changes the rates governing the transitions from “deep” to “shallow” desensitized conformations and effectively increases the overall rate of recovery from desensitization. Long-lasting dephosphorylation may underlie the “permanent” inactivation of α4β2 receptors observed after chronic Nicotine treatment
- PKC enhanced rate of recovery: α4β2 receptors containing a mutant α4 subunit that lacks a consensus PKC phosphorylation site exhibited little recovery from desensitization.
- Recovery from desensitization of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of rat chromaffin cells is modulated by intracellular calcium through distinct second messengers
- Desensitization of nAChRs, evoked by 2 sec focal application of nicotine, which largely raised [Ca2+]i, was not affected by intracellular application of agents that activate or depress protein kinase C (PKC) or A (PKA) or inhibit phosphatase 1, 2 A and B.
Expression
- Located on MSNs. Not sure where else it’s mostly expressed besides the stritum. Both post- and pre-synaptic.
- Higher availability of α4β2 nicotinic receptors (nAChRs) in dorsal ACC is linked to more efficient interference control
- Finds itself on GABAergic neurons in the VTA.
α4β2α5
-
- Suggests a regulatory role for α5 nAChR?
- Subunit Composition and Pharmacology of Two Classes of Striatal Presynaptic Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Mediating Dopamine Release in Mice
- α5 nAChR knockout: diminished nicotine-sitmulated dopamine release
- The β2 subunit is an absolute requirement for both classes. In contrast, deletion of β4 or α7 subunits had no effect
- Virtually all of the α5-containing nAChRs in the rat hippocampus, striatum, cerebral cortex, and thalamus are α4β2α5 nAChRs.
- The α5 subunit is associated in ~37% of the nAChRs in the hippocampus, ~24% of the nAChRs in striatum, and 11–16% of the receptors in the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and superior colliculus.
- The fact that this resistance to up-regulation was seen in four different brain regions, suggests that it is the presence of the a5 subunit, rather than factors such as specific brain region or cell type that confers this property on a4b2a5 receptors in vivo.
- Density is not even increased by chronic administration of nicotine.
- Nicotine-induced increases in nAChRs in brain or neuronal cell lines are not accompanied by changes in subunit mRNAs, nor is de-novo protein synthesis of nAChR subunits required (Penget al.1994; Wanget al.1998).
- Therefore, studies of the mechanisms underlying nicotine-induced up-regulation of nAChRs have focused on post-translational changes, including:
- Increased assembly of the subunits intoreceptors (Wanget al.1998; Nashmiet al.2003)
- The much higher level of nicotine-induced up-regulation in most transfected cells may result from the constant driving force of their constitutively active promoter leading to over-expression of nAChR subunits. Thus, the large nicotine-induced increase in nAChRs seen in most transfected celllines may reflect, to a large extent, enhanced assembly and/orincreased maturation of nascent nAChR oligomers formedfrom excess subunits and, to a lesser extent, decreased receptor degradation.
- Decreased degradation of the receptors (Peng et al.1994;Wang et al.1998)
- In brain, where a large excess of subunits is less likely to be the norm, this may be a more important mechanism.
- α4β2 is perhaps rapidly regraded, while nicotine slows this, leading to upregulation (demonstrated in Peng et al.1994; Kuryatov et al.2005), and α5 may slow this down.
- In brain, where a large excess of subunits is less likely to be the norm, this may be a more important mechanism.
- Increased maturation of nascent receptors (Kuryatovet al.2005;Salletteet al.2005)
- Conversion of receptors from alow affinity to a high affinity conformation (Buisson andBertrand 2001; Vallejoet al.2005).
- Increased assembly of the subunits intoreceptors (Wanget al.1998; Nashmiet al.2003)
- Therefore, studies of the mechanisms underlying nicotine-induced up-regulation of nAChRs have focused on post-translational changes, including:
-
α5 lacks a Y190 residue found in all other a subunits (Karlin and Akabas 1995), and without this residue it probably cannot contribute to an agonist binding site.
- In fact, although α5 has the two cysteine residues at approximately positions 192 and 193 that are common to all nAChR α subunits, it has highest sequence homology with the b3 subunit (Boulter et al. 1990). Thus, the a5 and b3 subunits may represent a branch point at which these two classes of subunits diverged.
- Interestingly, the presence of β3 in α6β2β3 provides resistance to downregulation by nicotine.
- In fact, although α5 has the two cysteine residues at approximately positions 192 and 193 that are common to all nAChR α subunits, it has highest sequence homology with the b3 subunit (Boulter et al. 1990). Thus, the a5 and b3 subunits may represent a branch point at which these two classes of subunits diverged.
-
- Increased Ca2+ conductance several fold vs. regular α4β2.
- α4, α5, and β3 subunits all have a homologous glutamate in M2 that contributes to high Ca2+ permeability, whereas β2 has a lysine at this position.
- We show that Ca2+ permeability is determined by charged amino acids at the extracellular end of the M2 transmembrane domain
- Increased Ca2+ conductance several fold vs. regular α4β2.
Agmatine
Rating: ★★. Helps misophonia, probably from antagonizing eNMDAR (due to being a polyamine site antagonist). eNOS giving you better pumps while antagonizing iNOS and nNOS is really unique as well. I can attest to it being somehow vaguely therapeutic for depression. It’s not too bad of a general supplement, but it’s not all good either (CB1 agonism, nAChR antagonism, PPAR, β-oxidation, etc.)
-
https://men-elite.com/2020/05/22/agmatine-an-absolutely-amazing-amino-acid-for-your-whole-body/
-
Oxidative stress-induced nNOS deactivation: Agmatine enhances the NADPH oxidase activity of neuronal NO synthase and leads to oxidative inactivation of the enzyme I mean, I wonder if it’s a net negative in terms of NOS activity?
-
Agmatine acts as an antagonist of neuronal nicotinic receptors.
-
The molecular and metabolic influence of long term agmatine consumption (Nissim et al., 2014)
ALCAR
I personally never bothered with it due to the anti-thyroid/pro-FAO and pro-cortisol effects of carnitine.
-
Upregulates D1 without acute dopamine increase or D2 upregulation; ALCAR upregulating D1 increases PKA→CREB, which seems meh at first but apparently ALCAR does NOT activate ΔFosB or CDK5:
Amphetamine
Rating: ★★★. I’m scared it destroys your brain and that I would become addicted, but with the few times in my life I’ve tried it, it made studying advanced topics as effortless as reading the morning paper and yet more engaging than they’ve ever been (this is not news to anyone who knows the slightest thing about adderall) so one simply cannot dock too many points. In fact I think stacking it with (afaik yet-to-exist) compounds that abolish neurotoxicity (such was the dream with antioxidants like Deferoxamine, SkQ1, and Selegiline) is a possible route to ’nootropic escape velocity’. (Related is the study of MDMA by QRI, et al. which is a whole different monster)
- https://www.astralcodexten.com/p/know-your-amphetamines
- Sensitization/upregulation of dopamine via microdosing stimulants - a viable strategy? is this real?
- Leo’s Biohacking Protocol To Make His Adderall Prescription More Effective
- The rationale behind how amphetamines are prescribed is suboptimal and (more) unsustainable. Instant release and low doses (<10 mg, but even just a few mg is efficacious) is preferable.
- Cycle off at least weekly, adding in GDNF and PGC-1α activators to repair oxidation, and σ1 agonists.
Dextroamphetamine
Stick with this. More dopaminergic and mental without the peripheral side effects.
Methamphetamine
The neuroprotective potential of low-dose methamphetamine in preclinical models of stroke and traumatic brain injury HED = 0.08 mg/kg = ~5.5mg.
Ashwagandha
Like most herbals, it does way too many things. I wouldn’t fuck with it.
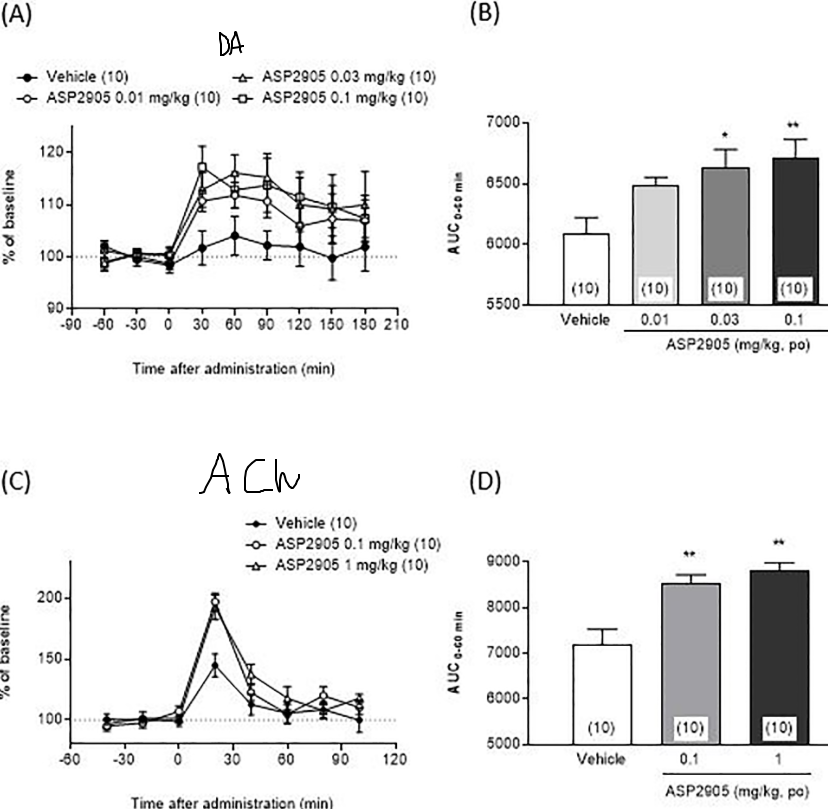
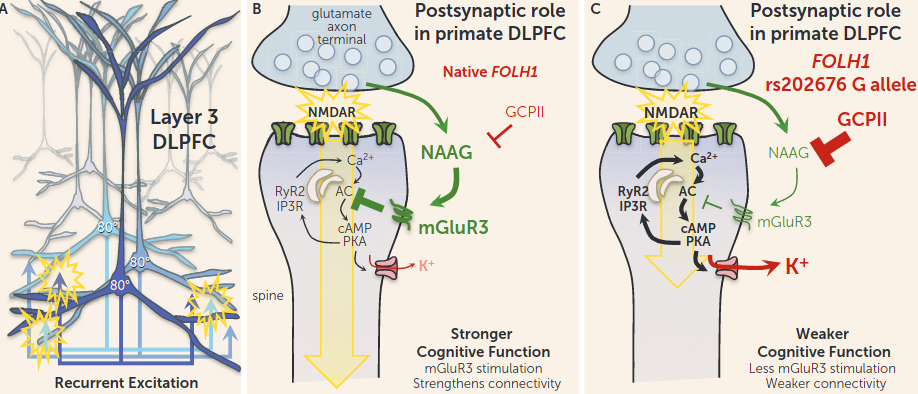
ASP2905
KCHN3 inhibitor, which is concentrated in the frontal lobe. This potentiates the recurrent excitation of delay neurons via preventing K+ efflux out of the dendritic spine in the PFC, a central component of working memory (cf. Amy Arnsten’s research on the dlPFC, guanfacine, etc.):
-
-
- Inhibited meth-induced hyperlocomotion, but did not affect spontaneous locomotion.
- Treats certain symptoms of Schizophrenia
-
- KCNH3 overexpression in mice is associated with cognitive deficits, and knockout mice exhibit enhanced performance in attention.
- Increased efflux of Dopamine and Acetylcholine in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex.
-
-

Anecdote: methylphendate-like headspace.
ASP4345
D1 PAM.
Atomoxetine
- NET inhibitor. The thing about this is that NET is responsible for Dopamine reuptake in the Prefrontal Cortex (where DAT expression is minimal) rather than striatum/NAcc like traditional stims.
- NMDA antagonist (to some extent). Possible μ antagonist? Yeah, I think it has some off-target effects. Liver toxic. How fun. See reboxetine instead.
- Altered gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of young rats induced by the ADHD drug atomoxetine (Lempp et al.)
Bacopa
- AChEi, ChAT activation, monoamine potentiation, lowers blood pressure.
Brilliant Blue G
P2x7 antagonist.
- Completely suppresses Amyloid β-induced neuronal death, while not affecting APP cleavage, via inhibiting the NLRP inflammasome.
- Brilliant Blue G improves cognition in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease and inhibits amyloid-β-induced loss of filopodia and dendrite spines in hippocampal neurons (2014)
- Amyloid β-induced loss of filopodia and spine density in cultured hippocampal neurons was prevented… BBG prevents the learning and memory impairment and cognitive deficits induced by the toxicity of soluble Aβ, and improves the development of dendritic spines in hippocampal neurons in an Alzheimer’s model mouse.
P2X7
-
ATP receptor; ionotropic. Found in microglia, macrophage, retina, endometrium.
- Requires higher ATP levels than other P2X, but response is potentiated by reducing concentration of divalent cations, as they block it.
- Some P2X receptors rapidly desensitize ATP, while ones like P2X2 remain open as long as ATP is bound.
- Technically, ADP and AMP are weak agonists.
- The ionotropic ATP receptor subunits P2X1–6 receptors play important roles in synaptic transmission, yet the P2X7 receptor has been reported as absent from neurons in the normal adult brain. R
- Requires higher ATP levels than other P2X, but response is potentiated by reducing concentration of divalent cations, as they block it.
-
Usually a dimer but can form heteromers with a few other P2X subunits.
-
Activation leads to recruitment of Pannexin to form Panx1, a Ca2+-gated ATP export channel.
-
K+ efflux→PAF→NEK7 (NIMA-related kinase), binding to and activating NLRP3.
- Nek7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux
- So how the hell does intracellular potassium of all things disinhibit this binding of Hek7?
-
A2A is the entry point from which cumulative sleep deprivation (ie aging/time passing) upregulates P2X7. P2X] also upregulates A2A, so it’s a positive feedback loop. ATP release from extended P2X7 activation also activates P2X7, more positive feedback loop. This whole area is a ripe target.
-
- Activation of the purinergic P2X7 receptors is necessary and sufficient to convert maternal immune activation (MIA) to Autism-like features in male offspring mice.
-
Hyperactivation of P2X7 receptors as a culprit of COVID-19 neuropathology
-
P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Extracellular ATP
- The Elusive P2X7 Macropore
- Extracellular ATP causes reversible permeabilization of mammalian cell plasma membranes due to P2X7R-dependent formation of a large conductance pore (the ‘macropore’).
- Cholesterol in Lipid Rafts inhibits P2X7R-associated permeability increases. Palmitoylation opens it.
- Regulation of P2X Purinergic Receptor Signaling by Cholesterol
- Defects in the C-terminal inhibited plasma expression of the receptor, probably leading to ubiquination.
- The activation of Acid Sphingomyelinase in microglia cells was shown to be necessary for P2X7 receptor-dependent microvesicle shedding and the release of IL-1β: Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells
- This causes a positive feedback mechanism as Ceramide and other sphingolipid is then able to displace cholesterol.
- This is not directyl related to obesity: The ATP-P2X7 signaling axis is dispensable for obesity-associated inflammasome activation in adipose tissue
- In macrophages, the synthesis of Leukotrienes through activation of PLA2 and mobilization of arachidonic acid is required for the P2X7-mediated reduction in the parasitic load of infected cells.
- Inhibition of connexin 43 hemichannel-mediated ATP release attenuates early inflammation during the foreign body response
Neurogenesis
- As a ‘pattern recognition receptor’, its function is perhaps recognizing malformed/damaged neurons in response to extracellular ATP activity on Microglia. This is how cohesive connections are assessed during Neurogenesis. In highly neuroinflammatory states (like Alzheimer’s?) this process “feed forward”.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pattern_recognition_receptor also includes TLR, and some other things (CLR, RLR, NLR/NLRP).
- The role of P2X7 receptors in a rodent PCP-induced schizophrenia model
- P2X7 knockout in mice promotes defects in cognition and social activity. IT Doubles surface expression of NR2A and NR2B.
- Impaired interleukin-1beta and c-Fos expression in the hippocampus is associated with a spatial memory deficit in P2X(7) receptor-deficient mice
- immature neurons fire much more quickly and are more disinhibited and have a much higher p2x7 receptor expression than should mature neurons. Increased p2x7 activity should disinhibit young neurons and that would be responsible for increased plasticity in young neurons but it also contributes to cell death
Bromantane
Rating: ★★★. Never noticed much besides an increase in verbal fluency, especially since the benefits are long-lasting.
- https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/11n3m3g/an_update_to_the_literature_of_bromantane/, https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/ufdwng/bromantane_spray_research_dump_shipping_prices/, https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/sfisay/a_breakdown_on_bromantane_nasal_spray/, https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/pyyuwz/finally_elucidating_the_mysterious_bromantane/
Its primary action is upregulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase, AADC, and increasing GDNF (possibly via HDAC1 inhibition, extrabolating from the other adamantane-containing drugs like amantadine and memantine). PDE10 inhibitor. GAT-3 inhibitor in high doses. Possible inhibitor of Kir2.1.
- Mechanisms of Action of Ladasten: Activation of Gene Expression for Neurotrophins and Mitogen-Activated Kinases
- This paper suggests the increase in striatum BDNF and following ERK1/2 expression underlies Bromantane’s long-term dopaminergic effects
- Time Course of Histone Deacetylase 1 and Acetylated H3 and H4 Histones in the Brain of Rats Treated with Ladasten
- Effects of ladasten on dopaminergic neurotransmission and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in rats
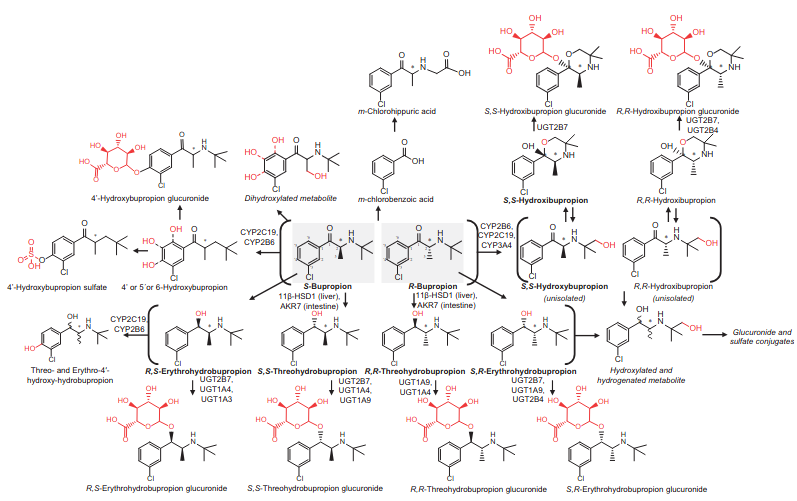
Bupropion
Some bad some good.
- Atypical antidepressant. NET/DAT (in high doses) inhibitor and non-competitive antagonist of α4β2, α3β4, and α1β1γδ.
-
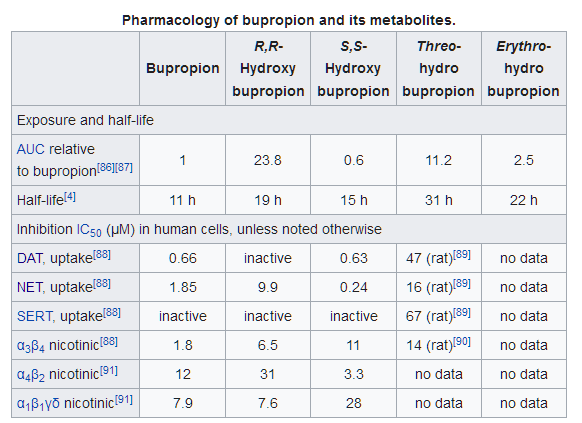
- Compare to dl-Methylphenidate’s DAT/NET IC50 of 20 and 51 respectively (.35 vs .39 ratio). The difference is in the metabolites as you can see.
-
- Associated with a high risk of release of mediators from mast cells. I don’t think it activates H1 though.
- Psychopharmacology of bupropion in normal volunteers.
- α3β4 nAChR antagonism isn’t cognitively impairing.
- [Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic of bupropion: integrative overview of relevant clinical and forensic aspects]
- Dwoskin (2006) can exacerbate depression and increase suicidal thoughts.
- Should be administered early in the morning as it exacerbates insomnia.
- Vivid dreams, hallucinations, unusual thoughts/behavior, confusion, tremors, agitation, anxiety, swollen glands, joint pain, increased blood pressure
- Inhibits CYP2D6 (58 mM IC50?)
- [Seizures after overdoses of bupropion intake]
- Pronounced increase in catecholamines is the main factor, I believe. QT prolongation can be seen.
- [Alcohol significantly lowers the seizure threshold in mice when co-administered with bupropion hydrochloride]
- In mice, 116mg/kg (660 HED) without, or 89.4 for ethanol/bupropion.
- Bupropion increases striatal vesicular monoamine transport
- Rapidly, reversibly, and dose-dependently increased vesicular DA uptake; an effect also associated with VMAT2 protein redistribution.
- Molecular interaction of bupropion with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- Where in the brain it binds is important: binds to presynaptic α4β2 on GABAergic neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area and α3β4 nAChR in the habenulo-intrerpeduncular pathway.
- Bnding affinity for α4 is rougly equal to α1.
- Recent Developments in Novel Antidepressants Targeting α4β2-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Acute effect of the anti-addiction drug bupropion on extracellular dopamine concentrations in the human striatum: An 11C raclopride PET study
- Bupropion , 100 mg, had no effect alone but abolished the sedation and auditory vigilance impairment produced by alcohol when co-administered.
Caffeine/Coffee (Coffeine)
Rating: ★★★★. Pure Wakefulness is capable of eliciting divine euphoria and connection to the universe, and I thrive on the noradrenergic drive it gives, BUT I think the long-term effects on the brain are questionable. I am currently taking a break until further notice.
- Antagonizes the IP3 receptor, competitive antagonist of the ionotropic Glycine Receptor, and voltage-independent activator of the ryanodine receptors.
- Antagonizing Adenosine A1-D1 heterodimers increases release of dopamine in the dorsal Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens core (not shell).
- Adenosine is a vasodilator?
- Moderate inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase R R
- Increases BDNF in the Hippocampus
- Activatives Histaminergic neurons?
- Suppressess TRPA1
- Prevents or even reverses various forms of Fibrosis in the liver. R
- Reduces atherogenesis R
- Caffeine increases striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor availability in the human brain
- Caffeine inhibits exercise-induced increase in tryptophan hydroxylase expression in dorsal and median raphe of Sprague-Dawley rats Red Ginseng also does this. Idk mechanism
- Enhances Estrogen metabolism/detox R
- By competing for the Cytochrome P450 oxidase system, can inhibit clearance of Estrogen from the Liver? R
- Caffeine does not entrain the circadian clock but improves daytime alertness in blind patients with non-24-hour rhythms
- Caffeine reduces low-frequency delta activity in the human sleep EEG
- Delta waves
- Ergogenic effects of caffeine are mediated by myokines - via being an Ca2+ ionophore andor AMPK activator, enhancing secretion of Myokines.
- Increases IL-6 in skeletal Muscle and blood but not the liver of mice. But, the IL-6 in skeletal muscle alleviates rodent model NAFLD.
- [Caffeine enhances acetylcholine release in the hippocampus in vivo by a selective interaction with adenosine A1 receptors.]
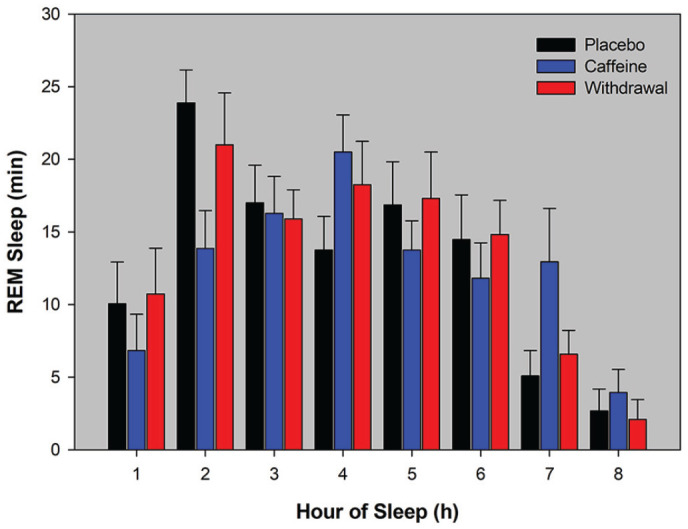
- Regular Caffeine Intake Delays REM Sleep Promotion and Attenuates Sleep Quality in Healthy Men
- 20 male coffee consumers who reported 478 +- 102.8 mg/day: they were given 3x150 mg for 10 days, or 3x150 mg caffeine for 8 days then placebo (for the last 2 days I suppose)
-
- The effect of caffeine on working memory load-related brain activation in middle-aged males
- Load-related encoding activation was greater in the DLPFC, and lower in the thalamus.
- [Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptors mediate the arousal effect of caffeine]
- Increased wakefulness in wild-type and A1 knockout, but not in A2A knockout.
- Chronic Caffeine Alters the Density of Adenosine, Adrenergic, Cholinergic, GABA, and Serotonin Receptors and Calcium Channels in Mouse Brain
- Saw no A2A upregulation!
- In platelets, neutrophils, etc. it is upregulated, but that’s different from the brain. What’s more significant is other studies on the brain.
- [A1 and A2A adenosine receptors and A1 mRNA in mouse brain: effect of long-term caffeine treatment (1997)]
- Upregulated A2A in the striatum
- [A1 and A2A adenosine receptors and A1 mRNA in mouse brain: effect of long-term caffeine treatment (1997)]
- In platelets, neutrophils, etc. it is upregulated, but that’s different from the brain. What’s more significant is other studies on the brain.
- 5-HT1 and 5-HT2: +26-30%
- mAChR & nAChR: +40-50%
- Benzodiazepine-binding site: +65%, and slightly decreased affinity.
- Density of cortical nitrendipine-binding sites in Calcium Channels: +18%.
- Saw no A2A upregulation!
Cerebrolysin/Cortexin
As a vegan I haven’t exactly bothered into looking into it too much, but there’s a lot of info and anecdotes on the NooTopics discord server. (This goes for most things).
It’s pretty infamous for a certain Longecity thread where he was convinced prions were giving him strange autoimmune reactions. There have been absolutely zero reports of this in the literature. The presence of prions is impossible: prions are ≥25 kDa, whereas peptides are filtered such that they don’t contain peptides >5 kDa. This single user did quite a number on cerebrolysin’s whole reputation; something truly surreal.
Citicoline
Rating: ★★. I’m super sensitive to this stuff and get existential depression from taking any dose worth its salt. It does increase concentration before that kicks in though.
One of the better choline sources.
-
Intravenously injected CDP-choline increases blood pressure and reverses hypotension in haemorrhagic shock: effect is mediated by central cholinergic activation (increases Vasopressin)
-
- ONLY citicoline at the 5 mg/kg dose had shifted its status from being noneffective to become significantly effective in the co-administered group ~30mg HED.
Choline
Made primarily in the liver via phosphatidylethanolamine methylation.
-
https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/blog/2010/12/04/meeting-choline-requirement-eggs-organs/
- The Sweet Truth About Liver and Egg Yolks — Choline Matters More to Fatty Liver Than Sugar, Alcohol, or Fat
- Lab rats are choline deficient. It is capable of completely protecting lab rats against NAFLD induced by sugar+fat+alcohol.
- So, pregnant rats fed 3x their normal amount had their progeny see a lifelong 30% increase in visuospatial and auditory memory.
- Effect of different dietary fats on choline requirement of rats (1957)
- Saturated fats require more choline than PUFAs to prevent liver steatosis.
- This is rather remarkable, because much lower concentrations of sucrose started spontaneously producing fatty liver disease in lab rats in the late 1970s and early 1980s once the American Institute of Nutrition set standards for purified rodent diets that relied exclusively on isolated vitamins and minerals rather than whole-food supplements like cod liver oil, yeast, and wheat germ.
- Lab rats are choline deficient. It is capable of completely protecting lab rats against NAFLD induced by sugar+fat+alcohol.
- The Sweet Truth About Liver and Egg Yolks — Choline Matters More to Fatty Liver Than Sugar, Alcohol, or Fat
-
Choline Redistribution during Adaptation to Choline Deprivation
- Deprivation is achieved by feeding PEMT-/- mice a choline-deficient diet. Lethal due to liver failure. Apparently lacking MDR2 (multiple drug-resistant protein 2) allows hepatic choline recycling!
- The mice lacking PEMT still initiated choline redistribution.
- Normal levels of choline-containing metabolites were maintained in the brains of choline-deficient Mdr2–/–/Pemt–/– mice for 90 days despite continued choline consumption via oxidation. Choline oxidase activity had not been previously detected in the brain. Plasma levels of choline were also maintained for 90 days, whereas plasma phosphatidylcholine levels decreased by >60%.
- Deprivation is achieved by feeding PEMT-/- mice a choline-deficient diet. Lethal due to liver failure. Apparently lacking MDR2 (multiple drug-resistant protein 2) allows hepatic choline recycling!
-
By weight, the more common forms:
- PC increases choline stores and is ~13%.
- Alpha-GPC is more for enhancing its release in the brain, and is 40% choline by weight.
- ‘Lecithin’ is 10-20% PC, thus like 1-2% choline.
- Phosphatidylcholine = 15%.
- Citicoline is ~18.5% by weight.
- Betaine is worth something like 25% its does in choline?
- CMJ recommends to have it be ≤50% of choline intake if you choose to supplement with it.
-
I think supplementation-induced depression is possibly from excessive methylation via conversion into Trimethylglycine and onwards to DMG → sarcosine. Longecity. Another explanation is maybe overencoding of negative experience due to excessive brain ACh R
-
Water-soluble choline bompounds (PChol/GPC) can enter the portal circulation of the liver intact. Lipid-soluble (PC/SPM (sphingomyelin) are either hyrdrolysed by phospholipases or enter the lymph incorporated into chylomicrons. R
Requirements
- CMJ - Meeting the Choline Requirement — Eggs, Organs, and the Wheat Paradox
- Bear in mind only methionine can actually be used to make choline, while B6/8/12 and TMG merely spare it.
- PEMT ctually creates homocysteine in the process of creating choline! So, if your PEMT is running smoothly, you can make your own choline, but you still need more betaine and B vitamins to neutralize the homocysteine that’s generated in the process. If your PEMT engine is working like this, however… well, then, you’ve got another problem: If PEMT isn’t using up your methionine to make choline, the methionine is just going to go further on down that pathway shown above and make more homocysteine anyway! Thus, although having a PEMT gene that Uncle Buck would surely envy might lower our choline requirement, consuming lots of methionine won’t help us at all. In fact, extra methionine just gives us more homocysteine and thereby increases our need for choline, betaine, folate, B12, and B6.
- The Chris Masterjohn calculator says I need 1124 mg Choline daily. WTF!
- The calculator uses SNPs in the folate transporter (SLC19a1, rs1051266, G80A), the enzyme that helps make the precursor to methylfolate (MTHFD1, rs2236225, G1958A), and the enzyme that helps make methylfolate itself (MTHFR, rs1801131, A1298C and rs1801133, C677T) to develop a “methylfolate score.” This is used to calculate how much choline you should aim for.
- It then uses a polymorphism in the enzyme that helps make phosphatidylcholine, a specific form of choline that protects against fatty liver disease, promotes gall bladder health, and facilitates healthy digestion of dietary fats and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (PEMT, rs7946, 5465G>A). This is used to tell you the likelihood that missing your choline requirement will hurt these functions in your body.
Clausenamide
- The anti-dementia drug candidate, (−)-clausenamide, improves memory impairment through its multi-target effect (2016)
- Mild elevation of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations -> neuron survival + outgrowth & antagonism of neural apoptosis induced by growht factor deprivation.
- Intracellular Ca2+ levels are mainly regulated by the following factors: (1) extracellular Ca2+ influx into the cytoplasm, (2) Ca2+ release from intracellular stores, (3) Ca2+ clearance via either outflow from the cytoplasm to the extracellular space or accumulation into internal Ca2+ stores, and (4) cytoplasmic Ca2+ buffering.
- Modulation of the cholinergic system
- In vitro promotion of ChAT in frontal cortex neurons -> suppored cholinergic neuron survival + neurite outgrowth & synaptosomal ACh release.
- In vivo: Increased ChAT in the neocortex, hippicampus, and sitratum: [Effects of (-), (+)clausenamide on anisodine-induced acetylcholine decrease and associated memory deficits in the mouse brain (1998)]. reversibly inhibited ACE with much lower potency than inhibitors like galantamine.
- Upregulation of synaptic plasticity
- There are two forms of LTP in the hippocampus: N-Methyl-D-aspartate-(NMDA-) or VGCC-dependent LTP. Clau induced the latter. LTP is not inhibited by nimodipine, indicating VGCC (potentiation) is only necessary for induction but not maintenaince.
- Did not bind to NMDAR, indicating it is NMDAR independent: [Effects of (-), (+) clausenamide on central N-methyl-D-asparate receptors in rodents (1997)].
- APV, an NMDAR blocker, had no effect on clau-induced LTP: [Two forms of long-term potentiation induced by different compounds (Xu et al 2007)]
- However, chronic administration of clau promoted the expression of synaptic NMDA receptors:
- (1) increasing NMDA receptor density in synaptic membranes,
- (2) increasing NMDA receptor affinity to their endogenous ligands as indicated by the (-)-clau-increased Bmax values of NMDA receptors in the synaptic membrane, and
- (3) ameliorating oxidative stress-induced synaptic membrane fluidity, which facilitates NMDA receptor turnover in synaptic membrane.
- Increased mossy fiber sprouting and expression of GAP43
- Activation of cellular and molecular signaling pathways involved in learning and memory.
- Inhibits Tau hyperphorsphorylation and Amyloid β-induced intracellular Ca2+ overload.
- APP mice are generated by overexpression of the mutant APP gene and are characterized by senile plaque overload and related apoptosis in the central nervous system.
- There’s a Chinese study out there where it improved symptoms in human Alzheimer’s patients - 400mg/week, once a week.
- Anti-apoptotic in five regards:
- (1) low potassium in cerebellar granule cells, (2) growth factor deprivation in cortical neurons,
- (3) 6-OHDA in high BAXα-expressing PC12 cells,
- Inhibited BAX-α-induced cytochrome C release, possibly by increasing glutathione content?
- (4) ischemia/reperfusion in rats, and (5) Aβ1-40 infusion- and natural aging in rat brain
- Inhibits expression of p53, c-Myc, etc.
- PKC-MEK negatively regulates GSK-3β (-> Tau hyperphosphorylation.) Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase enhance C-type lectin-like receptor 2-mediated platelet activation by inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3α/β (CLEC-2 and GPVI (potentiated by AKT/MAPK:) activate platelets through Src, Syk, and PLCγ-2)
- And Clau surely increases PKC, which was shown in Xu 2005. Clau-induced microtubule protection was at least in part mediated by PP1, responsible for tau dephosphorylation.
- They go relatively in-depth regarding its chemistry. Its nootropic effects are chirality-dependent. Clau was more potent than piracetam (5-10mg/kg vs. 500mg/kg respectively) for improving performance in memory-impaired animals.
- Mild elevation of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations -> neuron survival + outgrowth & antagonism of neural apoptosis induced by growht factor deprivation.
- Previously, Recent advances in the study of (–)clausenamide: chemistry, biological activities and mechanism of action (Oct 2014)
- NGF & BDNF induce small elevations of Ca2+ in neurons
- Shown to be a potassium channel antagonist (preventing efflux) and inducing membrane depolarization.
- (−)Clausenamide facilitates synaptic transmission at hippocampal Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses (2012)
- Calcium release from endoplasmic reticulum is mediated by two main types of receptors: RyRs and IP3-Rs. Ryanodine blockage of RyR suppressed synaptic facilitation, whereas IP3 blockage showed no effect, suggesting even PLC might not even be involved.
- CAMKII dependent.
- PKA inhibitor: no effect.
- So it’s turning out to be a slightly exotic cascade, I guess. VGCC -> RyR -> CAMKII -> CREB -> Egr1, BDNF, etc. - CAMKII -> p-ERK peaked 5 and 30 minutes in hippocampus and cortex respectively. p-nCREB 9 minutes after.
- Study on the Nootropic Mechanism of (-)Clausenamide - Influence on the Formation of Synapses in Mouse Brain (Jiang & Zhang (1998/2006)
- Increased cortical thickness by 10% in 4 weeks.
- Gintrux links this for demonstrating cortical thickness and intelligence: Cognitive ability changes and dynamics of cortical thickness development in healthy children and adolescents (2013)
- Could be due to intracellular Ca2+ influencing neuronal cytoarchitecture.
- 29% growth of synapse density in a region of the CA3.
- Increased cortical thickness by 10% in 4 weeks.
- ()-Clausenamide Potentiates Synaptic Transmission in the Dentate Gyrus of Rats (Xu et al 2005)
- Physiological signature of a novel potentiator of AMPA receptor signalling (Szulc et al., 2018) not even chinese
- We have synthesized a novel small molecule based on the pyrrolidinone–containing core structure of Clausenamide.: BRS-015
- Overall quite similar to clausenamide; no NMDAR effects, chirality, etc. They hypothesize AMPA potentiation is via CAMKII -> γ-8.
- Potentiated inward currents evoked by local application of l–glutamate onto CA3. It facilitated the induction of mossy fibre LTP, but the magnitude of potentiation was smaller than that observed in untreated slices.
- Asymmetrical synapses between large mossy fibre terminals and thorny excrescences in CA3 pyramidal neurons contain an average number of AMPA receptors exceeding 4 times the number reported for C/A synapses.
- [Age-dependent pre- and postsynaptic distribution of AMPA receptors at synapses in CA3 stratum radiatum of hippocampal slice cultures compared with intact brain]
- Cell type and pathway dependence of synaptic AMPA receptor number and variability in the hippocampus (1998)
- C/A (not CA) synapses can be void of AMPAR, while mossy fibre synapses have smaller variability.
- High-resolution immunogold localization of AMPA type glutamate receptor subunits at synaptic and non-synaptic sites in rat hippocampus
- Higher GluR1 expression at A/C (associational/commissural synapses) synapses, compared to mossy fibre synapses which have subtypes more equally.
- Well that’s a whole other rabbithole.
- Higher GluR1 expression at A/C (associational/commissural synapses) synapses, compared to mossy fibre synapses which have subtypes more equally.
- [Activation of ERK1/2-CREB pathway during potentiating synaptic transmission of (-)clausenamide in rat dentate gyrus. (2012)]
- Increases Choline Acetyltransferase.
- Gintrux: The cortex begins to thin after the age of five or six as part of the normal aging process. This study is the first to show the association between cortical thickness and development in full scale IQ, and has potentially wide-ranging implications for the pedagogical world and for judicial cases in which the defendant’s IQ score could play a role in determining the severity of the sentence
- Could this be a correlate for the cut-off point for development intelligence in early life?
Cordyceps Militaris
Rating: ★★. Noticeable increase in endurance, but I think its long-term effects on D2, adenosine, and lovastatin content are questinoable.
D21
aka TAT-D21.
-
The heteromer flips the relationship between dopamine concentration and which receptor gets stimulated: D1 gets active in low concentrations and D2 in high cincentrations, contrary to norm. Though I’ve also heard that it essentially just nullifies dopaminergic signaling, and that splitting the dimer essentially ‘differentiates’ D1 and D2 and allows much more flexible LTP and LTD that is seen in adolescence; D21 increases with age.
-
D21 is much more prevalent (~250% d21/d1 ratio compared to control) in those with Depression. Naturally then, the peptide has standard antidepressant effects. ==Induces calcium release by being Gq-coupled== somehow. R. Many studies will measure D1 or D2 individually, and they do no such thing. Only co-expressive cells.
- Probably driven by D1: certain in vitro thingies resulted in PIP turnover. Possibly from high concentrations activating another receptor. R
-
Differential receptor crosstalk in DRD1-DRD2 heterodimer upon phasic and tonic dopamine signals (May 2021) & Visualization of differential GPCR crosstalk in DRD1-DRD2 heterodimer upon different dopamine levels (June 2022) looks like a refined version if biorxiv is for drafting or something
- High dopamine levels preferentially make the heteromer inhibit D1 signalling, whilst low dopamine levels make the heteromer inhibit D2 signalling:Upon treatment of 10 nM dopamine, D21 heterodimer induces a similar level of cAMP to D1 only (possibly because D2 activity in the heterodimer is inhibited at this nanomolar DA level) In contrast, at 10 µM dopamine, the cAMP level by D21 was significantly lower than the one by D1.
-
Intranasal Delivery of a Peptide with Antidepressant-Like Effect (Brown & Liu 2014)
- It doesn’t split the peptide or anything, or change protein levels, (idk, maybe Cogmetics’ does?) but simply prevents the interaction between D1 and D2 at the dimer.
- Lowered locomotor activity. Thus it is not a stimulant. However it is anti-immobility - they swam more. Yeah idfk.
- Elevates BDNF in the Prefrontal Cortex, and decreased levels are seen in major depressive disorder.
- However, Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer signaling pathway in the brain: emerging physiological relevance (Hasbi et al. 2011) suggests that D21 activation could result in transcription of BDNF in cultured neurons derived from the ventral striatum.
- There is “requisite” D1/D2 synergism for certain reward processes:
- However, Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer signaling pathway in the brain: emerging physiological relevance (Hasbi et al. 2011) suggests that D21 activation could result in transcription of BDNF in cultured neurons derived from the ventral striatum.
-
There are also D1-D3 and D2-D5 heterodimers, as well as D1-NMDAR and D5-GABA-A heterodimers.
-
Δ-Tetrahydrocannabinol Increases Dopamine D1-D2 Receptor Heteromer and Elicits Phenotypic Reprogramming in Adult Primate Striatal Neurons BUT CBD attenuated most of this.
-
Dopamine Negatively Regulates Insulin Secretion Through Activation of D1-D2 Receptor Heteromer
-
Differential receptor crosstalk in DRD1-DRD2 heterodimer upon phasic and tonic dopamine signals
-
- Bam says the Orbitofrontal Cortex is possibly receiving translocated d21, from areas where the difference in mRNA and presence is the inverse, such as the Olfactory Tubercle.
Calcium
- Perhaps it’s been known well that D1 activates phospholipase C? D2 agonists potently enhance AA release, initiated by increasing intracellular Ca2+ or stimulating constitutive purinergic receptors - which trigger Ca2+. Naturally, all this stimulates phospholipase A2. R.
- Calcium signaling cascade links dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer to striatal BDNF production and neuronal growth
- CAMK IIα increases BDNF expression.
- Rats have a lower prescence and importance of the heteromer in their brains than humans. The further up in intelligence you go across species, the more prevalent. It implies that the heteromer counteracts brain power/force in some way, and it does play the role of a negative dopamine regulator (it lowers dopamine transmission in general by lowering dopa release). In theory, society is like a Swiss army knife in making the d1/d2 heteromer appear. (wtf? lol stoner.)
- Dopamine D1 and D2 Receptor Co-activation Generates a Novel Phospholipase C-mediated Calcium Signal (Lee et al. 2004)
- Coexpression barely changes adenylyl cyclase activity in these cells compared to D1 alone. PKA, PKC, or PI3K inhibition did not change calcium levels, but PLC inhibiton shut it down >90% (and blocked Gq-coupled P2Y receptors along the way).
- Gi/o is not directly involevd in the calcium signal. Gi and Gq crosstalk does not appear to underlie, since neither couple to Gq to begin with. Good reasoning?
- Virtually all Medium Spiny Neurons that express D1 also technically express D2.
- Coexpression did not affect the ligand binding pocket of either receptor.
- In the rat frontal cortex, interneurons only expressed D2, unlike pyramidal neurons.
- Heteromers of the CCR2 and CCR5 chemokine receptors and heteromers of the μ- and δ-opioid receptor may couple to G proteins distinct from those associated with homogeneous populations of their constituent receptors, but interestingly the cellular responses is not different from that of the individual receptors.
- Dopamine receptor-mediated Ca(2+) signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons (Tang et al. 2004)
- ~40% MSN elicit robust repetitive Ca2+ oscillations following application of dopamine - PLC-dependent.
Deferoxamine
Rating: ★. Didn’t notice anything. See: Scattered Notes: Deferoxamine
Dihexa
High affinity to hepatocyte growth factor and potentiates c-Met, the protein it encodes.
Pretty controversial. It’s supposedly 7x more potent than BDNF for improvint alzheimer’s-like cognitive impairment. This sounds awesome to a lot of people but it really dosen’t help.
- Dihexa is not bdnf
- Bam says Dihexa mainly works in the sensory systems, but notes it’s weird how the cortical systems increase autistic symptoms from being given different sensory information?
Donepezil
- Developed under the ‘cholinergic hypothesis’ of Alzheimer’s, i.e. over-activation of ACE, which isn’t always the truth let alone the whole story.
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and σ1 agonist (14.6 nM).
- Non-competitive inhibitor, unlike galantamine
- Inhibits voltage-activated Sodium Channel currents and delays Kir currents and fast transient potassium currents.
- [Mechanisms of alpha7-nicotinic receptor up-regulation and sensitization to donepezil induced by chronic donepezil treatment.]
- Upregulates α7 nAChR in the hippocampus. This was prevented by coadministration with PI3K inhibitor.
- Donepezil impairs memory in healthy older subjects: behavioural, EEG and simultaneous EEG/fMRI biomarkers
- Donepezil modulates nicotinic receptors of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurones
- Modulates α4β2, I think.
- Depressed Nicotine currents that were in vitro “induced by brief puffer pulses, through a glass micropipette positioned above the slice”.
D-Serine
Obsoleted by Neboglamine. Sarcosine is also a safer option.
-
Antibiotic, and not in a good way; apparently it kills important microbes involved in sugar metabolism.
-
Metabolism by DAAO (highly expressed in the kidney) produces pyruvate, ammonium, and hydrogen peroxide. Not fun.
Erythropoietin
There’s demonstrated proof that engaging in cognitive work increases the long term potentiation or the “connections between neurons” through a variety of mechanisms and models that test this are called “environmental enrichment” within the literature. Increasing the load or demand that we place on our neurons when we learn strengthens the connections between neurons as well as neuronal morphology through induction of functional hypoxia.
- Introducing neuroepo:
- Nasal administration of the neuroprotective candidate NeuroEPO to healthy volunteers: a randomized, parallel, open-label safety study n=25 and 20% them got headaches and 20% saw increase in liver enzymes. They call that ‘well tolerated’.
- The Effect of Neuroepo on Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease Patients Is Mediated by Electroencephalogram Source Activity
- Erythropoietin: a candidate compound for neuroprotection in schizophrenia showed 5,000 IU/kg in mice injected ip.
- Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system
-
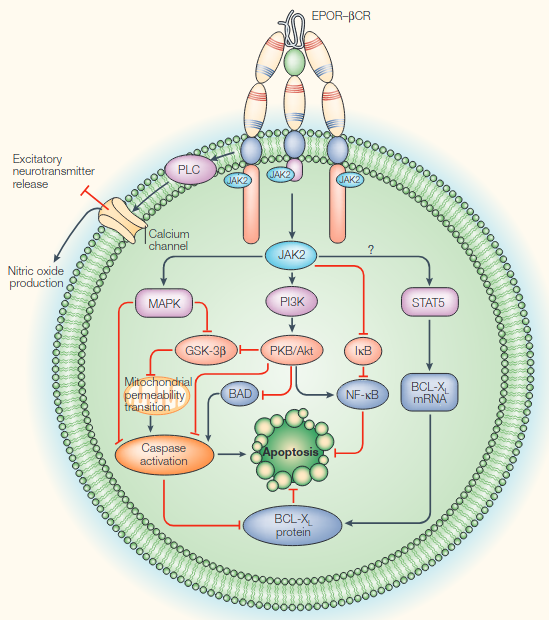
- JAK2-STAT is found on the C-terminus of Erythropoietin Receptor (and βCR)
-
- Erythropoietin Enhances Hippocampal Response during Memory Retrieval in Humans
- In healthy humans, 40,000 IU rhEPO IV increased the hippocampal response during memory retrieval 1 week later!
- Erythropoietin enhances hippocampal long-term potentiation and memory (in young healthy mice)
- This selective improvement was maintained for an EPO treatment-free period of another 3 weeks
- It exerts hematopoieis-independt effets on the NS. Maybe this was obvious but I assumed it was all by proxy of something to do with hematology at least.
- Derivatves like CEPO (carbamoylated EPO) exert similar neuroprotective properites, but not erythropoietic effects. Epobis counts too I’m sure.
- Made some interesting electrical changes in CA1 slices, especially quite a huge drop in short-term depression fEPSP slope.
- Decreased amplitude and frequency of spontaneous EPSC in CA1 and increased SIPSC frequency - 50%?
- Did not reveal differences in epression of synaptic proteins or postsynaptic receptor proteins and their subunits.
- Evoked excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) amplitudes in EPO-treated neurons were reduced to about 60% of control in these autapic neurons… why did they choose them..? No diference in NMDA/AMPA ratio.
- Synaptic boutons per neuron increased, but reduces the amount of primed vesicles? EPO is likely to reduce the number of active synapses without altering total synapse number
- Hematocrit seems irrelevant. In our study, the hematocrit was already back to control levels when we still observed a significant effect on
- Expression of constitutively active erythropoietin receptor in pyramidal neurons of cortex and hippocampus boosts higher cognitive functions in mice
- Constitutively active = no need for agonist.
- Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on cognition and neural activity in remitted patients with mood disorders and first-degree relatives of patients with psychiatric disorders: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- Differential effects of erythropoietin on neural and cognitive measures of executive function 3 and 7 days post-administration
- Erythropoietin improves operant conditioning and stability of cognitive performance in mice
- It is not produced solely by the kidneys, but is also produced in astrocytes. In line with renal production, hypoxia enhances it here, too.
- Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes: they did not directly stimulate it, rather they increased mRNA level.
- They did the 5CSRTT (Five Choice Serial Reaction Time Task). It was consistenyl superior in like every measure.
- α7 nAChR knockout exhibits defecit in 5-CSRTT. R
- It is not produced solely by the kidneys, but is also produced in astrocytes. In line with renal production, hypoxia enhances it here, too.
- Acute and chronic elevation of erythropoietin in the brain improves exercise performance in mice without inducing erythropoiesis
- The increase in maximal exercise performance is independent of changes in total hemoglobin mass, whole blood volume, and cardiovascular parameters. Also greater self-esteem and mood/euphoria.
- Tg21 transgenicity overexpresses rhEPO independent of oxygen.
- Effects of erythropoietin administration on cerebral metabolism and exercise capacity in men
- 3 days of high-dose NO effect in healthy subjects on exercise capacity or cognition.
- Effects of erythropoietin administration on cerebral metabolism and exercise capacity in men
- Recombinant erythropoietin improves cognitive function in chronic haemodialysis patients
- Adjusting for control, their WAIS IQ increased by about 6 points.
- Prolonged astrocyte-derived erythropoietin expression attenuates neuronal damage under hypothermic conditions
- Regulation of muscle and metabolic physiology by hypothalamic erythropoietin independently of its peripheral action
- While blood EPO raises with aging and obesity, hypothalamic EPO decreased.
- Aged mice were chronically treated with EPO in the hypothalamic ventricle, showing an increase in lean mass, while body weight and fat mass decreased as a result of a moderate reduction of food intake. Both muscle and metabolic functions were improved.
- Intranasal erythropoietin therapy in nervous system disorders
Neurogenesis
- One of the most promisingly yet somehow inconspicuously framed studies on cognitive enhancement I’ve seen Introducing the brain erythropoietin circle to explain adaptive brain hardware upgrade and improved performance
- rhEPO (recombinant human) treatment of young rodents or EPO receptor (EPOR) overexpression in Pyramidal Neuro]s caused remarkable and enduring cognitive improvement, together with enhanced LTP. The ‘brain hardware upgrade’, underlying these observations, includes an EPO induced ~20% increase in Pyramidal Neurons and Oligodendrocytes in CA hippocampi in the absence of elevated DNA synthesis.
- Reduces Microglia numbers and dampens their activity as prerequisites for undisturbed EPO-driven differentiation of pre-existing local neuronal precursors.
- It’s extremely potent and thus very sparse and hard to measure its relative expression.
- Erythropoietin protects primary hippocampal neurons increasing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- Revisiting adult neurogenesis and the role of erythropoietin for neuronal and oligodendroglial differentiation in the hippocampus (2016)
- Similar group to the study below.
- BrdU labels mitotic brain cells I guess.
- At week 4 we found a reduction in BrdU+ cells in DG/SVZ, likely as a consequence of temporary depletion of progenitors or negative feedback on neurogenesis.
- Increased apoptosis, potentially because of abnormal crowding of maturing neurons.
- Healthy young mice (starting at 4 weeks old or 11 weeks old) 3-week EPO administration i.p. (5000IU/kg = HED ~27k) every other day.
- Increased number of pyramidal neurons and oligodendrocytes in the hippocampus of ~20%. Under ’enduring cognitive challenge’, they were preserved. This is concomitant with an increased hippocampal volume. in the 11->14 week mice.
- They of course both increased, in similar amounts, because new axons need to be myelinated.
- OPC = olgodendrocyte precursor cells. Can differentiate into them without dividing.
- this EPO effect involves stimulation of precursor differentiation rather than proliferation or anti-apoptosis
- Decreased number and diameter of ’neurospheres’, culture of clustered NSCs. Inhibitory of their proliferation.
- Pax6 and doublecortin-positive cells (i.e. immature) were reduced after 3 days compared to control. This may imply that the increase in neurons was due to accelerated differentiation of neural progenitors.
- They used leucine incorporation as a marker of protein synthesis sans proliferation. And it actually increased ~20%.
- Functional hypoxia drives neuroplasticity and neurogenesis via brain erythropoietin (2020)
- High-ose EPO amplifies auto-/paracine EPO/EPOR signaling prompting emergence of new CA1 neurons and enhanced dendritic spine densities.
- Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and MMP9 secreted by erythropoietin-activated endothelial cells promote neural progenitor cell migration
- EPO activates endothelial cells, which promote endogenous neuroblast migration by secreting MMPs that degrade extracellular matrix (ECM) components.
- Regeneration in the nervous system with erythropoietin
- Relies on WISP1 signaling to foster stem cell survival and to block FOXO activity. Relies on mTOR for induction of plasticity/differentiation/etc.
- In contrast to its mTOR activation I suppose, in some conditions it increases AMPK and auotphagy activity.
- EPO increases WNT signaling expression.
- +Wnt3 expression: Survival, neuron-like differentiation and functionality of mesenchymal stem cells in neurotoxic environment: the critical role of erythropoietin
- NGF levels remained the same, contrary to hypothesis. LIF (type of IL-6) was upregulated in hypoxia and normoxia.
- +Wnt3 expression: Survival, neuron-like differentiation and functionality of mesenchymal stem cells in neurotoxic environment: the critical role of erythropoietin
- Expression is increased by cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. Stimulated by Selenium depletion, xenon, and microglial inhibitors.
- Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes
- Stimulatory effect of IGF-1/2 on EPO was not affected by oxygen concentration, obviously unlike its normal induction from hypoxia.
- Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes
Epobis
- Epobis is a Nonerythropoietic and Neuroprotective Agonist of the Erythropoietin Receptor with Anti-Inflammatory and Memory Enhancing Effects
- A new agonist of the erythropoietin receptor, Epobis, induces neurite outgrowth and promotes neuronal survival
Galantamine
I don’t believe it has tolerance, but it and other rapidly irreversible AChEis upregulate AChE with long-term use: Acetylcholinesterase and its inhibition in Alzheimer disease
Ginkgo Bilboa
Rating: ★★. I don’t really notice anything (Swanson brand. Maybe I’ll try Ginkgold one day).
- Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) influences monoaminergic neurotransmission via inhibition of NE uptake, but not MAO activity after chronic treatment
- Inhibits NET, SERT, DAT, and in high concentrations, MAO. After 14 days, only NET is significantly decreased.
- Terpene Trilactones from Ginkgo biloba Are Antagonists of Cortical Glycine and GABAA Receptors (2003)
- Contains Bilobalide, a Glycine Receptor antagonist.
- Role of glycine receptors and glycine release for the neuroprotective activity of bilobalide (2008)
- GABA-A NAM. Apparently it upregulates GABA-A after 1-2 weeks.
- Very weak Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Inhibits NOS. Blocks Aldosterone.
- Strongly potentiates α1 Glycine receptors.
- Upregulates GABA-A5 or some shit?
- In rats it may inhibit MAO-B but apparently this has not been demonstrated in humans.
- Blood thinner via PAF (platelet-activating factor) inhibition.
- Contains Amentoflavone.
- A single amino acid determines the toxicity of Ginkgo biloba extracts
- their lack of toxicity in humans is not in doubt. These extracts are, however, highly toxic to insects.
- Insect GABA receptors contain Ala at their 2’ position in the pore. Substitution with Val, which is the equivalent residue in vertebrate GABA-A receptor α-subunits, decreases ginkgolide potency by up to 10,000-fold.
- Ginkgo biloba extract promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a pathway involving Wnt/β-catenin signaling
- Impaired tricarboxylic acid cycle flux and mitochondrial aerobic respiration during isoproterenol induced myocardial ischemia is rescued by bilobalide
- Inhibits PDH, SDH, SUCLG, CS
- Stabilization of mitochondrial function by Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761)
- https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/ginkgo-biloba-is-anti-serotonin-and-pro-dopamine.34051/post-520338
- Polysomnographic effects of adjuvant ginkgo biloba therapy in patients with major depression medicated with trimipramine
- Good for bones:
- Ginkgo Biloba improves bone formation during fracture healing: an experimental study in rats
- Effects of the extract of Ginkgo biloba on the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro
- Ginkgo biloba extract promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a pathway involving Wnt/β-catenin signaling
- Potential antiosteoporotic effect of ginkgo biloba extract via regulation of SIRT1-NF-kB signaling pathway
- Gingkgolic acid is a toxin. Extracts aim to achieve a minimum concentration of this. Life Extension may be the lowest according to Odder_Sea.
- Action Mechanism of Ginkgo biloba Leaf Extract Intervened by Exercise Therapy in Treatment of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
- I don’t get this experimental model, tbh. They applied T and E2 to these rats.
- Ginkgo alone had no effect on T, 5α-reductase, and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), but suppressed androgen receptor (AR), aromatase, E2 and estrogen receptor (ER), and the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA); Ex alone significantly reduced T, aromatase, E2, ER, AR, and PCNA, but highly raised DHT. While Ginkgo + Ex androgenically downregulated T, aromatase, E2, and ER, but upregulated DHT, AR, and PCNA, implying Ginkgo + Ex tended to worsen BPH.
- Ginkgo biloba and cerebral bleeding: a case report and critical review
- We report the case of a young woman who made chronic use of G. biloba and suffered from cerebral bleeding without any structural abnormalities.
The anecdotes: improves focus and (long-term) memory.
Guanfacine
Rating: ★★. It’s not for me—but I can see it being very helpful for some. When you read about people being prescribed Intuitiv (guanfacine XR), etc. they’ll describe it as removing an element of anxiety, and that removing sudden drives to action makes it easier to focus. But I’m on the other side of the coin; having that ‘push’ is totally how I’ve learned to work.
- Scientific rationale for the use of α2A-adrenoceptor agonists in treating neuroinflammatory cognitive disorders (Arnsten et al. 2023)
- α2A agonists deactive macrophages; should reduce the release of kynurenine and GCP-II.
-
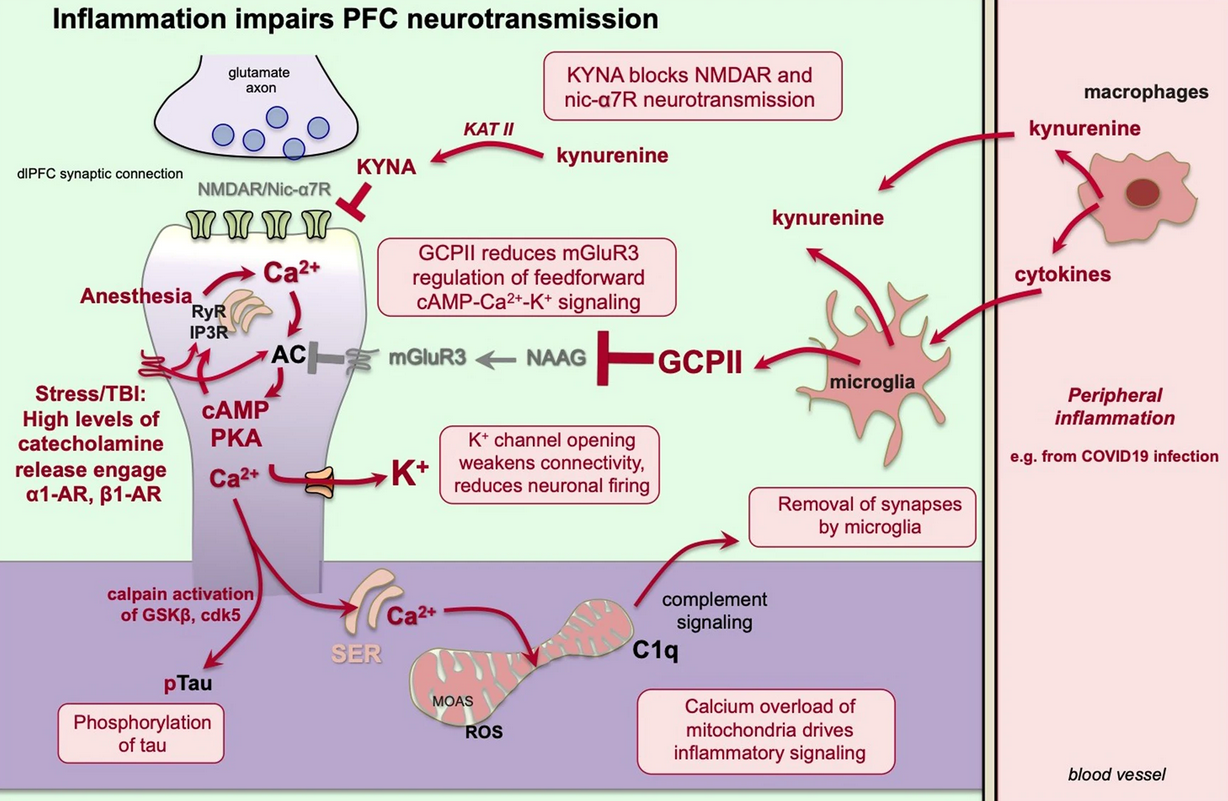
- Guanfacine’s mechanism of action in treating prefrontal cortical disorders: Successful translation across species (Arnsten 2007)
- In classic circuits, such as in the visual cortex PKA (and therefore increased PDE4 activity) enhances plasticity. Well welcome to opposite world.
-
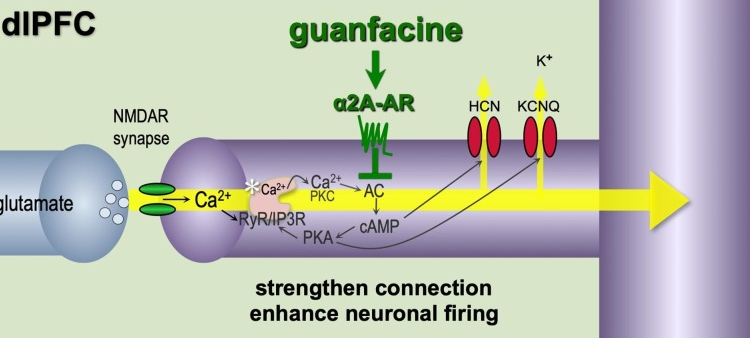
- Notice the omission of RER-mediated signaling in ‘classical’ circuits. Why though?
- Effects of acute and sub-chronic administrations of guanfacine on catecholaminergic transmissions in the orbitofrontal cortex
- Sub-chronic (7 days iirc) systemic administration:
- Reduced norephinephrine release in OFC, LC, and thalamic reticulra nucleus.
- Reduced GABA release in Medial Dorsal Nucleus
- Enhanced AMPA-induced glutamate, NE, and DA release in OFC.
- Obviously subchronic is the name of the game, but checking what the acute effects are could be relevant for learning how long benefits take to kick in.
- **Attenuation of direct noradrenergic LC-OFC transmission at the resting stage and enhancement of direct co-releasing catecholaminergic LC-OFC transmission via GABAergic disinhibition in the intermediate LC-OFC pathway. **
- Inhibiting HCN (via (guanfacine) inhibiting cAMP or blocking HCN directly) (which colocalizes with α2A) activates limbic-frontal cortex network connectivity, enhancing signal-to-noise ratio and improving focus on a particular stimulus:
- Alpha2A-adrenoceptors strengthen working memory networks by inhibiting cAMP-HCN channel signaling in prefrontal cortex (Wang, Arnsten et al. 2007)
- Commentary: Molecules to remember
- Guanfacine, But Not Clonidine, Improves Planning and Working Memory Performance in Humans
- The 29 μg/kg dose of guanfacine improved spatial working memory and planning… had no effect on attentional set-shifting.
- An attentional set is formed when a subject learns that a set of rules can be applied to complex stimuli in order to differentiate relevant from irrelevant cues. Two stages within the AST protocol measure aspects of cognitive flexibility: reversal and the extra-dimensional shift. At the reversal stage, the previously negative stimuli within one dimension (medium in this example) is now positive. At the extra-dimensional shift stage, when the irrelevant dimension (odor in this example, perhaps as opposed to visual) becomes the relevant dimension. R
- *The neural circuits underlying behavior during the AST are highly conserved across humans, nonhuman primates and rodents..
- An attentional set is formed when a subject learns that a set of rules can be applied to complex stimuli in order to differentiate relevant from irrelevant cues. Two stages within the AST protocol measure aspects of cognitive flexibility: reversal and the extra-dimensional shift. At the reversal stage, the previously negative stimuli within one dimension (medium in this example) is now positive. At the extra-dimensional shift stage, when the irrelevant dimension (odor in this example, perhaps as opposed to visual) becomes the relevant dimension. R
- Clonidine is nonselective for α2 Adrenergic Receptor.
- The 29 μg/kg dose of guanfacine improved spatial working memory and planning… had no effect on attentional set-shifting.
- α2A blockade profoundly impairs spatial Working Memory. R (using yohimbine)
- Recent studies indicate that elevated cAMP signaling in PFC impairs behavioral measures of WM. In contrast to LTM obviously.
- Alpha2A-adrenoceptors strengthen working memory networks by inhibiting cAMP-HCN channel signaling in prefrontal cortex (Wang, Arnsten et al. 2007)
- Sub-chronic (7 days iirc) systemic administration:
- Chronic Administrations of Guanfacine on Mesocortical Catecholaminergic and Thalamocortical Glutamatergic Transmissions
- chronic guanfacine administration did not affect intrathalamic GABAergic transmission, but it phasically enhanced thalamocortical glutamatergic transmission
- Acutely: postsynapic LC→OFC/VTA efferents reduces noradrenergic neurotransmission.
- Proposed downregulation of α2A in the LC
- Chronic stimulation of alpha-2A-adrenoceptors with guanfacine protects rodent prefrontal cortex dendritic spines and cognition from the effects of chronic stress (Hains, Arnsten et al. 2015)
- Guanfacine as an alpha-2-agonist inducer of growth hormone secretion—a comparison with clonidine
- Role of Alpha2a-Adrenergic Heteroreceptors in Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Cocaine Associated Behaviors: Implications for the Pharmacological Treatment of Stress-Driven Relapse of Drug Use
- (Along with α2A of course), guanfacine also activates excitatory Gi-coupled heteroreceptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST). I think α2A-x heteroreceptors, whatever they are
- Okay so basically α2A can act as a typical autoreceptor, but it can also act as a ‘heteroreceptor’. mGluR3 also doies this.
- A key brain region in driving stress-induced relapse.
- (Along with α2A of course), guanfacine also activates excitatory Gi-coupled heteroreceptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST). I think α2A-x heteroreceptors, whatever they are
dlPFC
https://beta.nootropicswiki.org/article/dlpfc-modulation
-
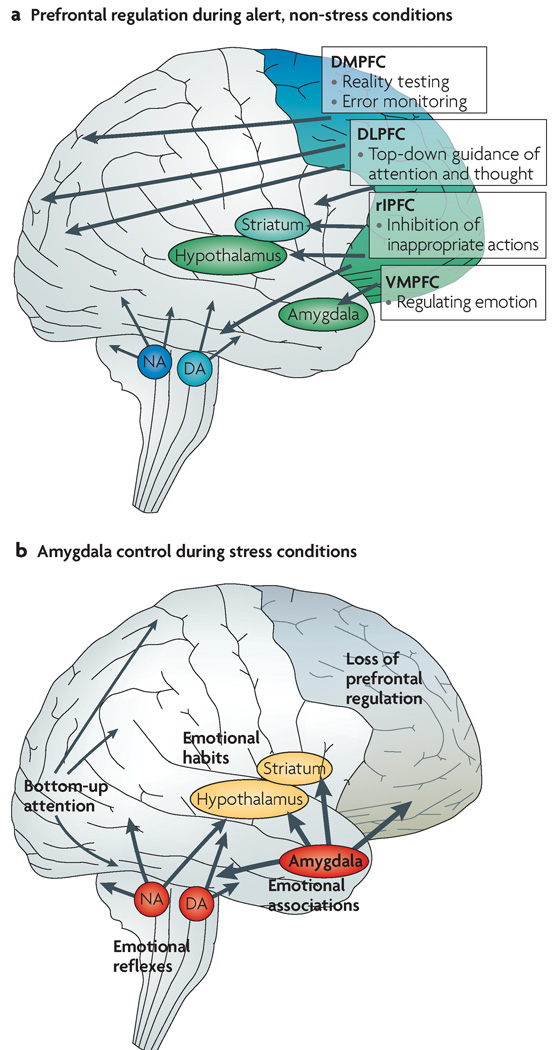
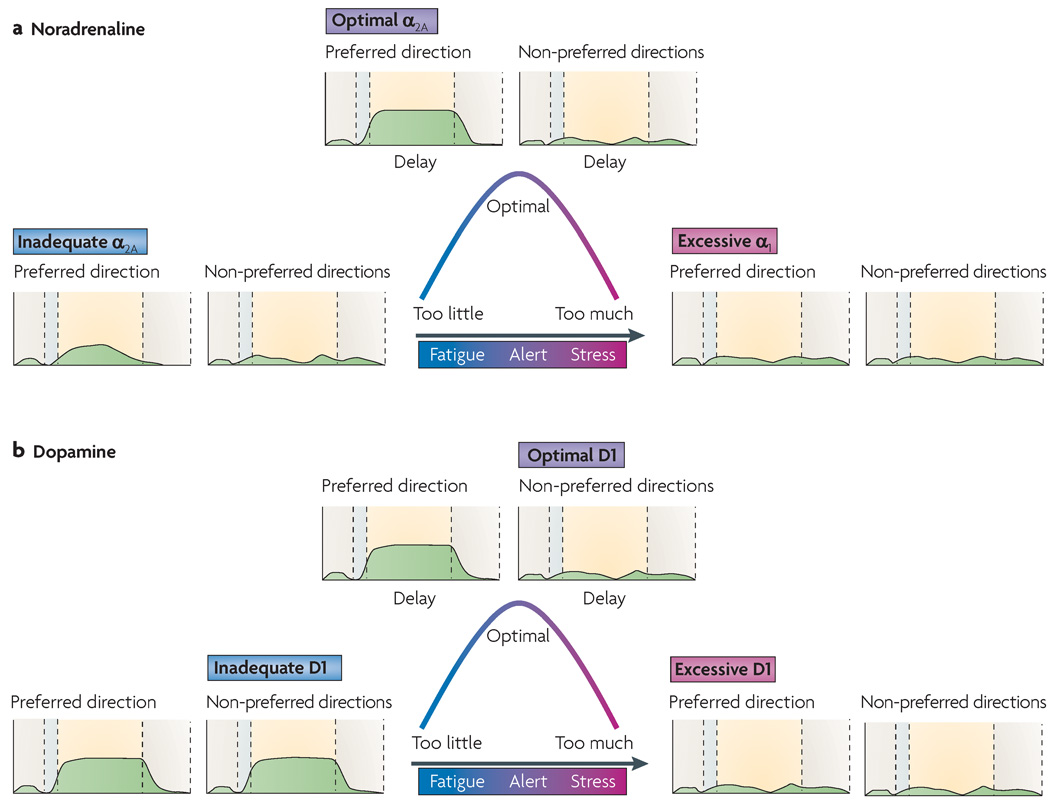
Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function (Arnsten 2009)
- So the bad thing about Ca2+ in the dlPFC microcircuits is that it opens SK channels.
-
-
-
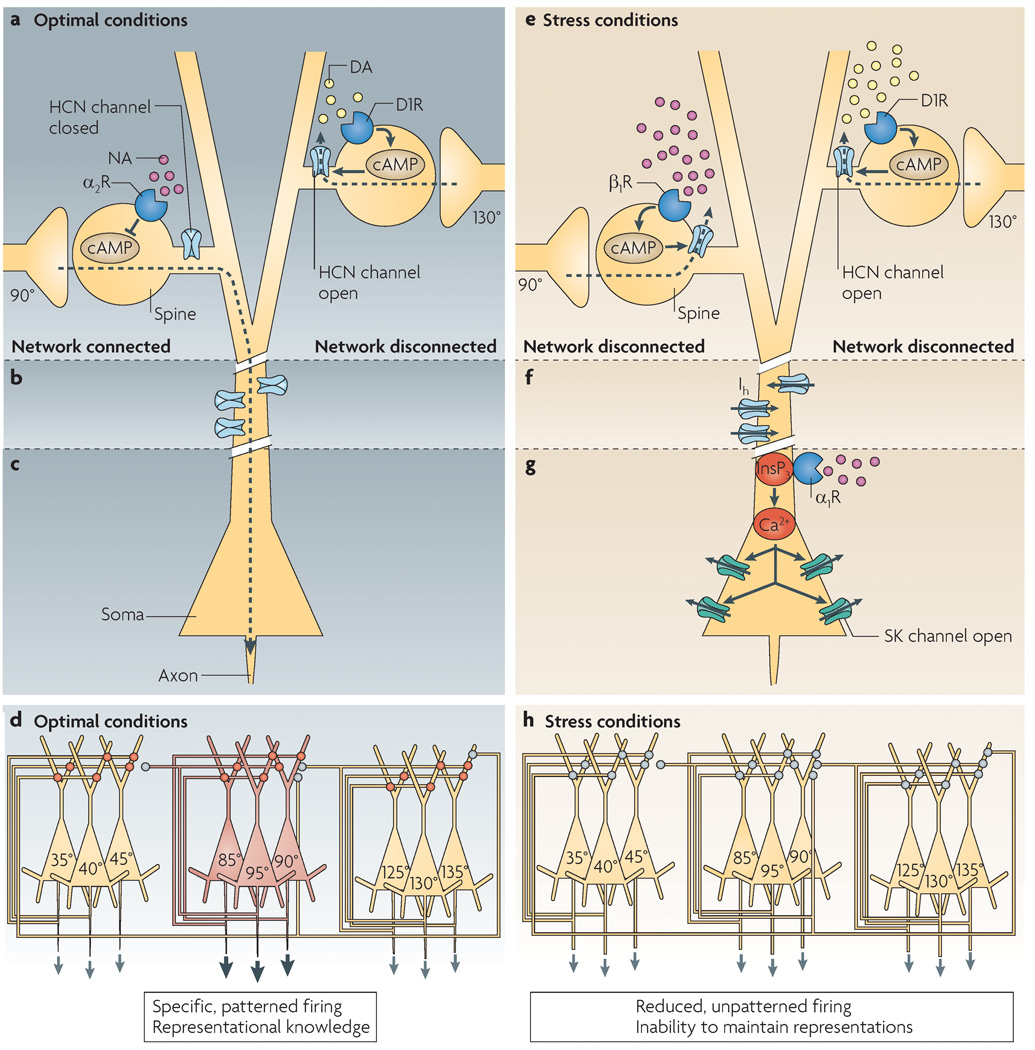
-
- Dynamic network connectivity = neuromodulators rapidly and flexibly altering efficacy of synaptic connections (in the dlPFC III recurrent excitatory microcircuits, of course) without changing the architecture.
- Dynamic Network Connectivity: A new form of neuroplasticity (Arnsten et al. 2010)
- neuromodulation plays an essential role in shaping the contents of our “mental sketch pad”, thus coordinating arousal state with cognitive state.
- Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey
- Depletion of catecholamines from the dlPFC was as detrimental as ablating the dlPFC itself!
- Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey
- neuromodulation plays an essential role in shaping the contents of our “mental sketch pad”, thus coordinating arousal state with cognitive state.
- Genetic insults to DNC proteins are commonly linked to Schizophrenia.
- Impairment of NMDA for sure
- Dynamic Network Connectivity: A new form of neuroplasticity (Arnsten et al. 2010)
- Gives us a walkthrough on Goldman-Rakic’s findings from start to finish.
- dlPFC neurons can represent visual space in the absence of sensory stimulation, the foundation of abstract thought—beautifully put
- this basic representational operation is the building block of more complex dlPFC operations such as behavioral inhibition and cognitive control The prefrontal landscape: implications of functional architecture for understanding human mentation and the central executive (Goldman-Rakic 1996)
- Intrinsic circuit organization of the major layers and sublayers of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey Layer V also exhibits all this stuff, but to a lesser extent.
- It is likely that most Response cells reside in layer V, as they are selectively influenced by D2
- Layer V neurons bear the majority of mRNAs encoding the five distinct dopamine receptor subtypes in the primate prefrontal cortex
- Thus, levels of D1 and D2 mRNAs are noticeably stronger in the striatum than in the cortex, whereas D4 and D5 expression is clearly higher in the cortex. D3 transcripts are equivalent
- dlPFC neurons can represent visual space in the absence of sensory stimulation, the foundation of abstract thought—beautifully put
- Ramón y Cajal: In mice the basal dendrites [of pyramidal cells] are short and have few branches, in man they [the basal dendrites] are numerous, long and highly branched……as one ascends the animal scale the psychic cell becomes larger and more complex; it’s natural to attribute this progressive morphological complexity, in part at least, to its progressive functional state
- Patricia Goldman-Rakic A Remembrance (Arnsten 2003) and similar work of hers in realation to Goldman-Rakic. Arnsten has many
- Delay cells are usually spatially tuned, firing across the delay period for the neuron’s preferred direction, but decreasing firing for all other nonpreferred directions (the preferred direction for this Delay cell is indicated by a red asterisk). The microcircuits underlying Delay cell firing reside in deep layer III (and possibly in layer V as well) and are described in detail in the text. In contrast to Delay cells, Response cells are often inhibited during the delay period and instead fire leading up to, during, and/or after the motor response, initiating action and/or providing feedback. These neurons are thought to reside in layer V.
- Unlike other areas in the cortex where LTP/CREB induces rapid changes in dendritic morphology, layer III dlPFC neurons remain long and thin, even in very old monkeys.
- This geometric shape facilitates the rapid gating of synapses via ion channel opening, likely by limiting the spine’s volume and extending the distance that the signal must travel.
- E.g. something histological: The spine neck filters membrane potentials
- This geometric shape facilitates the rapid gating of synapses via ion channel opening, likely by limiting the spine’s volume and extending the distance that the signal must travel.
- even mild pressure can impair the ability to find insightful solutions to problems A brain mechanism for facilitation of insight by positive affect
- *positive mood enhances insight, at least in part, by modulating attention and cognitive control mechanisms via ACC, perhaps enhancing sensitivity to detect non-prepotent solution candidates. *
- There is also endogenous catecholamine production in the dlPFC of some primate species, including humans
- Dynamic network connectivity = neuromodulators rapidly and flexibly altering efficacy of synaptic connections (in the dlPFC III recurrent excitatory microcircuits, of course) without changing the architecture.
- A dopamine gradient controls access to distributed working memory in the large-scale monkey cortex this is some 200 IQ shit:

- Depletion of dopamine from the prefrontal cortex and complete ablation of the prefrontal cortex cause similar working memory deficits
- Too little or too much presynaptic PFC D1 stimulation disrupting delay period activity:
-
[A novel dopamine D1 receptor agonist excites delay-dependent working memory-related neuronal firing in primate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex]
-
-
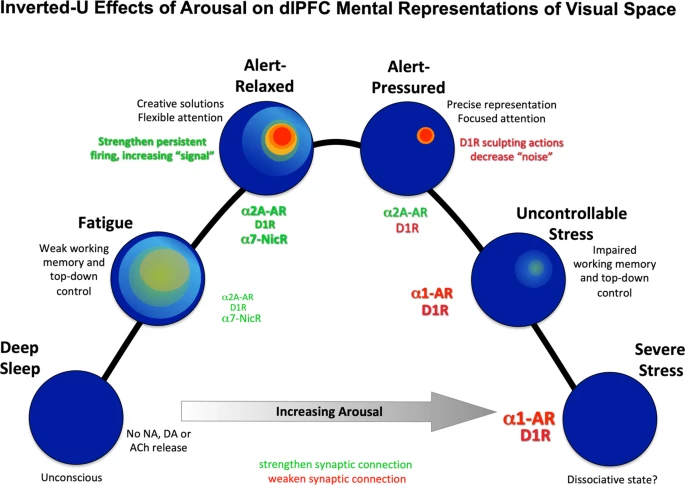 delay cell firing. Low levels of D1 receptor stimulation are associated with noisy neuronal representations of visual space.
delay cell firing. Low levels of D1 receptor stimulation are associated with noisy neuronal representations of visual space.
- (There are additional dimensions to this if you want an accurate picture of working memory and arousal, but it’s a decent approximate model)
- As for left vs. right while still being optimal, it’s something like creativity vs. focus:
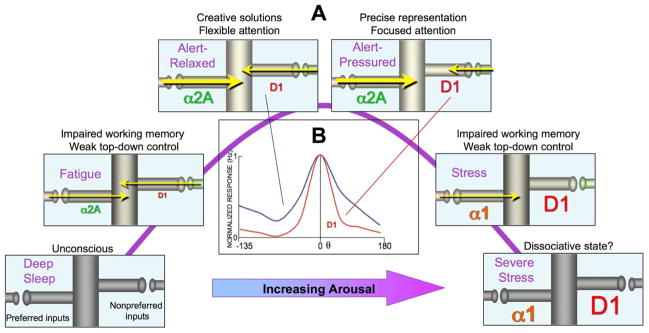
- D1 agonists had suppressive effects on firing of PFC neurons engaged in working memory tasks: moderate levels of suppression preferentially reduced firing to NPDs, leading to an enhancement in spatial tuning, whereas at higher levels of D1R stimulation, physiological suppression became overwhelming, leading to losses in spatial information capacity and detuning of spatial memory-related information
-
-
- Dorsolateral Prefrontal Contributions to Human Working Memory
- DlPFC damage was associated with deficits in the manipulation of verbal and spatial knowledge, with left dlPFC necessary for manipulating information in working memory and right dlPFC critical for manipulating information in a broader range of reasoning contexts.
- Monitoring operations are thought to support the active retention of information in WM and computational mechanisms for manipulating items are recruited for updating/selecting between these representations:
Human Studies
- Guanfacine extended release in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a placebo-controlled trial
- Even though the half life is pretty long, it rapidly peaks in plasma—hence XR.
- Guanfacine and clonidine, alpha 2-agonists, improve paired associates learning, but not delayed matching to sample, in humans .1 or 2mg. increased subjective feelings of sedation.
- Effect on Primary Sleep Disorders When Children With ADHD Are Administered Guanfacine Extended Release aged 6-12
- REM, NREM, and SWS were reduced in proportion to the overall sleep reduction.
- Central effects of guanfacine and clonidine during wakefulness and sleep in healthy subjects
-
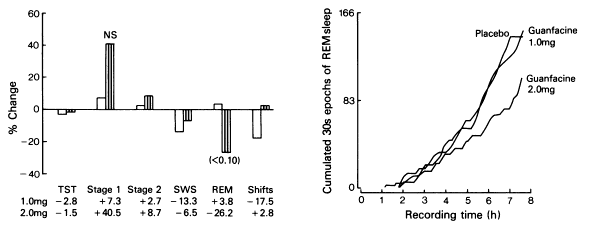
- Both drugs (1 or 2mg for guan) reduced systolic blood pressure without significantly altering diastolic blood pressure, pulse rate and objective performance parameters.
- Guanfacine 1.0 mg did not alter REM sleep and 2.0 mg of guanfacine had less effect than both doses of clonidine in this respect.
- guanfacine’s action on REM sleep began 5 h after the dose
- Guanfacine’s peak effects were 4-6 hours after ingestion (observations were limited to 6 hours). 26% suppression.
-
- [Efficacy of guanfacine extended release assessed during the morning, afternoon, and evening using a modified Conners’ Parent Rating Scale-revised: Short Form.]
- Response is consistent throughout the day regardless of time of administration.
- Lack of effects of guanfacine on executive and memory functions in healthy male volunteers 1 or 2 mg.
- This study found no improvement of prefrontal memory or executive functions after guanfacine. Negative effects on blood pressure and poorer effects on digit span backward and slower reaction time indicate a mild sedative effect of guanfacine at these doses, possibly via mechanisms of autoreceptor down-regulation.
- Methylphenidate, Guanfacine, and Combined Treatment Effects on Electroencephalography Correlates of Spatial Working Memory in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder age 7-14.
- Spatial working memory task, measuing ACC and primary visual cortex.
- Both monotherapies had limited effects on EEG measures, with guanfacine further showing detrimental effects o performance.
- The Effects of Guanfacine on Working Memory Performance in Patients With Localization-Related Epilepsy and Healthy Controls (2008)
IDRA-21
Obsoleted by TAK-653, and arguably retroactively obsoleted by (pi)racetam. Read this for some ampakine lore.
Insulin (Intranasal)
Rating: ★★. More stable postprandial energy levels, and appetite suppression is alright when cutting. But it’s not very prominent to a young lad such as myself.
- Insulin signaling inhibits the 5-HT2C receptor in choroid plexus via MAP kinase
- Broadening the Defintion of Brain Insulin Resistance in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s brains displayed region-specific reductions in insulin concentrations together with elevations in Insulin Receptor densities Rng
- The brain even has localized insulin production.
- Insulin promotes glycogen storage and cell proliferation in primary human astrocytes
- Role of Insulin in Neurotrauma and Neurodegeneration: A Review
- Hyperinsulinemia Induces Insulin Resistance in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
- Chronic treatment (this means prolonged! Cells were in insulin soup for 24 h.) resulted in increased basal AKT phosphorylation. More importantly, acute insulin stimulation after chronic insulin treatment resulted in blunted phosphorylation of Akt, S6K, and GSK-3β.
- In obese rats, insulin-stimulated Akt1 activity is decreased in muscle and adipose tissue but increased in liver and vice versa for Akt2
- AKT phosphorylation is reduced in Adipocytes and skeletal Muscle of type 2 diabetic patients or from chronic insulin treatment inducing IR.
- Interestingly, when the cells were treated with PI3K pathway inhibitor, but not MAPK pathway inhibitor, chronic insulin treatment did not block acute insulin treatment-induced Akt phosphorylation
- Hyperinsulinemia increases Drp1, used for Mitochondrial Fission
- Chronic treatment (this means prolonged! Cells were in insulin soup for 24 h.) resulted in increased basal AKT phosphorylation. More importantly, acute insulin stimulation after chronic insulin treatment resulted in blunted phosphorylation of Akt, S6K, and GSK-3β.
- Insulin promotes rapid delivery of N-methyl-D- aspartate receptors to the cell surface by exocytosis (2001) (Xenopus oocytes)
- Increases open time probability and NR1 surface expression.
- Insulin modulates hippocampal activity-dependent synaptic plasticity in a N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor and phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase-dependent manner (CA1)
- Insulin reduces neuronal excitability by turning on GABA(A) channels that generate tonic current (CA1)
- Insulin enhances striatal dopamine release by activating cholinergic interneurons and thereby signals reward
- Brain insulin receptors and spatial memory. Correlated changes in gene expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and signaling molecules in the hippocampus of water maze trained rats
- Insulin receptor mRNA is raised during memory tasks. How’s that for LTP?
Intranasal
- Insulin increases excitation and reward through activation of Nachar receptors on somatostatin interneurons which promote synchronicity in the brain and disinhibition of dopamine expressing cells.
- Intranasal insulin protects against substantia nigra dopaminergic neuronal loss and alleviates motor deficits induced by 6-OHDA in rats
- Intranasal insulin administration may be highly effective in improving cognitive function in mice with cognitive dysfunction by reversing brain insulin resistance
- Intranasal insulin improves memory in humans: superiority of insulin aspart
- Intranasal Insulin Improves Age-Related Cognitive Deficits and Reverses Electrophysiological Correlates of Brain Aging Intranasal does not alter bodily insulin receptors. It just delivers it to the brain.
- Intranasal insulin administration appears safe, does not affect systemic glucose control, and may provide acute improvements of cognitive function in patients with type 2 DM R
- Awake intranasal insulin delivery modifies protein complexes and alters memory, anxiety, and olfactory behaviors
- Effect of intranasally administered insulin on cerebral blood flow and perfusion; a randomized experiment in young and older adults
- Young group was mean age 22 and not diabetic or anything.
- Central insulin administration improves whole-body insulin sensitivity via hypothalamus and parasympathetic outputs in men (2014)
- Nondiabetic participants. 10 of which ~21.8 BMI: + 41 $\pm$ 8% increase in peripheral insulin sensitivity. 5 33.2 BMI obese patients saw… -0.7 $\pm$ 18% change.
- This change was associated with hypothalamic activity.
- Began with 6.25 mU/kg insulin bolus followed by 0.25mU/kg/min iv. Then, 160 U insulin intranasal.
-
- Nondiabetic participants. 10 of which ~21.8 BMI: + 41 $\pm$ 8% increase in peripheral insulin sensitivity. 5 33.2 BMI obese patients saw… -0.7 $\pm$ 18% change.
- Dose-Dependent Effects of Intranasal Insulin on Resting-State Brain Activity
-
- Nine healthy young men. 0, 40, 80, or 160. After application of 160 IU as a nasal spray, ~0.1 enter the bloodstream, as shown in previous studies.
- No differences for LH, FSH, Test, ACTH, cortisol, TSH.
-
- Intranasal Insulin Administration Dose-Dependently Modulates Verbal Memory and Plasma β-Amyloid in Memory-Impaired Older Adults
- Plasma insulin and glucose levels were unaffected by treatment.
- 20 IU was the most efficacious dose.
- Promotes breakdown of Amyloid β
- CSF Amyloid β levels are reliably lower in Alzheimer’s! Evaluation of CSF-tau and CSF-Abeta42 as diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease in clinical practice Mixed results for plasma, though. In this study, it was usually increased.
- Intranasal insulin improves memory in humans reduced plasma Cortisol. This may facilitate Aβ clearance via Insulin Degrading Enzyme.
- It is reasonable to speculate that in the long term, chronic intranasal administration may produce similar adverse effects centrally. Long-duration trials that include a late-stage test of acute brain insulin resistance could address this concern. Even such trials may not go far enough: the extent to which dose timing and frequency impact central insulin resistance is also a mystery. This despite the fact that, for instance, insulin sensitivity of peripheral tissues exhibits a clear circadian pattern in healthy humans (Boden et al., 1996). Additionally, the impact of dose frequency is poorly understood. With these thoughts in mind, future trials investigating both timing and frequency may help to develop an optimal dosing “schedule” that effectively balances efficacy and safety. R
- Nasal insulin changes peripheral insulin sensitivity simultaneously with altered activity in homeostatic and reward-related human brain regions
- Effects of intranasal insulin on hepatic fat accumulation and energy metabolism in humans
- Overweight, elderly T2D group and lean healthy participants (control). Hepatic insulin sensitivity as not changed. In control, hepatocellular lipids decreased by 35% and hepatic ATP concentration increased by 18% after 3h.
- Intranasal Insulin Therapy for Alzheimer Disease and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Benefits persisted 2 months after for the 20 IU group.
- Insulin given intranasally induces hypoglycaemia in normal and diabetic subjects (1982) Hard to read graphs…
- 40IU QID: Intranasal insulin did not demonstrate statistically significant improvements on overall mood, aspects of emotional processing, neurocognitive function, or self-reported quality of life patient reported outcomes. R
Istradefylline
Rating: ★★★★. I thrive on the kind of ‘impulsivity’ it gives you (i.e. even on the level of micro-behaviors like googling 3 things that show up in my head to find the answer for something instead of lazily paying attention to one laconic query), but it’s too bad it’ll reliably give you insomnia if you take too much.
- A2A antagonist. Wikipedia mentions how this eventually leads to D2 disinhibition.
- Disrupting A2A-CB1 heterodimers will actually upregulate CB1.
- Weak CYP3A4 inducer (in vitro)? Metabolized by CYP1A1, CYP3A4, CYP3A5.
- Istradefylline, an adenosine A2a receptor antagonist, inhibits the CD4+ T-cell hypersecretion of IL-17A and IL-8 in humans
- Doesn’t even affect sleep: Istradefylline improves daytime sleepiness in patients with Parkinson’s disease: An open-label, 3-month study
- JC Denton says it will have an additive effect on striatal dopamine and partially restoring normal frontal DA (I guess that depends on parkinson’s/excess GDNF as in the study) whereas it’s guanfacine that will really balance out striatal and frontal.
- Lack of tolerance to motor stimulant effects of a selective adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonist
- No change in A1, A2A, D1, D2 or their mRNA.
- [Istradefylline is recommended for morning use: a report of 4 cases.]
- Role of adenosine A2A receptors in hot and cold cognition: Effects of single-dose istradefylline in healthy volunteers (20mg)
- Subjects on istradefylline interpreted social situations more positively (Social Information Preference)
- Effected risk adjustment loss on the cambridge gamble task (which is interesting, I suppose. It activates OFC)
- … we did not detect any other effects across a variety of hot and cold cognitive domains
- Habitual coffee drinkers display a distinct pattern of brain functional connectivity
- Higher stress levels, and associated with anxiety in males. Decreased functional connectivity in a network encompassing subcortical and posterior brain regions associated wtih somatosensory, motor, and emotional processing.
- Learning and cognitive flexibility: frontostriatal function and monoaminergic modulation
- Dopamine and Cognitive Control in Prefrontal Cortex
- Let’s get back into this paradigm: sensory gating, maintaining and manipulating WM contents, and relaying motor commands.
- How does adenosine control neuronal dysfunction and neurodegeneration? (Cunha 2016)
 (aaand it’s 77 pages of manuscript)
(aaand it’s 77 pages of manuscript)
- A2AR switch off A1R and CB1 receptors, bolster glutamate release and NMDA receptors to assist increasing synaptic plasticity in the ‘activated’ synapse; the parallel engagement of the astrocytic syncytium releases adenosine further inhibiting neighboring synapses, thus sharpening the encoded plastic change.
- A1R are a hurdle for damage initiation, but they desensitize upon prolonged activation. However, if the insult is near-threshold and/or of short-duration, A1R trigger preconditioning, which may limit the spread of damage. Brain insults also up-regulate A2AR, probably to bolster adaptive changes, but this heightens brain damage since A2AR blockade affords neuroprotection in models of epilepsy, depression, Alzheimer’s, or Parkinson’s disease
- There is also evidence, from a double-blind controlled trial in previously caffeine-naïve human volunteers, that acute caffeine can impact memory consolidation according to an Inverted-U function: Post-study caffeine administration enhances memory consolidation in humans
- Pretty sure I heard fucking Huberman talk about this. Go figure it was published in Nature, his favorite. (In 2014)
- Influences mental tracking: ADORA2A genotype modulates interoceptive and exteroceptive processing in a fronto-insular network (rs5751876) (no result for me)
- The first thing to ask is if this is ‘moar A2A’, or less. Not sure. They do consume less caffeine, probably because of heightened sensitivity. So more??
- TC was previously shown to be related to anxiety-related phenotypes.
- TT risk genotype was associated with increased connectivity between the insula and the prefrontal cortex. The strength in connectivity correlated with interoceptive accuracy.
- Carriers of the TT risk genotype furthermore displayed a reduced activity or deactivation in the striatum during executive control and decreased insula-striatal connectivity during the resting-state.
- Working memory deficits in transgenic rats overexpressing human adenosine A2A receptors in the brain
Adenosine A2A
- Gs-protein coupled. As opposed to Adenosine A1, it is found in sleep-promoting neurons. It antagonizes the Histaminergic system.
- Modulation of adenosine A2A receptor function by interacting proteins. New targets for Huntington’s disease (2012) - a 133-page dissertation.
- An adenosine A2a agonist increases sleep and induces Fos in ventrolateral preoptic neurons
- A2A antagonist blocks the sleep induced by PGD2 (which activates sleep-promoting neurons in ventrolateral preoptic area)
- Adenosine A2A receptors enhance GABA transport into nerve terminals by restraining PKC inhibition of GAT-1
- Reduces Histamine and increases GABA, and promotes sleep.
- PKA→GAT-1 and GABA uptake via reducing PKC.
- Downregulates M1 Macrophage phenotype.
- Differential effects of presynaptic versus postsynaptic adenosine A2A receptor blockade on Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) self-administration in squirrel monkeys
- Accumbal adenosine A2A receptor inactivation biases for large and costly rewards in the effort- but not delay-based decision making
- “Go big or go home” mindset?
- Nucleus Accumbens is important for cost-benefit decision making.
- Striatopallidal adenosine A2A receptor modulation of goal-directed behavior: Homeostatic control with cognitive flexibility
- Striatum projects MSNs to the globus pallidus.
- Striatopallidal A2AR exert an overall “break” control of a variety of cognitive processes. - antagonism enhances goal-directed behavior and cognitive flexibility.
-
- A2AR indirectly increases GABA via dopamine/D2 activation or via increasing Glutamate release Effect of adenosine A2A receptor stimulation on GABA release from the striatum of young and aged rats in vivo
- In contrast, A2AR antagonists inhibit Glutamate release: Modulation of glutamate release and excitotoxicity by adenosine A2A receptors.
- Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists Affects NMDA Glutamate Receptor Function. Potential to Address Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Adenosine A2A receptors in neuronal outgrowth a target for nerve regeneration?
- Neurite outgrowth depends on the receptor repertoire present at each moment: A2A activation promotes TrkB-induced dendritic branching, and PI3k/MAPK/PLC-induced axonal elongation!
- An Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonist Improves Multiple Symptoms of Repeated Quinpirole-Induced Psychosis
- Quinpirole: D2 and D3 agonist. Induces OCD-like behaviors. May have CB1 effects as well.
- Increases during aging, it seems:
- Age-related shift in LTD is dependent on neuronal adenosine A2A receptors interplay with mGluR5 and NMDA receptors
- Targeted neurogenesis pathway-based gene analysis identifies ADORA2A associated with hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
- rs9608282 (no data for me): larger hippocampal volume (synaptic loss???). Upstream in the coding sequence, merely implying it could alter A2AR expression.
- There is compelling evidence from animal models of a cortical and hippocampal upsurge of A2AR in glutamatergic synapses upon aging and AD (then proceeds to give 7 references)
- A2A -> PKA/cAMP/CREB -> glutamate release & Ca2+ influx -> and then… hippocampus-dependent cognitive deficits?
- The caffeine-binding adenosine A2A receptor induces age-like HPA-axis dysfunction by targeting glucocorticoid receptor function
- A2AR overexpression -> loss of plasmatic corticosterone circvadian oscillation, and reduction of Glucocorticoid receptor levels in the hippocampus.
- The caffeine-binding adenosine A2A receptor induces age-like HPA-axis dysfunction by targeting glucocorticoid receptor function
- Targeted neurogenesis pathway-based gene analysis identifies ADORA2A associated with hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
- Age-related shift in LTD is dependent on neuronal adenosine A2A receptors interplay with mGluR5 and NMDA receptors
- Adenosine A2A Receptors Control Glutamatergic Synaptic Plasticity in Fast Spiking Interneurons of the Prefrontal Cortex
- A2AR are enriched at mPFC (layer V) synapses.
- At the network level, extracellularly induced LTP of population spikes was reduced by A2AR blockade. The interneuron-specificity of A2AR in controlling glutamatergic synapse LTP may ensure that during periods of high synaptic activity, a proper excitation/inhibition balance is maintained within the mPFC.
- Impact of in vivo chronic blockade of adenosine A2A receptors on the BDNF-mediated facilitation of LTP
- Most of BDNF synaptic actions, namely on LTP, require activation of A2A.
- … how? For one thing, is TrkB even expressed outside the basal ganglia? Or, why would synaptic effects of BDNF rely on adenosinergic efferents?
- results showed that chronic blockade of A2AR in male Wistar rats inhibits the facilitatory action of BDNF upon LTP on hippocampal CA1 area and decreases both mRNA and protein levels of the TrkB-FL receptor in hippocampus
- Most of BDNF synaptic actions, namely on LTP, require activation of A2A.
Heteromers
- G protein-coupled receptor heteromers are key players in substance use disorder.
- A2A homodimers as well.
- There A2A-D1 heterodimers along with A2A-D2 A2A-D2 Heteromers on Striatal Astrocytes: Biochemical and Biophysical Evidence
- A2A-CD73: Makes sense. Synergistic of course.
- Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73)-mediated formation of adenosine is critical for the striatal adenosine A2A receptor functions
- Confirmed with proximity ligation assays
- Moreover, CD73 KO mice displayed increased working memory performance and a blunted amphetamine-induced sensitization, mimicking the phenotype of global or forebrain-A2AR KO mice, as well as upon pharmacological A2AR blockade.
- Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73)-mediated formation of adenosine is critical for the striatal adenosine A2A receptor functions
- A2A-mGluR5: synergistic.
- A2A-D3: adenosine antagonizes affinity and signaling of D3.
- A2A-oxytocin! Heterodimer of A2A and Oxytocin Receptors Regulating Glutamate Release in Adult Striatal Astrocytes
CB1
-
A2A-D2-CB1 trimers as well.
-
A2A-CB1 and A2A-CB2. They are antagonistic; A2A antagonism increases CB2 signaling.
-
- Essentially absent from corticostriatal projections and striatonigral neurons, and, instead, is largely present in striatopallidal neurons
- Co-stimulation of both receptors leads to strongly reduced downstream signaling (I mean why does it have any magnitude?)
- DMR: dynamic mass redistribution - essentially a means to measure GPCR activation from light by a biosensor
- Label-free is a benefit
- Possibly facilitates Gαq signaling - just like D21?
- Gq inhibition abrogate A2A and CB1 evoked changes in DMR.
- Experiments with disrupting peptides on certain amino acids turned the heteromer into their respective classical signaling pathways.
- Lots of stuff on Huntington’s disease and how expression changes. For instance, functional A2A-CB1 heteromers are expressed in Huntington’s disease in advanced but not late disease stages.
-
- Cocaine+A2A antagonism synergizes in reducing the firing rate of cholinergic interneurons: Medium Spiny Neuron M1 AChR inhibition → disinhibition of of Cav1.3, triggering postsynaptic Endocannabinoid release and a reduction of glutamatergic transmission via activating presynaptic CB1:
- Indeed: in the presence of pirenzepine, a M1 receptor inhibitor, the electrophysiological effects of cocaine plus A2AR antagonists modulation on glutamatergic transmission were fully occluded.
- Ironic how it’s dependent on Cav1.3 channels. Maybe it comes down to localization? It’s conflicting with the study they cite; it should follow that M1 inhibition would reduce VGCC activity.
- Cites: Dopaminergic control of corticostriatal long-term synaptic depression in medium spiny neurons is mediated by cholinergic interneurons (2006)
- Induction of LTD: dependent on D2 on the postsynaptic membrane.
- These aspiny cholinergic Interneurons are autonomous pacemakers, leading to tonic ACh, thus tonic activation of striatal mAChR.
- Lowering M1 AChR tone promotes LTD induction by disinhibiting critical intraspine Cav1.3 Ca2+ channels.
- Previously: [The distinct role of medium spiny neurons and cholinergic interneurons in the D2/A2A receptor interaction in the striatum: implications for Parkinson’s disease]
- VTA CB1 can increase dopamine firing rate: Independent presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms regulate endocannabinoid signaling at multiple synapses in the ventral tegmental area
- Wtf at this point? Phasic dopamine release evoked by abused substances requires cannabinoid receptor activation
- Indeed: in the presence of pirenzepine, a M1 receptor inhibitor, the electrophysiological effects of cocaine plus A2AR antagonists modulation on glutamatergic transmission were fully occluded.
- Cocaine+A2A antagonism synergizes in reducing the firing rate of cholinergic interneurons: Medium Spiny Neuron M1 AChR inhibition → disinhibition of of Cav1.3, triggering postsynaptic Endocannabinoid release and a reduction of glutamatergic transmission via activating presynaptic CB1:
-
Endocannabinoid signaling mediates psychomotor activation by adenosine A2A antagonists
- eCB-mediated inhibition of indirect MSN increases movement. The theory is classical that direct MSN activation is pro-locomotion and iMSN = inhibiting movement.
-
Adenosine–cannabinoid receptor interactions. Implications for striatal function (2010)
-
Potentiation of cannabinoid signaling in microglia by adenosine A2A receptor antagonists
- Microglial A2A and CB2 (heteromers also) are upregulated in AD
- Blockade of A2ARi reduces amyloid burden and improves cognition in AD.
- A1 adenosine receptors accumulate in neurodegenerative structures in Alzheimer disease and mediate both amyloid precursor protein processing and tau phosphorylation and translocation (2003)
- High degree of colocalization for A1R and betaA4 amyloid in senile plaques and for A1R and tau in neurons with tau deposition, but without tangles, was seen.
- A1->PKC->sAPP, A1->p21 & ERK->p->Tau.
- adenosine A2A receptors, located mainly in striatal neurons in controls, appeared in glial cells in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of patients
- Indeed, idk if it’s usually expressed there: Adenosine A2 receptors: selective localization in the human basal ganglia and alterations with disease (1992)
- Exclusively restricted to the Basal Ganglia, specifically: caudate nucleus, putamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle and the lateral segment of the globus pallidus.
- Not exactly, since it exists peripherally? Novel Players in the Aging Synapse: Impact on Cognition: A2A are particularly expressed in the lungs, spleen, thymus, heart, blood vessels, muscle, and brain… whereas in the neocortex and hippocampus, they are present at residual levels.
- Plus this might be with AD patients anyways? Would need to check reference
- Not exactly, since it exists peripherally? Novel Players in the Aging Synapse: Impact on Cognition: A2A are particularly expressed in the lungs, spleen, thymus, heart, blood vessels, muscle, and brain… whereas in the neocortex and hippocampus, they are present at residual levels.
- Parkinson’s: density of adenosine A2 binding sites was comparable to that seen in control cases.
- Huntington’s chorea: Denstiy was dramatically decreased
- Exclusively restricted to the Basal Ganglia, specifically: caudate nucleus, putamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle and the lateral segment of the globus pallidus.
- Indeed, idk if it’s usually expressed there: Adenosine A2 receptors: selective localization in the human basal ganglia and alterations with disease (1992)
- A1 adenosine receptors accumulate in neurodegenerative structures in Alzheimer disease and mediate both amyloid precursor protein processing and tau phosphorylation and translocation (2003)
-
- Presynaptic: SCH-442416; Postsynaptic: KW-6002.
- SCH antagonized while KW-6002 potentiated reinforcing effects of THC!
- Previously: Reinforcing and neurochemical effects of cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists, but not cocaine, are altered by an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist (2011)
- Antagonist caused downward shifts of THC and anandamide dose-response curves (i.e. a decrease in effectiveness)
- MSX-3 neither promoted reinstatement of extinguished drug-seeking behavior nor altered reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior by non-contingent priming injections of THC.
- Presynaptic: SCH-442416; Postsynaptic: KW-6002.
BDNF
- Transactivated with Trk Receptors.
- Adenosine A2A receptor activation is determinant for BDNF actions upon GABA and glutamate release from rat hippocampal synaptosomes
- Both the inhibitory actions of BDNF on GABA release as well as the facilitatory action of the neurotrophin on glutamate release are dependent on the activation of adenosine A2AR by endogenous Adenosine. However, these actions could not be further enhanced by exogenous activation of A2AR.
- Regulation of TrkB receptor translocation to lipid rafts by adenosine A2A receptors and its functional implications for BDNF-induced regulation of synaptic plasticity
- A2A agonists increased the levels of TrkB receptors in the lipid raft fraction of cortical membranes and potentiated BDNF-induced augmentation of phosphorylated TrkB levels in lipid rafts… Lipid raft integrity was also required for the effects of BDNF on hippocampal long-term potentiation at CA1 synapses.
- Mimicked by Forskolin and blocked by PKA inhibitors… removal of endogenous adenosine or disruption of lipid rafts reduced BDNF stimulatory effects on glutamate release from cortical synaptosomes.
- Activation of adenosine A2A receptors induces TrkB translocation and increases BDNF-mediated phospho-TrkB localization in lipid raft: implications for neuromodulation
- Adenosine A2a receptors modulate TrkB receptor-dependent respiratory plasticity in neonatal rats
Isoxazole-9
- Effects of Isx-9 and stress on adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Experimental considerations and future perspectives
- It is also noteworthy that Isx-9-induced activation of endogenous neuronal gene programs is able to inhibit differentiation of neural progenitors into other cell types, even in the presence of strong gliogenic signals
- Isoxazole-9 reduces enhanced fear responses and retrieval in ethanol-dependent male rats
- Differential Effects of Isoxazole-9 on Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells, Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells, and Endothelial Progenitor Cells
- Possibly toxic!!!
- Isoxazole 9 (ISX9), a small molecule targeting Axin, activates Wnt/β‐catenin signalling and promotes hair regrowth (Jan 2023)
- Functional and mechanistic exploration of an adult neurogenesis-promoting small molecule
- ISX-9 potentiates CaMKIIδ-mediated BMAL1 activation to enhance circadian amplitude
- Anecdote: Permanently improved memory but also my limbs get numb/cold easier. It’s too fucking schizo to even talk about
- Anecdote: I megadosed intranasal multiple times. It feels so weird on my ears and brain but makes music way better and makes my brain so much more functionally awake. Weird side effects but super powerful with intranasal, sharpens mind a lot. What else activates wnt/beta-catenin as much as isx-9 then? The effects are phenomenal and the top 3 most powerful nootropics i have taken.
- GSK3α/β is a negative regulator of β-catenin, these studies imply that reducing activity of the Wnt pathway increases the vulnerability to depression, mania, psychosis, and autistic behavior. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in brain development and mental disorders: keeping TCF7L2 in mind
J147
Inhibitor of ATP synthase (sounds fucked up). Upregulates NGF, Egr, and AMPK.
Whitens skin via suppressing α-MSH induced melanogenesis.
Kanna
Rating: ★★★★. Puts a smile on my face. But it often just doesn’t work, though that could be a failure to dose properly or poor quality extract.

- Inhibits Acetylcholinesterase.
- VP doesn’t consider it much of an SSRI, I guess due to the dose required.
- Upregulates VMAT2, making it a monoamine-releasing agent (MRA) - this also includes histamine and GABA.
- VP says the VMAT2 upregulation might only be on serotonergic neurons.,
- Possible cannabinoid agonist.
- Increases C-Reactive Protein?
- Contains the alkaloids:
 - (Δ7-)mesembrenone: SSRI and PDE4 inhibitor.
- (Δ7-)mesembrenone: SSRI and PDE4 inhibitor.
- Mesembrine: SSRI, PDE4 inhibitor, MRA, VMAT2 upregulator.
- ~500μg pure is probably the highest safe does according to VP.
- MAO-Ai is basically negligible.
- Mesembrenol
- Tortuosamine
- Mesembrine: SSRI, PDE4 inhibitor, MRA, VMAT2 upregulator.
-

- High-mesembrine Sceletium extract (Trimesemine™) is a monoamine releasing agent, rather than only a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor - in vitro
- Only mild AChEi.
- 1 mg/ml of pure mesembrine achieved only a E30% AChE in hibition, while the complete alkaloid extract from Sceletium tortuosum inhibited AChE in a dose-dependent manner, with the highest concentration assessed (1 mg/ml) resulting in 87% inhibition, which suggests that the non-mesembrine portion of Sceletium may be responsible for the plant’s inhibitory effects on AChE activity. Somewhat surprisingly, a whole extract with low mesembrine content was reported to only inhibit acetylcholinester-ase activity by 7% (Harvey et al., 2011).
- Cannabinoid CB1 receptor binding and acetylcholinesteraseinhibitory activity of Sceletium tortuosum L.
- Modulation of glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid and androgen production in H295 cells by Trimesemine™, a mesembrine-rich Sceletium extract
Lion’s Mane
Rating: ★★. I’d be lying if I said I didn’t enjoy the headspace and weird dreams (enough to take it for like a year straight under the premise, which may have been successful for all I know) but I think it’s mostly overhyped/marketed trash (at least for healthy people) at this point.
Downregulates D2, 5-AR inhibitor, and κ-opioid agonist.
L-Histidine
Rating: ★★★. Inconsistent, but it can be pretty fun sometimes.
-
Tadaho Nakamura has interesting articles on histamine and cognition:
- [Oral histidine intake improves working memory through the activation of histaminergic nervous system in mice.]
-
Role of dietary histidine in the prevention of obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Obese middle-aged chinese women received 2g 2x/day for 12 weeks. Average fat loss in the histidine group was 2.71 kg and TNF-α, IL-6 decreased.
LSD
Rating: ★★★★★
- Agonizes 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C, partial agonist of 5-HT1A.
- David Nichols in a presentation said it’s a fairly weak agonist on 5-HT2A— something like 30%. This train of thought is why Ray Peat calls LSD a ‘serotonin antagonist’.
- Histamine H2 antagonist (as are other hallucinogens).
- Agonizes AMPAR and κ-Opioid Receptor, and antagonizes Acetylcholine -> mGluR2 antagonism -> PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway -> hippocampal synaptogenesis
- Defining the histamine H2-receptor in brain: the interaction with LSD
- Increased thalamic resting‐state connectivity as a core driver of LSD‐induced hallucinations
- LSD‐induced functional connectivity measures between the thalamus and the right fusiform gyrus and insula correlated significantly with subjective auditory and visual drug effects
- An important model suggested that hallucinogens disrupt thalamic gating of external and internal signals, leading to increased passage of information across the cortex: Serotonin research: contributions to understanding psychoses
- LSD‐induced functional connectivity measures between the thalamus and the right fusiform gyrus and insula correlated significantly with subjective auditory and visual drug effects
- Hallucinogens in Mental Health: Preclinical and Clinical Studies on LSD, Psilocybin, MDMA, and Ketamine
- Psyhcedelics Promote Structural and Functional Neuroplasticity
L-Theanine
Say hello to the laughing stock (?). You might enjoy adding it to coffee/stimulants to attenuate certain side effects but I don’t think it’s exactly anything pro-cognitive.
Memantine
-
NMDAR antagonist. D2 agonist, 5-HT3 antagonist, σ1 agonism but probably needs high doses
-
Increases acetylcholine in the Nucleus Accumbens and Ventral Tegmental Area R
-
Apparently nanostructured memantine selectively binds to eNMDAR not synaptic.
-
- 1.1 mg. This is what veganpermanently does (though he’s also done 5-25mg…)
- Memantine is an α7 nAChR antagonist.
- Ki 1 mM. Prolonged use upregulates it?
-
- GDNF upregulaton was associated with histone hyperacetylation.
-
How is it even used for dementia?
-
Efficacy of Memantine as Adjunct Therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children Aged <14 Years
-
Cancels/overpowers psychedelics via SLC7A11 (System Xc-) activation?
Modafinil
Rating: ★★★★★. It’s one of the most effective nootropics I’ve ever taken. See the post on Modafinil
NAC
More of a therapeutic (HPPD, tinnitus, OCD) than a nootropic for most people. Don’t expect it to be pro-cognitive.
Neboglamine
Rating: ★★★★. A scarily lucid potentiation of executive function and ‘motivation’ that feels purely rational and nothing to do with dopamine or anything. So many people get into nootropics for ‘getting things done’ and doing the things the better part of themselves wants to do without geting sidetracked on unimportant things, and I find negoblamine to be oddly effective at this.
- The only known NMDAR glycine site PAM, enhancing the binding of D-Serine.
- According to sirsadalot, oral D-Serine causing molecular-level oxidative stress could be due to it ending up in extrasynaptic regions it doesn’t normally exist in.
- NR3 agonist, which unfortunately is anti-cognitive. Nonameuser thinks it inhibits PFC function.
- CR 2249: a new putative memory enhancer. Behavioural studies on learning and memory in rats and mice (1996)
- Cognition Enhancing Profile of CR 2249, a New NMDA-Glycine Site Modulator
- Antipsychotic-like effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulator neboglamine: an immunohistochemical and behavioural study in the rat.
- Novel NMDA Receptor Modulators: An Update
- Characterization of a novel putative cognition enhancer mediating facilitation of glycine effect on strychnine-resistant sites coupled to NMDA receptor complex
- See also apimostinel (NRX-1074) (sold on TeamLTR) and rapastinel (GLYX-13), modulators that bind to unique domains independent of the glycine site.
- There is also NYX-2925 (aka AGN-241751) and NYX-458.
- (It’s not an antagonist but apimostinel could be? There’s a biphasic dose response.) GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects
- Weak selective Noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor at high doses (104.5μM/L, 10x that of being a glycine site PAM)
- Also has an NRI metabolite.
Nicotine
Rating: ★★
- Out of all the nAChR subtypes, its highest binding affinity is for α4β2, representing >90% of its binding in brain tissue, supposedly the primary mediatory of its addictiveness, since they release dopamine.
- Another mechanism of its addiction is α4 nAChR upregulating inhibitory GABAergic neurons.
- α4β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors on Dopaminergic Neurons Mediate Nicotine Reward and Anxiety Relief
- Mice lacking α4 nAChRs have elevated levels of basal anxiety.
- For instance, GTS-21, an α7 agonist, does not activate the ’nicotine cue’ R
- Nicotine reverses hypofrontality in animal models of addiction and schizophrenia
- The interesting part of the study is how it affects Somatostatin interneurons.
- α5 nAChR: rs16969968 (Asp398Asn) (A/A (Me: AG)). Associated with nicotine dependence but lower risk of cocaine dependence. Results in loss of function.
- Reduced resting-state functional connectivity, and circuits involving the PFC are altered: A genetically modulated, intrinsic cingulate circuit supports human nicotine addiction
- Specifically, α4β2α5 nAChR function, which somehow ‘incorporates’ itself into heteromers like α4β2.
- Previously: Association of nicotine addiction and nicotine’s actions with separate cingulate cortex functional circuits: Resting-state dACC-striatum functional connectivity may serve as a circuit-level biomarker for nicotine addiction
- Molecular genetics of successful smoking cessation: convergent genome-wide association study results
- The supplementary pdf has like a good 100 SNPs. Would like to see this on Nebula… it’s a lot of cool stuff; a lot of actin proteins. Even ADAM12 (one I have is rs7920207 AC)
- Reduced resting-state functional connectivity, and circuits involving the PFC are altered: A genetically modulated, intrinsic cingulate circuit supports human nicotine addiction
- Layer VI is one of only a handfyl of brain regions that express α5.
- Deletion α5 in mice leads to PFC-linked behavioral deficits, altered cholinergic excitation and aberrant neuronal morphology in the PFC: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in attention circuitry: the role of layer VI neurons of prefrontal cortex
-

- More smoking genes in the α3-α5-β4 cluster: Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior
- Strongest association was the α3 nAChR rs1051730 (A (Me: AG))
- rs1329650 (G (Me: –))
- rs1028936 (A (Me: AC))
- rs3733829 (G (Me: AG))
- EGLN2
- Smoking cessation: rs3025343 (G (Me: AG))
- BDNF: rs6265 (A (Me: TC (So AG?)))
- Implcated in introversion, quicker mental decline in Alzheimer’s, impaired motor skills learning. It may be protective against depression though R
-
- α5 nAChR is implicated in schizophrenia: ts. In α5-SNP-expressing and α5-knockout mice, lower activity of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) interneurons resulted in an increased Somatostatin interneuron inhibitory drive over layer II/III pyramidal neurons - this resembles hypofrontality, and was reversed by chronic nicotine.
- Sustained phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase at serine 40: a novel mechanism for maintenance of catecholamine synthesis
- Upregulates striatal Tyrosine Hydroxylase for a few days after administration, probably downstream of GDNF (itself downstream of FGF2)
- Releases Kisspeptin
- Nicotinic modulation of neuronal networks: from receptors to cognition
- Stimulates presynaptic α7 nAChR in glutamatergic neurons, enhancing projections to DA neurons.
- Nicotine Effects and the Endogenous Opioid System
- The endogenous opioid system participates in NIC-induced antinociception, but not HPA axis activation. Moreover, NIC-induced antinociception is mediated by α4β2 and α7 nAChRs, while NIC-induced HPA axis activation is mediated by α4β2, not α7, suggesting that the effects of NIC on the endogenous opioid system are mediated by α7, not α4β2.
- Activation and Desensitization of Nicotinic α7-type Acetylcholine Receptors by Benzylidene Anabaseines and Nicotine
- [Sustained Nicotine Exposure Differentially Affects α3β2 and α4β2 Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes]
- Nicotine decreases α4β2 responsiveness much faster than α3β2 nAChR.
- Inhibits 3α-HSD, boosting synthesis of DHT, etc. R
- 3 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks reduced 43% body weight gain and 65% blood insulin level, but had no effect on blood glucose level,… demonstrated that nicotine enhancement enhanced insulin sensitivity. R
- Chronic use downregulates NCAM
- Increased expression of VMAT2 in dopaminergic neurons during nicotine withdrawal
- Nicotine reduces discrimination between threat and safety in the hippocampus, nucleus accumbens and amygdala
- Overactivation of the VTA.
Tolerance
- Chronic Nicotine Cell Specifically Upregulates Functional α4 Nicotinic Receptors: Basis for Both Tolerance in Midbrain and Enhanced Long-Term Potentiation in Perforant Path
- Chronic nicotine does not change α4 receptor levels in dopaminergic neurons of VTA or Pars Compacta. Instead, upregulated, functional α4 receptors localize to the GABAergic neurons (Medium Spiny Neurons or interneurons??) of the VTA and Pars Reticula.
- Acute Nicotine-Induced Tachyphylaxis Is Differentially Manifest in the Limbic System
- … whereas profound tolerance was observed in many cortical regions after the second of two paired nicotine injections at either 0.1 or 0.3 mg/kg, subcortical limbic structures showed only a weak trend for tolerance.
- Temporal change in human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor after smoking cessation: 5IA SPECT study
- The binding potential of nAChRs in the brains of smokers decreased by 33.5% +/- 10.5% after 4 h of smoking cessation, increased by 25.7% +/- 9.2% after 10 d of smoking cessation, and decreased to the level of nonsmokers after 21 d of smoking cessation.
- β2-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Availability during Acute and Prolonged Abstinence from Tobacco Smoking
-
- The acute decrease of availability in the Thalamus is quite weird. Not sure how that happens.
- Nicotine induced increases in nAChR, termed “upregulation”, are conferred by a specific microdomain that is in the β2-subunit 34 and thus this upregulation is confined to nAChR that contain the β2-subunit
-
Noopept
Rating: ★★. Crazy laser focus. So crazy that I swear it bleeds into negatively affecting other cognitive faculties like short-term memory. It just felt weird sometimes. There are plenty of weird ass anecdotes out there, like it giving long-lasting 2D vision. So proceed at your own risk. There are better compounds out there for most of the things it does.
- AKA (N-Phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester) Converted into phenylacetic acid, prolylglycine, and Cycloprolylglycine, a naturally-produced neurodipeptide which I think is how noopept exerts its effects.
- I believe it is much more glutamatergic than the other racetams; its vasodilatory effects can cause headaches which seem to be not uncommon. It can be used to kill NMDA antagonist trips (like Ketamine).
- The drug action is based on the Antioxidant effect, the antiinflammatory action, and the ability to inhibit the neurotoxicity of excess calcium and glutamate, and to improve the blood rheology.
- Piracetam (400mg/kg (=~4.6g HED)) increased Alpha waves/Beta waves EEG activity in the left frontal cortex, and Alpha waves activity in both the right cortex and Hippocampus. Noopept (0.2mg/kg (=~2.27g HED)) increased Alpha waves/Beta waves activity… in all brain areas. The effect of Noopept in the alpha/beta1 ranges was replaced by increased beta2 activity after the eighth injection, while no effects were observed after the ninth one. R
- AMPA agonist: Studying specific effects of nootropic drugs on glutamate receptors in the rat brain
-
Effect of noopept and afobazole on the development of neurosis of learned helplessness in rats Noopept will make you a non-fearful rat.
-
- It was suggested that Noopept mediates its effect due to the activation of inhibitory Interneurons terminating on CA1 pyramidal cells. Results of current clamp recording of inhibitory interneurons residing in stratum radiatum confirmed this suggestion.
-
Nootropic dipeptide noopept enhances inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus (2010)
- 1mM significantly increased the frequency of spike-dependant spontaneous IPSCs whereas spike-independent mIPSCs remained unchanged, as well as the kinetic parameters (rise and decay time). It increasess the firing of GABA Interneurons.
- I wouldn’t jump to the conclusion that this “inhibits memory” or something. I think it just makes you more selective, right? Or, it’s more like it enhances recall at the expense or encoding? However:
- The original novel nootropic and neuroprotective agent noopept (2002)
- In contrast to piracetam facilitating only the early stages of the memory process, noopept positively influences the Memory consolidation and retrieval steps as well… produces an additional selective anxiolytic action. The pronounced neuroprotective effect of noopept was demonstrated both in vivo (in cases of various forms of brain ischemia) and in vitro (on various neuronal models).
- The original novel nootropic and neuroprotective agent noopept (2002)
- I wouldn’t jump to the conclusion that this “inhibits memory” or something. I think it just makes you more selective, right? Or, it’s more like it enhances recall at the expense or encoding? However:
- 1mM significantly increased the frequency of spike-dependant spontaneous IPSCs whereas spike-independent mIPSCs remained unchanged, as well as the kinetic parameters (rise and decay time). It increasess the firing of GABA Interneurons.
-
Molecular Mechanism Underlying the Action of Substituted Pro-Gly Dipeptide Noopept
- Increase in HIF-1α DNA-binding activity. Indeed, this may be its main MOA.
- Its effects on HIF suggest that it shouldn’t be used continuously. -Peat. Interesting, since It is known that activation of the HIF system is now regarded as one of the main mechanisms of neuroprotection during hypoxia, cerebral ischemia, and neurodegenerative diseases. Relation to CO2??
- Enhances Antioxidant activity.
- Represses the stress-induced pSAK/JNK and pERK1.
- Increase in HIF-1α DNA-binding activity. Indeed, this may be its main MOA.
NSI-189
Rating: ★★. It felt pretty awesome but I think it gave me chronic fatigue. Perhaps a shift from beta wave to alpha wave dominance increasing propensity for dissociation into more sedated states.
- Induces statistically-significant increases volume of the right Amygdala, which is reduced in size in major depressive disorder. The golden question is how bad this is, considering meditation atrophies it and all. R
- Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function by the Neurogenic Molecule NSI-189 Accompanies Reversal of Peripheral Neuropathy and Memory Impairment in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes
- This is a seriously underrated/potentially underappreciated mechanism. Apparently few compounds have such a comprehensive enhancement
- Elevated the expression of protein subunits of complexes III and V and activities of respiratory complexes I and IV in the cortex. Ameliorated loss of AMPK in sensory ganglia.
- An Early Valuation Of Neuralstem’s NSI-189 For MDD
- NSI‐189, a small molecule with neurogenic properties, exerts behavioral, and neurostructural benefits in stroke rats
- Increased MAP2 expression. BDNF and SCF upregulation.
Its mechanism is pretty much unknown but it’s speculated to be adrenergic somehow.
-
https://www.longecity.org/forum/topic/91594-nsi-189-mechanism-of-action/
- JAK-STAT pathway inhibitor?. Lol. 5-HT1A and D2/D3, most likely agonism.
- Some IC50s are supposedly: 14.2 DAT, 1.1 NET, 2.1 5-HT3, 11.1 5-HT7, 15.7 μ, 12.7 δ1.
-
- Works on the SCF complex (Skp, Cullin, F-box)
-
Allostasist says NET inhibitor and 5-HT3 antagonist. And other people suggest possible TrkB downregulation.
-
DAT: 14.2 IC50
-
NET: 1.1
-
SERT: >30
-
5-HT3: 2.1
-
5-HT7: 11.1
-
μ: 15.7
-
δ: 12.7
-
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1jMJ84rKR8lWHVkkEnsZsWTBvonVVArjzw7WxOWDtSG0/edit every anecdote you could ever ask for. Wtf.
Octreotide
Potent somatostatin mimetic.
Somatostatin
- Somatostatin Interneurons can express GABA but they also express SST. SST opposes the actions of GABA and promotes the inhibition of Parvalbumin interneurons which impart inhibition onto pyramidal cells. SST increases the efficiency of glutamate and the “fidelity” of neurotransmission.
- SST increases both muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine currents.
- He claims glutamate neurotoxicity is due to the starvation of glutamate neurons of glu and other excitatory AAs like I guess NMDA for example.
- Decline in SST = increased synorphin signalling/opioidergic tone hypothesis of brain aging.
- Opioids activate SST interneurons, suppressing parvalbumin interneuron activity on pyramidal neurons, disinhibiting pyramidal cell activity leading to reward: Morphine coordinates SST and PV interneurons in the prelimbic cortex to disinhibit pyramidal neurons and enhance reward
- In disorders such as autism, PV interneurons far outnumber those of SST leading to overinhibition.
- Decline in SST = increased D21 formation though GABA B, increasing D2, reducing NMDA via cholinergic deafferentation, and increasing mTOR signalling.
- Somatostatin dysfunction is the root cause of all neurodegenerative diseases and mental disorders including depression
- Hypothalamic inflammation via endotoxins, ceramides, SFA, is a lead cause of diabetes. This is all these pathologies are ultimately mediated by a decline in insulin sensitivity and SST interneurons
- Somatostatin inhibitory interneurons are one of three populations of gabaergic interneurons within the brain that send gamma (GABA?) currents to pyramidal cells The foundations for optimal human health are grounded upon somatostatin interneurons especially within the hypothalamus
- The only GABAergic interneurons that express α7 nAChR, meaning it mediates the rewarding effects of cholinergic signaling.
- Somatostatin down-regulates the expression and release of endozepines from cultured rat astrocytes via distinct receptor subtypes
- Agonists also inhibited cAMP formation dose-dependently, i.e. reduced Forskolin-induced endozepine release.
- The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain and its application in treating neurological disorders
-
2-Oxazolidinones
Discussed pretty extensively on /r/researchchimicals
Cyclazodone
TAAR1 agonist
N-Methyl-Cyclazodone
Possible serotonergic effects.
Fenozolone
Pemoline
Probably the only sustainable one in terms of safety, but also the most difficult to obrain. Unknown MOA but likely has dopaminergic actions and is a possible AADC inhibitor (Pemoline and urinary excretion of catecholamines and indoleamines in children with attention deficit disorder)
It faded into obscurity after cases of liver failure in kids being prescribed pemoline for ADHD. But it would seem hepatotoxicity is overblown.
Pitolisant
- Histamine H3 partial inverse agonist, which enhances memory retrieval:
- Central Histamine Boosts Perirhinal Cortex Activity and Restores Forgotten Object Memories
- New procognitive enhancers acting at the histamine H3 and AMPA receptors reverse natural forgetting in mice: comparisons with donepezil and memantine in the object recognition task Drugs are called S3809 and S47445 respectively.
- Histamine H3 receptor density is negatively correlated with neural activity related to working memory in humans
- Pitolisant, an inverse agonist of the histamine H3 receptor: an alternative stimulant for narcolepsy-cataplexy in teenagers with refractory sleepiness
- ‘Non-inferior’ to Modafinil at treating narcolepsy.
- Blocks hERG (Kv 11.2)
- Pitolisant-supported bridging during drug holidays to deal with tolerance to modafinil in patients with narcolepsy reverses Modafinil tolerance!
Phenidates
Methylphenidate
- Methylphenidate preferentially increases catecholamine neurotransmission within the prefrontal cortex at low doses that enhance cognitive function
- Methylphenidate Exposure Induces Dopamine Neuron Loss and Activation of Microglia in the Basal Ganglia of Mice
- Methylphenidate and μ opioid receptor interactions: A pharmacological target for prevention of stimulant abuse
- supra-therapeutic doses of MPH produce rewarding effects (surrogate measure for addiction in humans) in a conditioned place preference paradigm and upregulate μ-Opioid Receptor activity in the Striatum and nucleus accumbens, brain regions associated with reward circuitry
- This requires activation of D1, but not D2.
- supra-therapeutic doses of MPH produce rewarding effects (surrogate measure for addiction in humans) in a conditioned place preference paradigm and upregulate μ-Opioid Receptor activity in the Striatum and nucleus accumbens, brain regions associated with reward circuitry
Dexmethylphenidate (Focalin)
Probably the most sustainable of the DRIs prescribed for ADHD.
IPPH (Isopropylphenidate)
Has a much greater affinity for DAT than NET.
Pinealon
https://unyieldingvigor.com/resources/b/pinealon-glu-asp-arg & https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/12lvvjq/pinealon_improves_cognition_and_performance_in/
https://penchant.bio/products/pinealon-spray
Pregnenolone
Rating: ★★. Good stuff, but I’m too young to get much out of it.
“A couple of times I saw men who were not quite suicidal, but extremely depressed, talking about quitting their job and just giving up, and they both happened to be sitting in a dark corner of the room with a glass of wine, wanting to retreat, even within the room as well as from life in general. And, thinking about the old bayonet studies and such, I put a pinch of pregnenolone in their wine; and within about 15 minutes, in both cases, they were grinning and talking about projects and went back to work and were just as happy as they could ever be.”
-
Progesterone Pregnenolone & DHEA - Three Youth-Associated Hormones (Ray Peat)
-
Increases dopamine release/response to Morphine in rat nucleus accumbens R
-
Anti-Cancer.
-
Improves joint mobility in arthritis, tissue elasticity in lungs, and eyesight.
-
Enhances memory and mood (calms emotions, increased resilience) skin (improves circulation), normalizes aldosterone, and lowers estrogen.
-
The most potent inhibitor of the stress signal: Ray Peat Forum
-
Activates TRPM1/3 channels.
-
Interferes with TLR4 activation.
-
CB1 negative allosteric modulator.
-
Excitatory neurosteroids DHEA(-S) and PGL at physiological concentrations participate in the inhibition of cortical neuronal degeneration elicited by staurosporine and glutamate, whereas the most potent positive modulator of GABA-A receptor - Allopregnanolone - has no effect. R
-
- Pregnenolone and Progesterone were inhibitory, but Testosterone was stimulatory.
- Pregnenolone itself doesn’t do much in the nervous system, but pregnenolone sulfate does exhibit cognitive/memory enhancing, antidepressant, anxiogenic, and proconvulsant effects.
- Potent negative allosteric modulator of GABA-A; weak positive allosteric modulator of NMDAR.
- To a lesser extent, acts as a negative allosteric modulator of AMPAR, Kainate Receptor and Glycine receptors.
- Subtype-dependence of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor modulation by pregnenolone sulfate
- Shown previously how P-S potentiates A>B and inhibits C$\approx$D: Inhibition of the NMDA response by pregnenolone sulphate reveals subtype selective modulation of NMDA receptors by sulphated steroids
- the structure of the extracellular loop between the third and fourth transmembrane domains of the NR2 subunit is a key determinant for the PS effects
- Acts at 2 distinct binding sites.
-
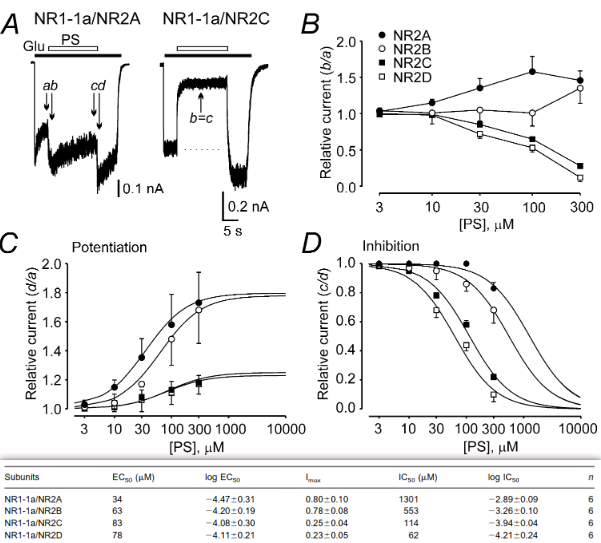
- Interesting stuff in A: it initially inhibits the current, and then when it unbinds,
-
- 20-oxo-5β-Pregnanolone-S (3α5βS) inhibits the responses.
- responses induced by NR1A/NR2A and -NR2B receptors are potentiated five- to eight-fold more by pregnenolone sulfate than responses of NR2C and NR2D.
- Hypothalamic pregnenolone mediates recognition memory in the context of metabolic disorders
- Acute obesogenic diet administration in mice impaired recognition memory due to defective production of pregnenolone in the hypothalamus.
- POMC neurons have a far superior neuroSteroidogenesis capacity than AgRP neurons.
- loss of Stard1 in POMC neurons impaired recognition memory performance in the face of normal metabolic and energy balance status. These findings indicate that inadequate neurosteroid production by POMC neurons is fundamentally implicated in cognition, but it is dispensable for energy homeostasis control
- The neurosteroid pregnenolone promotes degradation of key proteins in the innate immune signaling to suppress inflammation
- Promotes ubiquination of TLR2/TLR4 adaptor protein TIRAP and TLR2 in Macrophages and microglia, and suppressed TLR2/TLR4-mediated IL-6 and TNF-α secretion.
- Brain distribution and behavioral effects of progesterone and pregnenolone after intranasal or intravenous administration
- Nanomolar Concentrations of Pregnenolone Sulfate Enhance Striatal Dopamine Overflow In Vivo
- Stabilizes Microtubules and stimulates assembly. RPF
- Pregnenolone binds to microtubule-associated protein 2 and stimulates microtubule assembly Binds to MAP2. (Pregnenolone sulfate does not)
LTP
- Pregnenolone sulfate enhances long‐term potentiation in CA1 in rat hippocampus slices through the modulation of N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate receptors
- Neuroactive steroid pregnenolone sulphate inhibits long-term potentiation via activation of alpha2-adrenoreceptors at excitatory synapses in rat medial prefrontal cortex.
- PREGS inhibited induction of LTP in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex and had no influence on NMDA
- Neuroactive steroid pregnenolone sulphate inhibits long-term potentiation via activation of alpha2-adrenoreceptors at excitatory synapses in rat medial prefrontal cortex.
- PREGS induces LTP in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of adult rats via the tyrosine phosphorylation of NR2B coupled to ERK/CREB [corrected] signaling
- Total p-ERK levels increased but not levels of ERK. This is thanks to the calcium influx in NMDAR, and this is important for plasticity:
- Which number on tyrosine NR2B? Not sure
- May have interactions with nACh receptors as well.
- Steroid pregnenolone sulfate enhances NMDA-receptor-independent long-term potentiation at hippocampal CA1 synapses: role for L-type calcium channels and sigma-receptors
Supplementation
Peat has said that literally every source on the market today is unsafe for one reason or another.
-
70-80% oral bioavailability.
-
Men/women age 30 produce ~30-50mg/day. A dose of 300mg acts for a week. Dosing actually improves the body’s ability to produce its own pregnenolone. But high doses such as >100 inhibit androgens/DHT?
-
We produce 5% as much in old age than we do in our youth - as is the case with DHEA and progesterone.
-
30-50 for DHEA+progesterone pthway, while 100-150 is more like mainly in the way of progesterone.
Intranasal
- Intranasal pregnenolone increases acetylcholine in frontal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala-Preferentially in the hemisphere ipsilateral to the injected nostril (Fazari et al. 2019)
- The second caveat is extremely interesting. Similarly, Previous studies have shown that the unilateral IN administration of l-DOPA increased extracellular dopamine only in the ipsilateral neostriatum of male Wistar rats, excluding the systemic transport of the drug from the nose to the central nervous system (De Souza Silva et al., 1997; Silva et al., 1997).
- *Nuwayhid and Werling (2003) demonstrated that PREG *inhibits the NMDA-stimulated dopamine release in the striatum via Sigma Receptors with involvement of the coupled-Protein Kinase Cβ pathway.
- Steroids modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated 3H dopamine release from rat striatum via sigma receptors
- I mean sure, everything probably expresses a little bit of anything. But it’s literally major a dopaminergic input - how much do its outputs matter? I’d say this study seems very significant but at the end of the day
- 3H-dopamine lacks a double bond on the benzene. Are the consequences for this massive or what?
- Steroids modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated 3H dopamine release from rat striatum via sigma receptors
- Brain distribution and behavioral effects of progesterone and pregnenolone after intranasal or intravenous administration (Ducharme et al., 2011)
- ~23% entered the blood. Brain levels were about two fold lower after intranasal administration.
- From 10 to 60 minutes, Brain: 35 ± 2.6 -> 45 ± 18
- Serum 3.7 -> 7.6
-
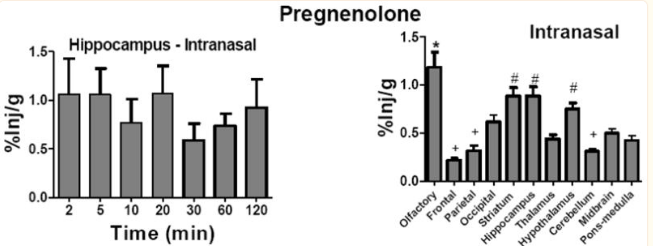 (Inj/g = percent of amount administered.) All this really asserts is preg’s affinity for brain regions.
(Inj/g = percent of amount administered.) All this really asserts is preg’s affinity for brain regions.
- 200pg was the goldilocks zone for memory enhancement, while 1fg or 200ng were without effect. They weighed 0.025 - 0.03kg, so that’s 0.00015pg/kg. HED = 0.0000229995pg/kg = 20 fucking femtograms of pregnenolone. I probably get more than that by just happening to be inhaling when I open the jar.
- ~23% entered the blood. Brain levels were about two fold lower after intranasal administration.
- Promnestic effects of intranasally applied pregnenolone in rats
- 0.187 or 0.373 mg/kg = 0.056 or 0.112 mg = HED 2.1 or 4.2 mg.
-
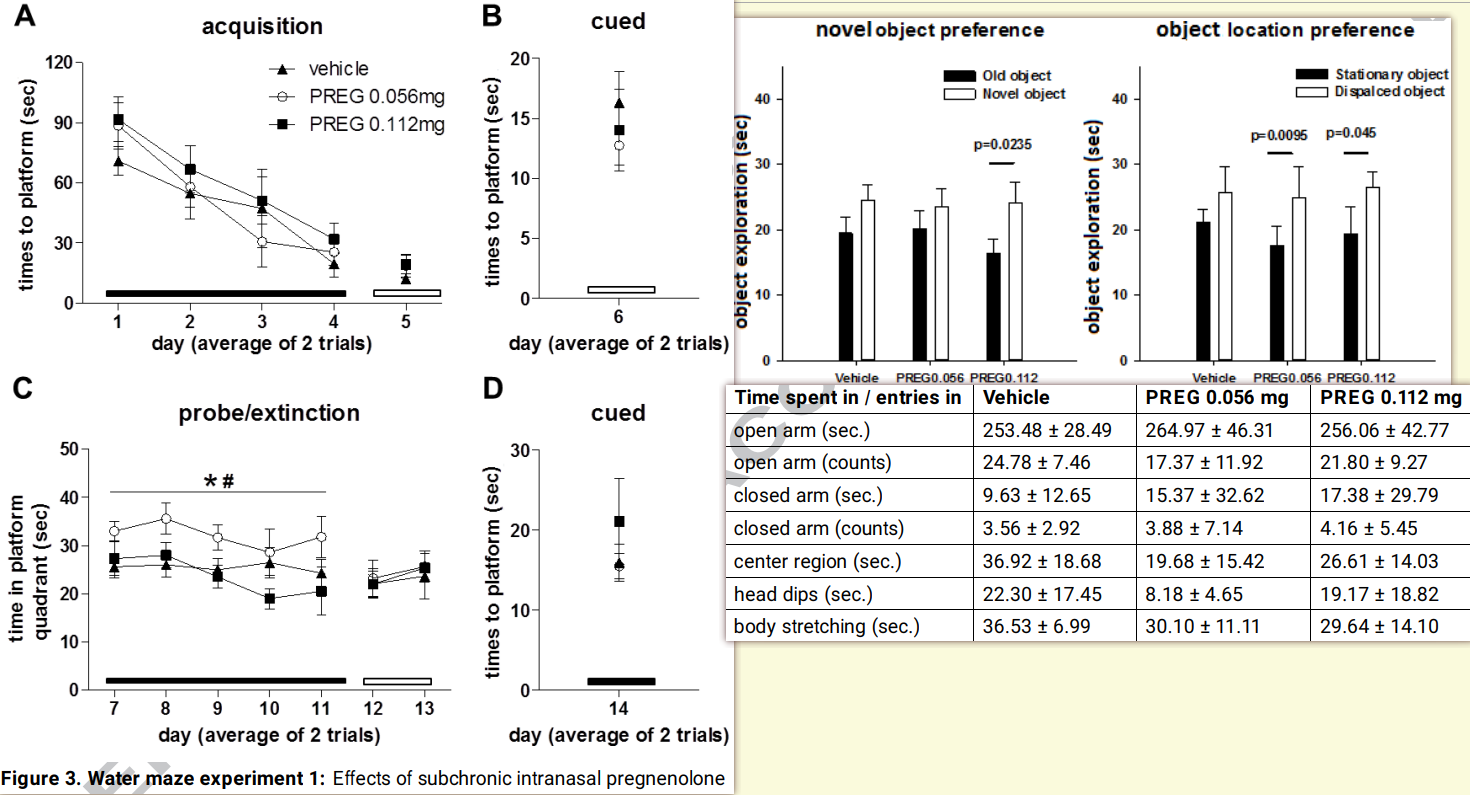
- C depicts how much time they spent in previous reward platforms as opposed to the new ones - this is a measure of relearning or whatever.
PRL-8-53
Rating: ★★★. 5mg sublingually definitely enhances both working and long-term memory (I’ll never forget how one time I photographically recalled the image of a wikipedia article I had been reading earlier because I wanted to read the rest of it) but it also feels kind of dirty. I don’t feel comfortable taking compounds with unknown MOAs.
Hypermnesic, spasmolytic. Only two studies done on it, in ‘74 and ‘78.
Derived from benzoic acid and Phenylmethylamine.
-
Increased learning of words by 87.5-105% in poor performers, and 7.9-14% in high performers - but that’s just due to a ceiling effect. Was #1 by a decent margin in the /r/nootropics survey for memory.
-
Displays Cholinergic properties (probably ACh uptake/synthesis). potentiates Dopamine and partially inhibits Serotonin signaling, and maybe synthesis.
- I’ve heard people say it doesn’t really work without choline. Especially when stacked with TAK-653, for whatever reason.
- It may inhibit the reuptake of dopamine, which depending on the mechanism such as DAT, may not be good long term. Also may be a direct agonist, though no stimulant-like symptoms have been shown even up to 200mg/kg.
- Possibly a M2 AChR agonist.
- Sirsadalot suspects it’s a DAAO inhibitor
-
Possibly a HDAC inhibitor. Very contentious. https://old.reddit.com/r/Nootropics/comments/5bqrpm/i_figured_out_prl853s_mechanism_of_action/
Dose: ~5-10mg or so sublingually. Caustic to the teeth though. Can also do 1-5mg intanasally in water; easily dissolves.
Psychoplastogens
Iso-DMT, Tabernanthalog, etc.
-
Evaluation of Isotryptamine Derivatives at 5-HT2 Serotonin Receptors
-
The Subjective Effects of Psychedelics May Not Be Necessary for Their Enduring Therapeutic Effects
- 6-MeO-iso produces no head twitch response. 6-MeO-Iso is an even more potent psychoplastogen than 5-MeO.
-
Psychoplastogens: A Promising Class of Plasticity-Promoting Neurotherapeutics
-
Psychedelics promote neuroplasticity through the activation of intracellular 5-HT2A receptors (Sheekey science show video)
- Psychedelics and Other Psychoplastogens for Treating Mental Illness
- Psychoplastogens are charactezied by, after single treatment, sustained effects on structural plasticity, notably in the PFC! Which means more excitatory projections to decrease depressive behavionr, addiction, etc.
- Pretty sure it’s from Gαq → Ca2+ → TrkB
- Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling and Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder
- BDNF was not reduced in the aCC, but TrkB was, and thus various markers that are downstrean/dependent on BDNF, like SST, NPY, COST, Glutamate Decarboxylase 2, etc. (they note that GAD1 isn’t BDNF-dependent)
- Psychoplastogens are charactezied by, after single treatment, sustained effects on structural plasticity, notably in the PFC! Which means more excitatory projections to decrease depressive behavionr, addiction, etc.
- Positive correlation between lipophilicity (thus able to pass the membrane, which serotonin is not capable of - notice the methylation on the amine with DMT/Psilocin, which serotonin does not have) and the psychoplastogenic effect, with DMT being the strongest.
- Clearly linked is a (mostly) inverse correlation between β-arrestin 2 Emax and Gq Emax and lipophilicity.
- The ability to pass through the membrane is significant due to the presence of intracellular 5-HT2A in cortical neurons.
- They gave the cells SERT, applied serotonin, and the dendritic outgrowth was similar to that of DMT.
- Psychedelics and Other Psychoplastogens for Treating Mental Illness
Racetams
Many would argue their AMPA PAM properties have been obsoleted by TAK-653. But they still have other actions (and some racetams have nothing to do with AMPA)
Aniracetam
Activates 5-HT2A, D2, D3.
- The aniracetam metabolite 2-pyrrolidinone induces a long-term enhancement in AMPA receptor responses via a CaMKII pathway
- Enhances GluR1, GluR2, GluR3
Coluracetam
- Increases HACU. Mild AMPA PAM.
Fasoracetam
- Upregulates GABA-B.
Oxiracetam
Rating: ★★★. My 3rd favorite racetam. Feels really clean and was relatively consistent.
- Increases HACU and LTP.
- Oxiracetam and Zinc Ameliorates Autism-Like Symptoms in Propionic Acid Model of Rats
Phenylpiracetam
Rating: ★★★★★. Higher doses with no tolerance feel very dopaminergic. Eugeroic too; amazing preworkout if timed correctly.
Apparently it was originally invented to be taken at ~100mg daily and that its stimulating properties (which are amazing and sustainable) are treated as a temporary side effect (indeed, unfortunately, it only lasts 1-3 days before a break of ~1-2 weeks is necessary), but I refuse to believe you don’t just slap a phenyl group on perfectly good piracetam and act like dopaminergic properties were an accident.
-
Affects the Casein Kinase enzymes. It could possibly exacerbate milk allergies due to this - very interesting.
-
Decreases iNOS, increases eNOS
-
Decreases the number of nAChRs and NMDARs???
-
Agonizes α4β2 nAChR with IC50=5.86μm.
-
- 100mg/kg (HED>1g: madness)
- I’ll have to look and see if all the effects measured were all after taking scopolamine.
-
Possible actions on DAT: S-phenylpiracetam, a selective DAT inhibitor, reduces body weight gain without influencing locomotor activity .
-
https://www.freepatentsonline.com/EP2891491A1.pdf (Rats) (10mg HED = ~113mg)
Methylphenylpiracetam
σ1 PAM. Nothing like regular phenylpiracetam.
Phenylpiracetam Hydrazide (RGPU-95)
Piracetam
Rating: ★★★★. Inconsistent, but the way it increases fluidity of thought is fantastic. I had an amazing honeymoon period with it at the very least. Everyone should try a cycle of piracetam.
- Decreases the destabilizing effects Amyloid β, which causes lipid disorganization within cell membranes. Other racetams do this as well.
- Increases (synthesis of) cytochrome B5
- Inhibits stress-induced Prolactin increase
- Reduces Erythrocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium, hinders vasospasm, and facilitates microcirculation. R
- Influences Membrane fluidity in the whole body; protecting the cell against Hypoxia.
- Increases brain O2 consumption, in connection to ATP metabolism.
- Aldosterone receptors are involved in the mediation of the memory-enhancing effects of piracetam
- Adrenalectomy blocks memory-enhancing effects of piracetam. This is abolished with administration of corticosterone or aldosterone so long as aldosterone receptors (Type I mineralcorticoid receptor) are not blocked.
- Piracetam Defines a New Binding Site for Allosteric Modulators of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors (Ahmed & Oswald 2010)
- GluR2/GluR3.
- Along with Aniracetam, Both drugs bind to GluA2 and GluA3 in a very similar manner, suggesting little subunit specificity.
- Piracetam binds to multiple sites along the dimer interface with low occupation, one of which is a unique binding site for potential allosteric modulators.
- However, the binding sites for piracetam and Aniracetam differ considerably.
- Increases Dopamine in cerebral cortex and striatum, and Serotonin in the cortex, while reducing serotonin in the Striatum, Brain Stem and Hypothalamus. R
- Increases Noradrenaline by increasing Locus Coeruleus firing. R
- Increases Noradrenaline and Serotonin turnover in Hippocampus.
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, in contrast to some other racetams that increase its synthesis.
- Increases hippocampal acetylcholine, and in aged mice, increases population of mAChR in frontal cortex by up to 40%.
- Carbachol-induced accumulation of Inositol Monophosphates was elevated, suggesting piracetam can normalize functional deficits associated with aging
- Profound effects of combining choline and piracetam on memory enhancement and cholinergic function in aged rats
- 200mg/kg increased Choline content in Hippocampus by 88%, and decreased Acetylcholine levels by 19%.
- Choline administration raised choline content about 50% in the Striatum and Cerebral Cortex, and 6-10% increase in ACh levels. None in hippocampus.
- The combination of choline and piracetam did not potentiate these effects seen with either drug alone, and in some cases, were worse.
- Rats given 100mg/kg of piracetam+choline exhibited retention scores several times better than piracetam alone. 200mg/kg of choline or piracetam alone was still inferior.
Glutamate
- Enhances efficacy of AMPA-induced calcium influx and maximal density of AMPARs in synaptic membranes, due to the recruitment of a subset of AMPA receptors which normally don’t contribute to synaptic transmission.
- Normalized the age-related elevated affinity of L-glutamate for NMDAR
- Binds to AMPARs with much lower affinity than ampakines or Aniracetam, but it can bind to multiple sites on the AMPA receptor, potentiating what binds to it, including piracetam itself.
- Larger doses can potentiate potassium-induced release of glutamate from hippocampal nerves.
- Significantly increases NMDAR density by 20% after 14 days of treatment.
- Allosteric modulator of certain CNS glutaminergic receptors. I wanna know how this prevents overactivation, because it does.
Pramiracetam
-
More efficacious than coluracetam at increasing HACU. Not proven to be an AMPA PAM.
-
Inhibits prolyl endopeptidase (aka prolyl oligopeptidase): Prolyl Oligopeptidase Enhances α-Synuclein Dimerization via Direct Protein-Protein Interaction
-
There are multiple reports on Longecity/Reddit of this racetam causing long-term damage to cognition/working memory due to nitric oxide synthesis may result in glutamate excitotoxicity! 300mg/kg in rats (so >3g in humans…) increased NOS by approximately 20%, which is quite dangerous apparently.
RAP-103
Long-lasting inhibitor of CCR5 (also CCR2/CCR8). Downstream inhibition of GSK-3β reactivates myelinating cells in the brain, improving LTP/cognition. This also enhances opioid analgesia and reduces anxiety.
Rapamycin
The basic premise as a nootropic is intranasal adminitration to facilitate synaptic pruning.
Was originally discovered in the soil of Easter Island in 1975 from Streptomyces tsukubensis. Wtf. And that molecule: a macrolide.
-
It inhibits Candida and other fungal infections, but it supresses the immune system by inhibiting activation of T Cells and B cells via reducing their sensitivity to IL-2.
- Although, these things seem to have increased serum concentrations following treatment.
-
Treatment with TOR-I results in a decrease in testosterone level, and an opposite increase in LH. Moreover, spermatogenesis seems to be disrupted by TOR-I and FSH levels are increased. R
-
Independently increases PSD-95, NR2B expression, and glutamate recycling
-
High levels in the periphery promote Beta Cell rest (somehow less sensitive to glucose)
-
[Alternative rapamycin treatment regimens mitigate the impact of rapamycin on glucose homeostasis and the immune system]
- Many beneficial effects are via inhibiting mTORC1, and mTORC2 for the negative side effects.
-
- Decreases mTORC1, but not mTORC2.
-
Fasting and rapamycin: diabetes versus benevolent glucose intolerance
- This mirrors the effect of fasting and very low calorie diets, which improve insulin sensitivity and reverse type 2 diabetes, but also can cause a form of glucose intolerance known as benevolent pseudo-diabetes.
-
Induces Erythropoietin resistanec in kidney transplant patients - levels increase.
-
Intranasal produces 25x+ brain concentrations with 1% the systemic exposure.
-
Effects of Rapamycin on Insulin Brain Endothelial Cell Binding and Blood-Brain Barrier Transport
- Acute did not affect BBB binding but chronic insigifnificantly slowed BBB transport. It slightly raised serum concentration of insulin and:
-
Rapamycin for longevity: opinion article this is pretty informal
- It can be regarded not as an “immunosuppressant” so much as reducing hyperimmunity. That’s what it’s used for in organ transplants
- Whether this is by insulin or nutrients, overactivation of (mTOR->)S6K inhibits insulin signaling,
- [Nutrient overload, insulin resistance, and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, S6K1]
- Amino acids mediate mTOR activation via class 3 PI3K (aka hVps34), as opposed to class 1. Infusion of Amino Acids leads to S6K1 activation and inhibition of insulin-induced class 1, leading to insulin resistance.
- IRS-1 downregulatory phosphorylation is always by means of JNK??
- A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance
- Absence of JNK results in decreased adiposity, significanty improved insulin ressistance and recepto signalling capacity.
- A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance
- [Nutrient overload, insulin resistance, and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, S6K1]
- Balancing Akt with S6K implications for both metabolic diseases and tumorigenesis
- Ketogenic diets can cause symptoms of starvation psuedodiabetes (SPD)
-
Rapalogs downmodulate intrinsic immunity and promote cell entry of SARS-CoV-2
Disease
- One thing to keep in mind about it potentiating Amyloid β in some pathologies is that the stuff may be protective!
- Intranasal rapamycin ameliorates Alzheimer-like cognitive decline in a mouse model of Down syndrome
- Preventing systemic alterations avoids imunosuppresant effects in ther periphery. But the brain?
- Rapamycin Activates Mitophagy and Alleviates Cognitive and Synaptic Plasticity Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease Get access Arrow
- Effectively alleviates defecits of plasticity in APP models, promoting lysosome-mitophagosome fusion. Impedes Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis, etc.
- Restoration of aberrant mTOR signaling by intranasal rapamycin reduces oxidative damage: Focus on HNE-modified proteins in a mouse model of down syndrome
- Oxidation of Arginase-1 and PP2A play a part in brain damage associated with synaptic transmission failure and NFTs.
- InRapa reduced ARG-1 protein-bound HNE and rescues its activitiy.
- mTOR Attenuation with Rapamycin Reverses Neurovascular Uncoupling and Memory Deficits in Mice Modeling Alzheimer’s Disease
- Restores eNOS-dependent cerebrovascular function funcions in AD models. (Since mTOR inhibits eNOS)
- Intranasal administration dring any point in the lifespan, besides late stage alzheimers, where it increases the toxicity of Amyloid β, will suppress its formation and disease progression and increase memory/cognition/mood.
- Therapeutic effects of rapamycin on MPTP-induced Parkinsonism in mice
- IGF-1 inhibition mitigates MPTP-induced neurological dysfunction.
Roxadustat
Rating: ★★★. Increase in both physical and mental endurance. It gives an enjoyable headspace, though it’s all pretty subtle. 100 mg taken 4x/week (workout days).
- See also FG-4497.
- Elevated endogenous EPO by 2x
- Possible blood pressure increase - was not found in metanalyses and only in a small minority in clinical trial.
- Erythropoiesis gives a performance advantage due to additional oxygen capacity but too much over time can potentially become problematic if it leads to polycythemia. There should be low risk with roxadustat as it was shown to be safe in healthy men, but if you already have high rbc, hemoglobin, hematocrit or are on anabolic steroids for example(in which case you shouldnt use it anyway), the risk would be increased.
- The HIFα-Stabilizing Drug Roxadustat Increases the Number of Renal Epo-Producing Sca-1+ Cells
- Roxadustat: Not just for anemia
- In particular, it has the potential to increase the risk of pulmonary hypertension and vascular calcification, and aggravate inflammatory infections.
- However, this is just based off a single case study of a diseased 73 year old woman, lol.
- [Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Potential of Roxadustat (FG-4592), a Small Molecule Inhibitor of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase in CD-1 Mice and Sprague Dawley Rats]
- In particular, it has the potential to increase the risk of pulmonary hypertension and vascular calcification, and aggravate inflammatory infections.
- Roxadustat prevents Ang II hypertension by targeting angiotensin receptors and eNOS
- HIF-1α inhibits AT1 and activates AT2 and eNOS.
- FG-4592 Improves Depressive-Like Behaviors through HIF-1-Mediated Neurogenesis and Synapse Plasticity in Rats
- HIF-1α → CREB, BDNF, EPO, VEGF obviously, but also PSD-95 and Homer-1.
- Hypoxia inducible factor stabilization leads to lasting improvement of hippocampal memory in healthy mice
Selegiline
Rating: ★★. This is partially a longevity/health supplement, but acute effects are to be expected, and I didn’t notice too much besides increased ADHD-like symptoms, probably from an acute tyrosine hydroxylase inhibition that’s seen. It’s controversial whether it’s worth taking especially now that we know MAO-B isn’t selective for dopamine like originally thought, and instead is part of GABA biosynthesis (Glial GABA, synthesized by monoamine oxidase B, mediates tonic inhibition). It’s an interesting one though.
- Irreversible inhibitor of MAO-B, in the sense that MAO-B must be resynthesized. MAO-A is slightly inhibited in high doses (20+mg/day). The standard clinical dose is something like 10mg/day oral.
- Catecholamine release enancer
- Upregulates GDNF→VMAT2
- Anti-Cholinergic - so it can cause mydriasis (pupil dilation - is this the same as lsd?)
- Too much MAO-B inhibition can wreck sleep in the short term.
- Decently decreases amphetamine induced oxidative stress. Amphetamine still causes neurotoxicty through other mechanisms.
- Reversible transvestic fetishism in a man with Parkinson’s disease treated with selegiline ==WTF==
- Pharmacological aspects of the neuroprotective effects of irreversible MAO‑B inhibitors, selegiline and rasagiline, in Parkinson’s disease
- Increases NGF. Not sure if that’s just in strokes
- [The effect of 6-months l-deprenyl administration on pineal MAO-A and MAO-B activity and on the content of melatonin and related indoles in aged female Fisher 344N rats]
- 0.25mg/kg (HED ~2.6mg) for six months. MAO-A significantly inhibited but only after 5 hours of darkness. After 14 hours, before lights off, 5-HT, NAS, 5-HIAA and 5-HTOL levels did not differ.
- Chronic selegiline administration transiently decreases tyrosine hydroxylase activity and mRNA in the rat nigrostriatal pathway.
- This is observed in the corpus Striatum - not substantia nigra.
- It decreased at 3/7 days but recovered by 14. And then at 21 days, TH mRNA was raised by 3x.
- Evidence that Formulations of the Selective MAO-B Inhibitor, Selegiline, which Bypass First-Pass Metabolism, also Inhibit MAO-A in the Human Brain
- ‘Zelepar’ disintegrates and is absorbed through the buccal mucosa.
- 2.5mg/day wasn’t nothing. But in some people, the activity was actually raised.
- DAT levels were measured in 10mg group by means of cocaine binding. It’s hypothesized selegiline might inhibit it. There were only 3 subjects but yeah not a significant change.
- Inhibition of Bupropion Metabolism by Selegiline: Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Human CYP2B6 and Characterization of Glutathione and Peptide Adducts
- CYP2B6 substrates (that which it metabolizes) also include Ketamine and Sertraline (inhibitor) and some others. Selegiline inhibits, and other inhibitors are memantine, raloxifene, curcumin, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine
- Effects of selegiline on antioxidant systems in the nigrostriatum in rat
- 2mg/kg = 22 hed.
- Effect of low‐dose treatment with selegiline on dopamine transporter (DAT) expression and amphetamine‐induced dopamine release in vivo
- Effect of long-term treatment with selective monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors on dopamine release from rat striatum in vivo
- found no change of dopamine concentration in striatum acutely treated with selegiline and a small increase of dopamine on chronic treatment.
Semax
Rating: ★. Felt nothing.
-
Its mechanism of action is unclear. May act through Melanocortin Receptors which has an inhibitory action on D2 I believe.
-
Increases TrkB insofar as the Adrenocortocotropic Hormone system is working well. I think it basically mimics ACTH-10.
- Downregulation warrants cycling.
-
Antidepressant and axiolytic; attenuates behavioral effects of chronic stress.
-
Semax and Selank Inhibit the Enkephalin-Degrading Enzymes of Human Serum
-
- 50μg/kg (HED 581): 1.4-fold increase of BDNF protein levels accompanying with 1.6-fold increase of TrkB tyrosine phosporylation levels, and a 3-fold and a 2-fold increase of exon III (gene thing) BDNF and trkB mRNA levels, respectively, in the rat hippocampus
- Upregulates TrkB, unlike noopept. I mean think about it, that’s probably why it has reverse tolerance. The question of course is how long that lasts especially if you ragequit after you notice shedding and your shit is still upregulated.
-
Effects of Semax on Dopaminergic and Serotoninergic Systems of the Brain
- For the fans: Yeah decent increase in Hypothalamic Dopamine concentrations. Looks like a MAO-B inhibitor would do it well considering the dopac+HVA increase but this is probably the case with literally anything that increases dopamine to be honest. Basically no increase in 5-HT but a spike in 5-IAA I believe is a nice sign?
-
Another study showed 50% decrease in frontal cortex BDNF expression.
Reverse tolerance!
Other Forms
-
N-Acetyl-Semax: Possibly anxiogenic.
-
N-Acetyl-Semax Amidate: ~33% longer half life. Anxiolytic.
-
Adamax: 2x the half life of NAS, and better absorption.
SkQ1
Rating: ★★. I don’t notice anything.
-
Part of SkQ (which includes -R1, 2, 2M, 3,4,5, -berb, -palm, C12TPP, and MitoQ) which are mitochondrial Antioxidants. They’re lipophilic cations so they penetrate through membranes. They inhibit ROS directly due to plastoquinone oxidation, or reducing ΔΨ.
-
I suppose they’re pretty popular for Longevity. Mice in a study lived 335 days vs. 290.
-
- SkQ1-treated rats of both strains displayed significantly higher locomotor and exploratory activity in the open field (OF) and less anxiety in the elevated plus-maze (EPM)
- SkQ1-treated Wistar rats exhibited slower learning in the Morris water maze (MWM) task comparison to the control group… may be associated with differences in redox homeostasis.
-
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQ1 improves impaired dermal wound healing in old mice
- SkQ1 treatment resulted in accelerated resolution of the inflammatory phase, formation of granulation tissue, vascularization and epithelization of the wounds. Wounds contained increased amount of myofibroblasts which produce extracellular matrix proteins and growth factors mediating granulation tissue formation.
- Earlier we have found that SkQ1 stimulated production of active TGFβ by fibroblasts
- The TGF-β produced by SkQ1-treated fibroblasts was found to stimulate motility (and tubulogenesis) of endothelial cells in vitro, an effect which may underlie pro-angiogenic action of SkQ1 in the wounds. Movement of the epitheliocytes into the in vitro “wound” was directly stimulated by SkQ1
- Scavenging of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria induces myofibroblast differentiation
- Scavenging of ROS activated the Rho-ROCK-LIMK pathway, and stimulated MMP9 secretion, which activated TGF-β, which mediated differentiation of subcutaneous Fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. NAC inhibited MMP activity.
- Scavenging of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria induces myofibroblast differentiation
- Prevention of excessive reaction of endothelium to the pro-inflammatory cytokine(s) might account for anti-inflammatory effect of SkQ1.
-
Important to support Electron Transport Chain complex IV to prevent peroxide buildup.
Store in the fridge. Can be injected or administered intranasal (~33 μg/spray)
SR9009
Rating: ★★★. My first cycle of 10mg daily, it reduced my sleep drive/need by a whole REM cycle. But I don’t get this anymore. The benefits seem endless and I can’t think of any negatives besides the fact it is untested in humans and we don’t know if something bad could crop up.
- Rev-Erb-α ligand. This is epic because it basically potentiates proper cicadian rhythm.
- Pharmacological targeting of the mammalian clock regulates sleep architecture and emotional behaviour this is one of the main studies, I believe.
- I need to take a close look at the comparison between the 2. They might have slightly new effects?
- SR9009 has REV-ERB–independent effects on cellproliferation and metabolism
- SR9009 can decrease cell viability, rewire cellular metabolism, and alter gene transcription in hepatocytes and embryonicstem cells lacking both REV-ERBαand -β.
- Regulation of Circadian Behavior and Metabolism by Synthetic REV-ERB Agonists
- In addition to the decrease in fat mass we also observed a12% decrease in plasma triglycerides (TGs) and a 47% decrease in plasma total cholesterol (Chol) (Fig. 5c). Plasma non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA) were also reduced (23%) along with plasma glucose (19%) in the SR9009 treated animals (Fig. 5c). There was also a trend toward a decrease in plasma insulin levels (35%). Consistent with the decrease in adipocity we also noted an 80% decrease in plasma leptin and a decrease (72%) in the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6
- Treatment resulted increased glucose oxidation in addition to fatty acid oxidation
- SR9009 inhibits lethal prostate cancer subtype 1 by regulating the LXRα/FOXM1 pathway independently of REV-ERBs
- Somehow induces LXRα → blocks FOXM1, which is an inducer of PCS1 (a driver of prostate cancer) amongst other things.
- (This could be awesome since LXR in the brain is neurogenic)
- Somehow induces LXRα → blocks FOXM1, which is an inducer of PCS1 (a driver of prostate cancer) amongst other things.
- No effect on insulin sensitivity. Lowers cholesterol.
- Strong anxiolytic without any depressive/GABAergic effect.
- Could be due to Rev-Erb inhibiting NPAS2
- REV-ERBβ is required to maintain normal wakefulness and the wake-inducing effect of dual REV-ERB agonist SR9009
- REV-ERBβ-deficient mice administered with dual REV-ERB agonist SR9009, failed to show drug-induced wake increase
- Rev-erbα agonist SR9009 protects against cerebral ischemic injury through mechanisms involving Nrf2 pathway (Mar 2023)
- Identification of a small molecule SR9009 that activates NRF2 to counteract cellular senescence (2021)
- Activates NRF2 pathway.
- RNA sequencing data confirmed that the elevated SASP factors were reduced by SR9009, including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-8, IL-6, and CXCL-1.
- Attenuated p38.
- Weakened NF-κB and PI3K-AKT pathways.
- Activates NRF2 pathway.
- REV-ERB Agonist SR9009 Regulates the Proliferation and Neurite Outgrowth/Suppression of Cultured Rat Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
- Inhibited the growth of these AHPs.
- 9009 activated Rev-Erbβ downstream genes like Ccna2 and Sez6.
- Ccna2 = Cyclin A2. Promotes proliferation.
- Sez6 promotes neurite outgrowth
- REV-ERB agonism improves liver pathology in a mouse model of NASH
- Recruits Ncor1 (Nuclear receptor co-repressor 1).
- Pharmacological and Genetic Modulation of REV-ERB Activity and Expression Affects Orexigenic Gene Expression (2016)
- Not only orexin, but it also strongly represses transcription of the orexin receptors.
- Orexin signaling via OX1R in the striatum and nucleus accumbens is associated with reward feeding and addictive behavior toward nicotine and other drugs. SR9009 thus prevents this.
- I wonder it this provides some insight into inconsistency from Modafinil, given how the wakefulness-promoting effect is enhanced in orexin-KO and everything.
- mTOR inhibitor.
- SR9009 induces a REV-ERB dependent anti-small-cell lung cancer effect through inhibition of autophagy
- Via what exactly? Repressing Atg5
- Identification of a small molecule SR9009 that activates NRF2 to counteract cellular senescence
- SASP suppressor (via activating NRF2) , inhibiting senescence.
- Rev-erb-α regulates atrophy-related genes to control skeletal muscle mass
- KO mice have increased expression of muscle atrophy-related genes (atrogenes), while over-expression = increased muscle size.
- Suppression of atherosclerosis by synthetic REV-ERB agonist
- reduced REV-ERBα expression in hematopoetic cells in LDL receptor null mice led to increased atherosclerosis
- Reduced the polarization of bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages to proinflammatory M1 macrophage while increasing the polarization of BMDMs to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages
- REV-ERBα Regulates TH17 Cell Development and Autoimmunity Reduces incidence of autoimmunity.
- According to tyw’s citiation that is 404, it peaks around 10 PM - noon? ZT0 (zeitgeber time) = midnight to the system being studied, which is the opposite between mice and humans I suppose.
- (This post is a fantastic writeup on SR9009 though)
Metabolism
- No reported negative side effects afaik brotha.
- α IC50 = 670 nM and αβ IC50 = 800
- In vitro metabolism of the REV-ERB agonist SR-9009 and subsequent detection of metabolites in associated routine equine plasma and urine doping control samples
- To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first report of an adverse analytical finding in an equine sample for SR-9009 or its metabolites in equine doping control.
- Adverse meaning what exactly? Besides having evidence of administration. Since some studies it was undetected in urine.
- To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first report of an adverse analytical finding in an equine sample for SR-9009 or its metabolites in equine doping control.
- CYP stuff. A further insight into the metabolic profile of the nuclear receptor Rev-erb agonist, SR9009
SR9011
- There are ohter rev-erb-α ligands. For one thing, this has better bioavailability. Sonething like 5x? Idk if this matters when intranasal, though aerin has recommended intranasal for all of them.
- (α IC50 = 970 nM and αβ IC50 = 790)
- Far less studied. Idk, I’ll check it out some other time maybe? It’s hard to say what the differences are without going deep asf. I guess I’ll see what’s different between α and β.
SR10067 (1380548-06-2)
Also has strong Rev-Erb-β affinity. And something like 6-8x more potent in general. IIRC, this is orally available.
Dose
- 6-20mg intranasal. 4 hour half-life. Very poor oral bioavailability.
Nasal spray in caprylic acid (it’s lipophilic) is what you won’t see a lot of people discussing on the internet.
Rev-Erb
Rev-Erbα (NR1D) and Rev-Erbβ (NR1D2) (aka αβ). The latter was originally thought to be redundant, but it does have some more novel research into distinct actions.
Nuclear receptor transcription factors for the circadian clock.
- Rev-Erbα is also expressed in muscle, adipose tissue, and liver. Regulates Fatty Acid Synthase.
- TLR4 antagonist.
- Detects Heme, its endogenous ligand. Whatever that’s worth.
- Rev-erb-α modulates skeletal muscle oxidative capacity by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy
- Activates the Stk11–AMPK–SIRT1–PGC-1α signaling pathway.
- Indeed, STK11 (aka LKB1 (liver kinase B)) activates AMPK. mRNA levels are Increased by ERα activation.
- Inhibits mitophagy. (Thereby increasing mitochondrial content and oxidative capacity of myocytes)
- A Rev-erb-α/Ppargc1-α cross-talk pathway regulates heme synthesis in hepatic cells:
- increase in glutamate-malate-stimulated and ADP-driven respiration in absence and presence of succinate of permeabilized fibers
- Represses genes involved in autophagosome formation and lysosomal degradation.
- Activates the Stk11–AMPK–SIRT1–PGC-1α signaling pathway.
- Nuclear receptor Rev-erbα: up, down, and all around (2014)
- Nuclear receptor Rev-erbα: a heme receptor that coordinates circadian rhythm and metabolism (2010)
- Rev-Erb α dimers on RORE recruit NCoR (nuclear corepressor 1) in a Heme-dependent manner. NCoR recruits HDAC3
- Heme binding to Rev-Erbα induces feedback inhibition of its own synthesis (reducing ALAS1, via NPAS2/PGC-1α)
- In Brown Adipose (but not the liver), it promotes UCP1.
- Rev-erbα and Rev-erbβ coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic function
- Peaks in the liver (and brown adipose tissue. Wonder about the brain?) at mouse ZT 10 (and α is a bit higher) but so what, is this equivalent to 2 hours (before? After?) waking for humans? Considering that’s probably when they get up to start the
daynight.
- Peaks in the liver (and brown adipose tissue. Wonder about the brain?) at mouse ZT 10 (and α is a bit higher) but so what, is this equivalent to 2 hours (before? After?) waking for humans? Considering that’s probably when they get up to start the
- Behavioral Changes and Dopaminergic Dysregulation in Mice Lacking the Nuclear Receptor Rev-erbα
- Deficient mice had upregulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase, leading to increased hippocampal dopamine turnover. This lead to hyperlocomotion.
- This one is kind of surprising, maybe. Why does it repress TH?
- Decreased habituation in novel object paradigms and impaired short- and long-term memory.
- Deficient mice had upregulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase, leading to increased hippocampal dopamine turnover. This lead to hyperlocomotion.
(S)unifiram
Stimulates CAMK II and PKCα.
- Antagonizes barbituate-induced inhibition of glucose transport (as do racetams)
- [Pharmacological characterization of DM232 (unifiram) and DM235 (sunifiram), new potent cognition enhancers.]
- Increase Acetylcholine release in rat cerebral cortex.
- Unifiram increases fEPSP amplitude in rat hippocampal slices.
TAK-653
Rating: ★★★★. The impressionistic subjective report would be something like it makes everything slightly simpler, obvious, lubricated. Neboglamine can be described as quite similar except on the more behavioral side of things rather than cognitive. You can pretty much think of it like if observing the connections between things as nodes overlapping venn diagrams. TAK makes the overlapping bigger/more obvious. And realistically this corresponds nicely to what it’s doing physiologically. But for the first few days, it’s kind of a mess and can induce sensory overload and a dissociative feeling, because the context of those nodes is also part of the overlap. I.e., it’s hard to consciously parse these things into a more generalizable form if you know what I mean. (This might be mediated by A dentate gyrus-CA3 inhibitory circuit promotes evolution of hippocampal-cortical ensembles during memory consolidation) Whereas without TAK things feel more context/‘scale’-invariant, but as one might assume, that’s ultimately at the cost of nuance no? But after a few days though you just magically get used to it.
- A more selective TAK-137. Finally a bona-fide ampakine, as it has basically no agonist activity.
- Central nervous system effects of TAK-653, an investigational alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole receptor (AMPAR) positive allosteric modulator in healthy volunteers (Sep 2022)
- Improves Stroop test (proxy of Executive Function apparently): TAK-653 0.5 mg but not 6 mg decreased the number of correct responses in incongruent trials
- demonstrated a psychostimulant-like pharmacodynamic profile on the NeuroCart consistent with previously reported increase of cortical excitability following Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) of the human motor cortex.
- [Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of the investigational AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator TAK-653 after single and multiple rising doses in healthy volunteers]
- Tried 0.3-18mg.
- Maximum plasma concentrations were attained within 1.25 h to 5 h after dosing, the terminal half-life varied from 33.1 h to 47.8 h and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations were suggestive of rapid brain penetration
- Strictly regulated agonist-dependent activation of AMPA-R is the key characteristic of TAK-653 for robust synaptic responses and cognitive improvement (Suzuki et al. 15 July 2021)
- 3 and 10mg/kg in mice. The former had like a 20% greater effect on BDNF release after AMPA treatment.
- Did not show prominent subunit selectivity for homomeric AMPA-R
- In monkeys, the beneficial effect (~20%) on “delayed match-to-sample” task was maintained for 24 hours after administration. Its half life is 9.4 $\pm$ 3.8 hours at 0.03 mg/kg p.o in monkeys.
- Enhanced sustained attention in poor-performing mice. Increased novel objection recognition test results by like 10%. 0.03-0.3 mg/kg were all pretty similar.
- Ameliorated abnormal social interaction in models of schizophrenia (poly-I:C. No idea, but it made them complete antisocial and then back to near baseline)
- 10 μM in prefrontal cortex had the best effect on AMPAR-mediated EPSPs in the PFC: tripling EPSP duration and 6x the number of spikes.
- TAK-653, an AMPA receptor potentiator with minimal agonistic activity, produces an antidepressant-like effect with a favorable safety profile in rats (Dec 2021)
- 0.1 or 1 mg/kg p.o. The time to reach peak plasma concentration after the oral administration of TAK-653 at 1 mg/kg was between 1 and 2 h
- “Increased” phosphorylated and active forms of mTOR, P70S6, and AKT and ERK.
- Stimulated mTOR and BDNF production.
- Despite expectations, no relevant clinical effects have been demonstrated for the CX series.
- In vitro for 10 minutes wih 1μM tripled ERK phosphorylation. Nothing tooo crazy otherwise
- Virtually no agonist activity. Steric repulsion by GluR2 Ser750 of the closed AMPAR caused TAK-653 only to bind in the presence of a ligand.
- Otherwise, there would be some kind of bell-shaped dose-response curve whereby excess glutamate release could get you in big trouble.
- GluR2 Ser750 = GluR1 Ser743.
- [Novel AMPA Receptor Potentiators TAK-137 and TAK-653 as Potential Rapid-Acting Antidepressants (2021)]
THC
- Partial agonist of CB1 (25.1nM Ki), CB2 (35.2nM Ki), as well as other Endocannabinoid receptors like:
- ‘Orphan receptors’:
- GPR18 (0.96nM Ki)
- (N-Arachidonyl glycine receptor (indeed that’s a ligand, a metabolite of Anandamide) (but guess what it may not even an agonist))
- Resolvin (metabolite of DHA D2 is an agonist. Have I not heard about PUFAs and intraocular pressure?
- GPR18 ‘resolves’ inflammatory-responses.
- GPR55 (8.1nM Ki) (G13 G-protein coupled.)
- Forms heteromers with CB2
- Maybe GPR119 (endogenous ligand is Oleoylethanolamine but also binds is anandamide etc.)
- Expressed predominantly in the pancreas and GI; activation reduces food intake and weight gain.
- TRPV1/2, TRPA1
- GPR18 (0.96nM Ki)
- ‘Orphan receptors’:
- When cannabis is decarboxylated, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is converted into THC.
- When THC is taken orally, it is metabolized into 11-hydroxy-THC (then into 11-nor-9carboxy-THC), which are glucuronidated and excreted into the urine.
- Blocking both LTP and LTD makes sense why it’s used for escapism, no?
- PPAR-γ agonist.
- Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Disrupts Estrogen-Signaling through Up-Regulation of Estrogen Receptor β
- Suppresses Estradiol-induced MCF-7 cell proliferation. Inhibits E2-liganded ERα activation. Upregulates ERβ.
- Δ9-THC-caused synaptic and memory impairments are mediated through COX-2 signaling
- Mediated by the βγ of CB1.
- Ablation of COX-2 also eliminates Δ9-THC-impaired hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity, spatial, and fear memories.
- I’ve heard of problems regarding STAT3 though.
- Chronic cannabis promotes pro-hallucinogenic signaling of 5-HT2A receptors through Akt/mTOR pathway
- Supersensitive coupling of 5-HT2A toward inhibitory Gαi/o/etc. G proteins was observed, without alteration in canonical Gq signaling.
- Dissociation of the Pharmacological Effects of THC by mTOR Blockade
- Acute anxiogenic and amnesic-like effects were prevented by subchronic mTOR inhibition. But hypothermia, anxiolysis, etc.
- a clear tolerance to THC-induced anxiolysis, hypothermia, hypolocomotion, and antinociception was observed after chronic treatment, but not to its anxiogenic- and amnesic-like effects.
- The Role of Cannabinoids in Neuroanatomic Alterations in Cannabis Users (2016)
- Cannabinoid modulation of hippocampal long-term memory is mediated by mTOR signaling
- THC → GABAergic inhibition → NMDA signalling (!) → mTOR aberrant protein synthesis
- THC long-term memory deficits were mediated by CB1Rs expressed on GABAergic interneurons through a glutamatergic mechanism, as both the amnesic-like effects and p70S6K phosphorylation were reduced in GABA-CB1R knockout mice and by NMDA blockade.
- Hyper-priming in cannabis users: a naturalistic study of the effects of cannabis on semantic memory function
- Finding connections between unrelated concepts is due to ‘hyper-priming’ causing ‘fast and loose’ patterns of spreading activity.
- Bayesian causal network modeling suggests adolescent cannabis use accelerates prefrontal cortical thinning
Opioid
- Cannabis-Induced Hypodopaminergic Anhedonia and Cognitive Decline in Humans: Embracing Putative Induction of Dopamine Homeostasis
- it is possible to induce ‘dopamine homeostasis,’ that is, restore dopamine function with dopamine upregulation with the proposed compound and normalize behavior in chronic cannabis users with cannabis-induced hypodopaminergic anhedonia (depression) and cognitive decline
- I believe they’re referring to ‘Pro-Dopamine Regulator’ (KB220(Z)), which is an Enkephalinase inhibitor. As well as screening for risk alleles, and balancing dysfunctional dopamine with pro-dopamine reward genes - and they actually cite DAT1, D2, D4, and COMT.
- Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common mu1 opioid receptor mechanism (Tanda 1997)
- Increased extracellular dopamine concentrations selectively in the shell of the nucleus accumbens; these effects were mimicked by the synthetic cannabinoid agonist WIN55212-2.
- SR141716A, an antagonist of central cannabinoid receptors, prevented the effects of THC but not those of heroin. Systemic naloxone, or naloxonazine (selective μ-1 antagonist) infusion into the ventral tegmentum, prevented the action of cannabinoids and heroin on dopaine transmission.
- [Cannabinoid receptor and WIN 55 212‐2‐stimulated [35S]‐GTPγS binding in the brain of mu‐, delta‐ and kappa‐opioid receptor knockout mice (Latimer 1987)]: The efficacy of CB1 receptor activation by the cannabinoid agonist WIN 55 212-2 was dramatically reduced in the caudate-putamen of MOR knockout animals
- Cannabinoid withdrawal syndrome is reduced in double mu and delta opioid receptor knockout mice
- Acute effects and physical dependence were not modified in single deletion of μ-opioid receptor, δ-opioid receptor, or κ-opioid receptor.
- Antinociception and hypolocomotion induced by acute THC administration remained unaffected, whereas the hypothermic effect was slightly attenuated in these double knockout mice.
- During chronic THC treatment, knockout mice developed slower tolerance to the hypothermic effect, but the development of tolerance to antinociceptive and hypolocomotor effects was unchanged.
- The rewarding properties of THC, measured in the conditioned place preference paradigm, were reduced in knockout mice.
- Interestingly, the somatic manifestations of THC withdrawal were also significantly attenuated in mutant mice, suggesting that a cooperative action of MOR and DOR is required for the entire expression of THC dependence.
Neurotransmitters
I’d say it’s contentious.
- [Marijuana and Cholinergic Dynamics (Cheney 1981)]
- Modertate doses reduce acetylcholine release from the cat cortex, and reduces the rate of biosynthesis in the hypothalamic and striatal slices.
- Increases total brain Acetylcholine levels R R R; inhibits AChE
- Pre-treatment with D1 antagonist (barely) reduced THC-induced ACh release in PFCx and hippocampus. THC has been shown to increase DA release in Nucleus Accumbens via μ-Opioid Receptor-mediated mechanism in the VTA R
- Increases Pregnenolone synthesis via stimulation of CB1 (Gi/o), with it acting as an inhibitor reducing THC’s effects. R
- Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol decreases extracellular GABA and increases extracellular glutamate and dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex: an in vivo microdialysis study wtf?
- Delta(9)-THC (1 mg/kg, i.v.) significantly increased extracellular dopamine and glutamate levels and decreased GABA levels. These effects were prevented by the cannabinoid antagonist SR141716A
Prenatal
- Prenatal THC exposure raises kynurenic acid levels in the prefrontal cortex of adult rats
- [Cannabinoids promote embryonic and adult hippocampus neurogenesis and produce anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects (Jiang et al 2005)] wtf?
- Prenatal marijuana exposure and neonatal outcomes in Jamaica: an ethnographic study
- The neonates of heavy-marijuana-using mothers had better scores on autonomic stability, quality of alertness, irritability, and self-regulation and were judged to be more rewarding for caregivers.
Tropisetron
Rating: ★★★★. Laser focus, and it delivers every time. Not to mention it seems to be healthy and neuroprotective.
-
https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/uw3y4v/tropisetron_is_one_of_the_best_nootropics_v2/
-
https://old.reddit.com/r/NooTopics/comments/uu7se7/tropisetron_analysis_best_nicotinic_nootropic/
-
Inhibits IL-2 synthesis and transcription in stimulated T cells. Potent inhibitor of PMA+ionomycin-induced NF-κB activation, but TNF-α mediation is not affected.
-
Very anxiolytic. Also a lowering of rumination is confirmed in studies for the treatment of OCD.
-
- ~2.4 μM EC50 and 50 Imax for α7 nAChR partial agonism and 1.5 μM EC50 and 34 Imax @ α7β2 nAChR. And 20μM for α4 nAChR.
- Apparently has α3β4 nAChR blocking properties.
- 3 nΜ Ki for 5-HT3.
-
[The 5-HT3 antagonist tropisetron (ICS 205-930) is a potent and selective alpha7 nicotinic receptor partial agonist]
-
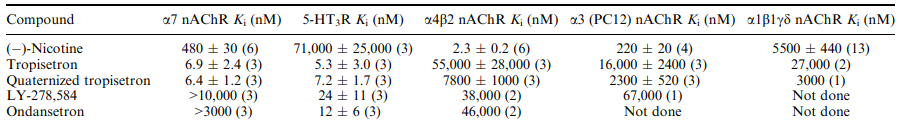
- 55 Ki on α4β2 nAChR isn’t nothing, I suppose.
-
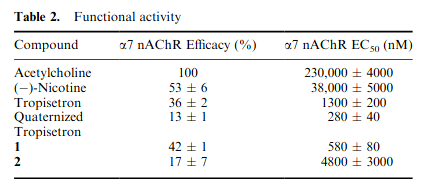 so 36% efficacy for α7, where ACh has 100%. Nicotine has 53% actually, but good luck getting it to ever bind.
so 36% efficacy for α7, where ACh has 100%. Nicotine has 53% actually, but good luck getting it to ever bind. - 1.3 μM EC50 for α7.
-
-
- The carbonyl oxygen in the ester linkage between the indole and tropane moieties contributes to stabilize a network of four water molecules located in the apical portion of the interface.
-
5-HT–induced alteration in the autophagy proteins LC3-II and p62 was significantly blocked by the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist tropisetron,…
-
- Inhibitory effects occur at micromolar concentrations, whereas the potentiating effects are shown here to occur at femtomolar concentrations at the homomeric alpha1 (glycine) receptor. Potentiation implying it only occurred in the presence of glycine.
-
- Administration of tropisetron at doses of 3 and 5 mg/kg (2x of 3) significantly increased the grooming activity time following the splash test. Forskolin showed similar results with 10 and 25 respectively. This is a nondepressive behavior.
-
- U-shaped curve for dopaminergic properties, with >5mg being the turning point.. This is what causes constipation, I think.
- Also interesting how there’s a Calcitonin increase after prolnged use?
-
- Minor 5-HT4 antagonism. This is what causes constipation, I think.
- This however showed partial agonism: 5HT4(a) and 5-HT4(b) receptors have nearly identical pharmacology and are both expressed in human atrium and ventricle
- Reduced the incidence of, or completely abolished, vomiting and retching induced by cytotoxic drugs such as cisplatin. Cytotoxic drugs cause gastrointestinal cellular damage which may result in the release of serotonin, activating vagal and possibly splanchnic afferent neurons which elicit the vomiting response. Tropisetron probably prevents emesis induced by cytotoxic agents by antagonising the effects of serotonin both at a peripheral (vagal) site and in the central nervous system at the terminus for vagal afferent fibres.
- Increased plasma and urine 5-HIAA in emetic patients.
- 52% for 20mg dose and 66% for 100mg dose Fischer et al 1992)
- Minor 5-HT4 antagonism. This is what causes constipation, I think.
-
Serotonin receptor type 3 antagonists improve obesity-associated fatty liver disease in mice.
- (.06 mg/kg HED) Tropisetron treatment significantly reduced liver fat content (-29%), liver inflammation (-56%), and liver cell necrosis (-59%) in ob/ob mice.
- Four-week-old ob/ob mice and lean controls were treated for 6 weeks orally with tropisetron or palonosetron at 0.2 mg/kg per day.
- Reduced liver fat content (-29%), liver inflammation (-56%), and liver cell necrosis (-59%). Decreased plasma Alanine Aminotransferase, and portal vein Endotoxin levels. Caused a reduction of elevated serotonin levels and an increase of SERT in the duodenum.
-
- Prolonged the theta and gamma currents
-
The acute effect of tropisetron on ECG parameters in cancer patients
- Did not result in QT interval, etc. @ 5mg IV.
-
https://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/Datasheet/t/tropisetronaftinj.pdf
- At very high repeated doses, visual hallucinations and, in patients with pre-existing hypertension, an increase in blood pressure, have been observed.
- At the 5 mg dose, constipation and, less frequently, dizziness, fatigue, somnolence, and gastrointestinal disorders, such as abdominal pain, diarrhoea and anorexia were observed as well.
Neuroprotection
- Tropisetron and its targets in Alzheimer’s disease (Hashimoto 2015)
- Promoted greater improvements in memory than current AD therapeutic drugs, such as memantine and Donepezil.
- WTF! The multi-functional drug tropisetron binds APP and normalizes cognition in a murine Alzheimer’s model
- Tropisetron as a neuroprotective agent against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity and mechanisms of action
- Neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity is mediated by α7 nAChR activation.
- caused internalization of NR1A
- activation of nAChRs in fetal rat cortical neurons by treatment with Nicotine and Donepezil caused internalization of glutamate receptors, resulting in attenuation of the glutamate induced Ca2+ influx, reduction in Caspase 3 activation, and protection of cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity.
- Decreases p38 levels.
- Several studies have suggested that Ca influx through activated nAChRs affects phosphorylation level of the p38 MAPK and Akt intracellular signaling pathways resulting in neuroprotection
- The effect of tropisetron on oxidative stress, SIRT1, FOXO3a, and claudin-1 in the renal tissue of STZ-induced diabetic rats
- Reversed decrease in SIRT1 and increase in NF-κB, p-FOXO3 and claudin-1.
- The multi-functional drug tropisetron binds APP and normalizes cognition in a murine Alzheimer’s model
- Incresed sAPPα/Aβ ratio; it binds directly to APP.
- Soluble amyloid precursor protein, which is actually a trophic factor. Inhibits caspase activation, cell eath, and neurite retraction.
- Aβ monomers eventually aggregate into soluble oligomers and insoluble plaques.
- Incresed sAPPα/Aβ ratio; it binds directly to APP.
- Reduces IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB and I’m sure other things in rat models of colitis. R
- Tropisetron upregulates cannabinoid CB1 receptors in cerebellar granule cells: Possible involvement of calcineurin
- It significantly inhibits calcineurin, which regulates the CB1 expression. Calcineurin is highly expressed in Granule Cells, and they do not express 5-HT3. Indeed, other calcineurin inhibitors like FK506/tacrolimus also increase CB1 expression.
- Constipating at ~10mg+.
Vinpocetine
-

-
PDE1 inhibitor, improving peripheral Vasodilation.
-
Compare to Ginkgo or Reserpine.
-
Inhibits The NF-κB cascade via inhibiting IKK.
-
-
Potent antioxidant. Used as a treatment for tinnitus.
-
Reduces neuronal calcium influx without blocking presynaptic Ca2+ channels.
-
[Effects of several cerebroprotective drugs on NMDA channel function: evaluation using Xenopus oocytes and [3H]MK-801 binding]
- These results suggest that the inhibition of NMDA channels by vinpocetine shows a similarity to the action of Zn2+ which closes the gate of the NMDA channel
-
[Vinpocetine preferentially antagonizes quisqualate/AMPA receptor responses: evidence from release and ligand binding studies.]
- Reduced the efflux of dopamine and acetylcholine evoked by glutamate, quisqualate and NMDA, but not that evoked by kainate**
-
- Seems to increase HO-1 and NF-κB inthis injury model unless I’m reading this wrong.
-
Unique alterations to the rheological properties of Red Blood Cells. Reduced MDA and increased GSH levels in models of neurological damage
-
Characterization of vinpocetine effects on DA and DOPAC release in striatal isolated nerve endings
- Does not modify baseline DA release or exocytotic release evoked by K+; it inhibits DA release evoked by veratridine reversal of DAT.
- Increases DOPAC levels suggesting an augmentation of dopamine metabolism, likely indepdendent of VSSC blockage, via increasing availability of the cytoplasm extravesicular DA; Impairs vesicular storage of Dopamine.
- Does not enhance MAO, rather it acts like reserpine (VMAT2 inhibitor (it’s over)) which decreases the monoaminergic tone.
- Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channel permeability, selectively inhibiting the transporter-mediated release of all neurotransmitters.
-
[Vinpocetine and Ischemic Stroke]
- Cerebral vasodilation enhances supply of oxygen & glucose, and ATP production.
-
[Psychopharmacological Effects of Vinpocetine in Normal Healthy Volunteers]
- Reported a lasting increase of cerebral 5-HIAA levels after treatment and transitorily enhanced 5-HT levels 2 h following (i.p.) treatment. Catecholamine levels were similarly increased 4-6 h following administration of vinpocetine.
- Twelve females age 25-40 had dose-dependent decrease in reaction time in this memory test thing. Placebo 600 and plumetted from 560 to 420 after 20=>40mg.
.](https://yana-log.net/img/nootropic.png)