- There is amyloidogenic processing, and nonamyloidogenic. The former is regulated by BACE1, the latter is α-secretase, which cleaves the dangerous stub (Forming the α-CTF (C-terminal fragment), or the APP intracellular domain (AICD)).
-
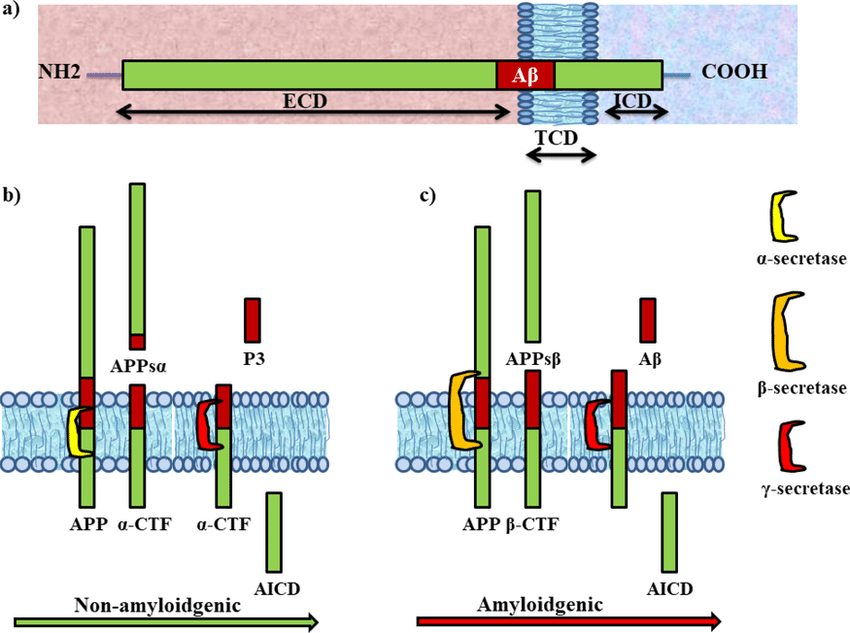
- Notice the fully intramembrane α-secretase. Real? Can’t be. Look at the cleavage site.
- Truncated and modified amyloid-beta species
-
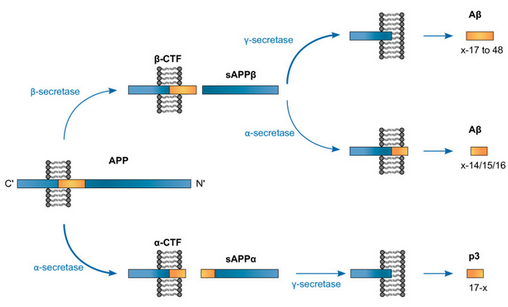 Note how there’s a possible BACE1→ADAM10 route. More fun is how there are other secretases like η and γ.
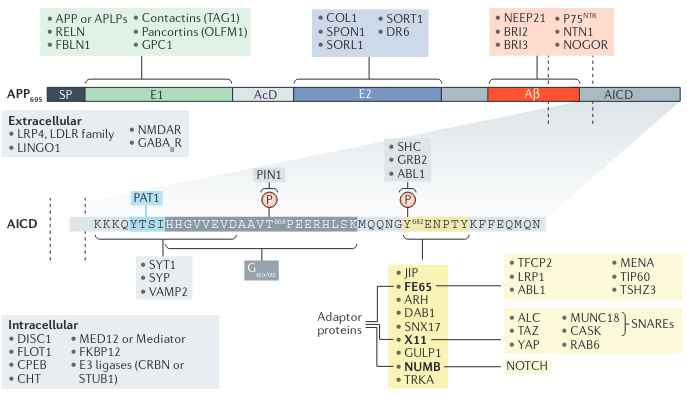
Note how there’s a possible BACE1→ADAM10 route. More fun is how there are other secretases like η and γ. - APP exists in several isoforms ranging from 695 to 770 amino acids in length, including the domain from which the Aβ peptide derives
-
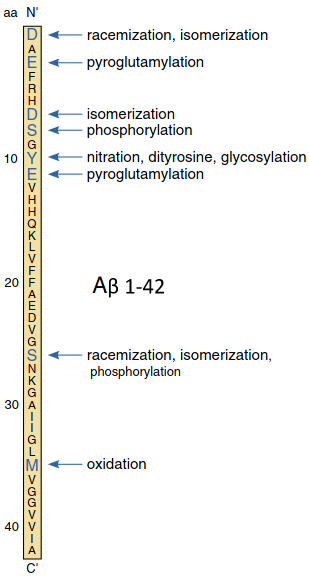
-
- Not just amyloid: physiological functions of the amyloid precursor protein family (Müller 2017) (Highly detailed, especially noncanonical δ/η stuff. But not super relevant.)
-
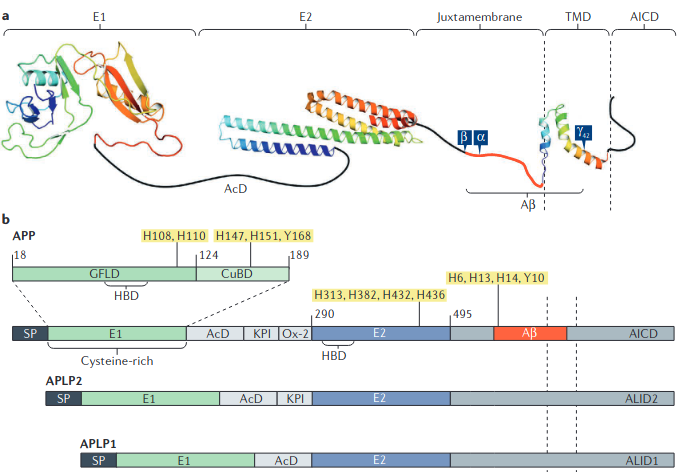
- Indeed RER is in that E2 domain.
-
-
- Spliced into three major isoforms, named according to the number of amino acids: APP695, APP751, and APP770.
- β-Secretases, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Down Syndrome
- In Down syndrome, APP is overexpressed on the cell surface. It exocytoses and Endosome mature, which is when BACE1 become more active with lower pH. Normally, P3 is able to be safely excreted, and I suppose it’s easy to excrete any Aβ:

- In Down syndrome, APP is overexpressed on the cell surface. It exocytoses and Endosome mature, which is when BACE1 become more active with lower pH. Normally, P3 is able to be safely excreted, and I suppose it’s easy to excrete any Aβ:
- Amyloid precursor protein compartmentalization restricts beta-amyloid production: therapeutic targets based on BACE compartmentalization
- ADAM17 inhibitor reduces constitutive and inducible α-secretase activity, but does not increase constitutive Aβ or sAPPβ.
- sAPP-α modulates β-secretase activity and amyloid-β generation
- Trafficking and Proteolytic Processing of APP
- ADAMs family members as amyloid precursor protein alpha-secretases
- Many of the ADAM proteins (not 12 tho) posess α-secretase activities: ADAM9, ADAM10, ADAM17/TACE, ADAM19
- Targeted disruption of individual genes that encode ADAM10/17/19 has no effect on constitutive α-secretase processing of APP, indicating that α-secretase activity is shared by a set of ADAM proteases. However: ADAM10 is the physiologically relevant, constitutive alpha-secretase of the amyloid precursor protein in primary neurons (Kuhn et al. 2010)
- Indeed, ‘α-secretase’ is/was not an identified enzyme, just something believed to be a metalloproteinase, with convincing evidence the main answer is ADAM10.
- ADAMs family members as amyloid precursor protein alpha-secretases
- The functional neurophysiology of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing pathway
- AD sees increased theta and delta, and decreased beta and alpha power.
- Successful encoding and recall of memory seems to necessitate simultaneous activation of PFC (association cortices) and Medial Temporal Lobe alongisde deactivation of the Default Mode Network!?
- Amyloid deposition is associated with impaired default network function in older persons without dementia
- So I did some looking: Evaluating functional connectivity of executive control network and frontoparietal network in Alzheimer’s disease: superior frontal gyrus and middle frontal gyrus of the executive network - and in the part paracentral Lobule of frontoparietal network have an increased functional connectivity, while the Superior Parietal Gyrus regions of FPN has shown decreased connectivity
sAPP (Secreted/Soluble APP)
- promotes mitochondrial protein synthesis and the traffixking of glua1 ampa, nr2a and nr2b nmda receptors to the cell surface by improving mitochondrial transport to synaptic vesicles to dwliver glutamate receptors to the cell surface.
- APP endocytosis and loss of alpha secretase processing/trafficking to synaptic vesicles and the accumulation of app intracellular domain presynaptically with increased processing at gamma and beta secretase leading to the formation of plaques, decline in mitochondrial homeostasis with endolysosomal accumulation of gangliosides, cholesterol, and iron s well as defects in the extracellular matrix lead to synaptic collapse, cell death, endothelial senescence as well as senescence throughout the body.This leads to the induction of alzheimers disease as well as aging itself
- Diseased neurons have less cholesterol and synthesize less neurosteroids because mitochondrial function breaks down and app undergoes endocytosis to the nucleus
- how we learn from activity dependant synaptic nmda receptor modulation is all dependant on sappa
- Ganglioside formation and cholesterol accumulation in the cell along with iron prevent app from being transported to synapses
- Cholesterol and ammonia accumulation within thw lipid membrane of neurons also reduced the axonal transport of sappa and may mediate an increase in soluble app alpha intracellular domain accumulation in the lipid membrane which promotes synaptic dysfunction
- In neurons this synaptic transport of sappa intracellularly acts presynaptically to increase gaba a receptor expression on the cell surface, reduces the expression of sodium transporters reducing exitability, and delivers nmda(?!) and ampa receptors to the synapse.
- sAPP-α is cleaved from APP via α-secretase (non-amyloidogenic processing).
- Iron dysregulates APP processing accompanying with sAPPα cellular retention and β-secretase inhibition in rat cortical neurons
- sAPPα remained in the cellular lysates instead of being secreted into the extracellular milieu. SAPPβ and Aβ levels were decreased.
- Ammonia induces amyloidogenesis in astrocytes by promoting amyloid precursor protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum
- Hyperammonemia increases mAPP (mature) content in astrocytes.
- BACE1 and γ-secretase are expressed in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol in APP trafficking and proteolytic processing, implications for Alzheimer’s disease
- Cholesterol and ammonia accumulation within the lipid membrane of neurons also reduced the axonal transport of sappa and may mediate an increase in soluble app alpha intracellular domain accumulation in the lipid membrane which promotes synaptic dysfunction. Removal of cellular cholesterol in senescent skin cell lines reverses the progression of cellular senescence and restores sappa transport to the cell membrane: Overexpression of Amyloid Precursor Protein Promotes the Onset of Seborrhoeic Keratosis and is Related to Skin Ageing
- Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Mediated Regulation of Ganglioside Homeostasis Linking Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology with Ganglioside Metabolism
- Ganglioside clusters in neuronal membranes take part in the formation of amyloid fibrils; GM1 increases Aβ production.
- Therapeutic Potential of Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein APPsα (Mockett 2017)
- Secreted amyloid-β precursor protein functions as a GABABR1a ligand to modulate synaptic transmission
- Directly bound the sushi 1 domain specific to GABA-B α1. Binding suppressed synaptic transmission and enhanced short-term facilitation via inhibition of synaptic vesicle release in mouse hippocampal synapses.
- Lentivirus-Mediated Expression of Human Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein-Alpha Promotes Long-Term Induction of Neuroprotective Genes and Pathways in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease (Ryan 2021)
- Upregulated key neuroprotective genes.
- Viral gene transfer of APPsalpha rescues synaptic failure in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model (Fol 2016)
- From synaptic spines to nuclear signaling: nuclear and synaptic actions of the amyloid precursor protein
- AICD regulates transcription: promotes p53, GSK-3β, BACE1, and - this one is good - neprilysin, a membrane metallo-endopeptidase. It degrades Amyloid β, as well as glucagon, enkephalin, substance P, neurotensin, oxytocin, etc.
Plasticity
- Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activation Stimulates α-Secretase Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing and Inhibits Amyloid-β Production
- A pool of APP is localized to the postsynaptic compartment in cortical neurons and observed partial overlap of APP with both NR1 and PSD-95.
- Increase in nonamyloidogenic APP processing, as expected, was inhibited by calcium chelation, NMDAR antagonist, or alpha secretase inhibitor, but not AMPAR antagonist or L-type calcium channel blocker.
- (NMDAR ->) SAP-97 mediates α-secretase ADAM10 trafficking and promotes its activity
- Glutamate Receptor Trafficking and Protein Synthesis Mediate the Facilitation of LTP by Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein-Alpha (Mockett 2019)
- Exposure converts short-lasting E(early)-LTP into protein-synthesis-dependent late LTP in hippocampal slices from male rats. These results are consistent with other studies suggesting that constitutive protein synthesis before LTP induction may be an important mechanism supporting L-LTP.
- Associated with CAMK II-mediated Ser831 enhancement. Ser845 was unaltered! Perhaps basal levels simply are sufficient. Yet, In a CAMK II and Protein Kinase G dependent manner, it promotes exocytosis of GluR2-lacking AMPARs, and NMDARs.
- CAMK II, ERK, and PKG-dependent stimulation of synaptic protein synthesis in synaptoneurosomes Secreted amyloid precursor protein-α upregulates synaptic protein synthesis by a protein kinase G-dependent mechanism (Claasen et al., 2009)
- So, PKG probably stimulates accessory proteins for AMPA’s surface accumulation, rather than Ser845.
- The secreted form of the Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid precursor protein stimulates a membrane-associated guanylate cyclase
- Inhibition of the formation of nitric oxide or carbon monoxide did not affect the ability of sAPP to lower rapidly intraneuronal calcium levels or elevate cGMP, suggesting that sAPP does not activate a soluble (cytosolic) guanylate cyclase.
- CAMK II, ERK, and PKG-dependent stimulation of synaptic protein synthesis in synaptoneurosomes Secreted amyloid precursor protein-α upregulates synaptic protein synthesis by a protein kinase G-dependent mechanism (Claasen et al., 2009)
- Cell surface receptor accumulation and LTP facilitation were present even after sAPPα washout and inhibition of receptor trafficking or protein synthesis, revealing a metaplastic capability of endogenous sAPPα administration.
- The idea is that the synapse’s previous history of activity determines its current plasticity.
- (Unlike BDNF) sAPPα does not by itself cause synaptic potentiation even though it is a potent stimulator of protein synthesis. Rather, it engages metaplasticity mechanisms, specifically a coordinated de novo protein synthesis and glutamate receptor trafficking that puts synapses in a state of readiness for future LTP and, presumably, learning
- No increase in the cell-wide levels of receptor subunits was detected following 30 min exposure to sAPPα, despite an increase of GluA1 and NR1/NR2..
- had no significant effect on LTD, indicating specificity for LTP modulation that bears a similarity to the pull–push effects of neuromodulation on LTP/LTD in visual cortex: PULL-PUSH NEUROMODULATION OF LTP AND LTD ENABLES BIDIRECTIONAL EXPERIENCE-INDUCED SYNAPTIC SCALING IN VISUAL CORTEX
- Previous studies have shown that Gs-coupled receptors directly promote LTP induction and Gq11-coupled receptors promote LTD.
- LTP and LTD An Embarrassment of Riches (2004) (>3k citations)
- Apparently E-LTP lasts ~60 minutes.
- They comment on the now dying idea that LTP involves presynaptic changes like via retrograde messengers like NO or AA. They think adhesion molecules are probably the right candidate if these presynaptic changes are worth looking at.
- LTP is induced by things like PKA/CAMKa IV/MAPK which activates CREB and Egr-1, etc.
- sAPPα may promote LTP by acting as a positive allosteric modulator at α7 nAChR! Distinct in vivo roles of secreted APP ectodomain variants APPsα and APPsβ in regulation of spine density, synaptic plasticity, and cognition (Ritcher 2018) (“The C terminal 16 amino acids that differentiate sAPPα from sAPPβ”)
- Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein-Alpha Promotes Arc Protein Synthesis in Hippocampal Neurons (Livingstone 2019)
- In vivo LTP in the dentate gyrus was depressed by ~50% by intra- hippocampal infusion of antibodies directed at sAPPa.
- Increase of synaptic density and memory retention by a peptide representing the trophic domain of the amyloid beta/A4 protein precursor
- Obviously the question is if this includes Ac-RER’s 3 amino acid sequences and what the differences are.
- Resulted in an 18% increase in the number of presynaptic terminals in the frontoparietal cortex. At the behavioral level, 17-mer-infused animals with nonimpaired learning capability showed an increased memory retention that seemed to interfere with reversal learning performance.
- Secreted form of beta-amyloid precursor protein shifts the frequency dependency for induction of LTD, and enhances LTP in hippocampal slices (Ishida 1997)
- LTD is harder to induce and LTP is easier to induce.
- Pretreatment of slices with 8-bromo-cyclic GMP mimicked the effect of sAPP alpha on LTD suggesting a role for cGMP in modulation of LTD. - this goes back to a dependence on PKG.
- Intrahippocampal infusion of sAPPα antibodies reduced LTP in the DG of adult rats by ~50%.
- [Acute function of secreted amyloid precursor protein fragment APPsα in synaptic plasticity]
- Memory-enhancing effects of secreted forms of the β-amyloid precursor protein in normal and amnestic mice
- The effects of APPss on LTD induction are in agreement with their cGMP-mediated ability to potently stimulate potassium currents, and hence decrease intracellular calcium levels: Activation of K+ channels and suppression of neuronal activity by secreted beta-amyloid-precursor protein - mimicked by cGMP analogue
- Signaling events regulating the neurodevelopmental triad. Glutamate and secreted forms of beta-amyloid precursor protein as examples (1997)
- counteract effects of glutamate on growth cone behaviors, and increase synaptic complexity. Acute actions of sAPPs appear to be transduced by cGMP which promotes activation of K+ channels and reduces [Ca2+]i.
- Signaling events regulating the neurodevelopmental triad. Glutamate and secreted forms of beta-amyloid precursor protein as examples (1997)
- The effects of APPss on LTD induction are in agreement with their cGMP-mediated ability to potently stimulate potassium currents, and hence decrease intracellular calcium levels: Activation of K+ channels and suppression of neuronal activity by secreted beta-amyloid-precursor protein - mimicked by cGMP analogue
- Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR1alpha stimulates the secretion of the amyloid beta-protein precursor ectodomain!
- mGluR1. It is coupled to APP processing via protein kinases and PLA2 (so probably Gp1’s Gq->Ca2+)
- Endogenous secreted amyloid precursor protein-alpha regulates hippocampal NMDA receptor function, long-term potentiation and spatial memory
- Pharmacological inhibition of alpha-secretase and other a-disintegrin-and-metalloproteases by TAPI-1 reduced both LTP and tetanus-evoked NMDA receptor-mediated currents in dentate granule cells… ==indicating that sAPPα is a key contributor to plasticity!==
- High concentrations of exogenous sAPPα strongly reduced LTP induction, indicating that signaling pathways inhibitory to LTP can also be activated
- The neuroprotective effects (PI3K/AKT, p42/p44, NK-κB) may be mediated by the N-terminal, while the Guanylate Cyclase/cGMP effects may be mediated by the C-terminal (which RER is not part of) - The effect of a secreted form of β‐amyloid‐precursor protein on intracellular Ca2+ increase in rat cultured hippocampal neurones (Koizumi 1998) Ca2+i elevation mimicked by amino terminal peptides of APPS, but not by carboxy terminal peptides. This sounds like the opposite of what they just said…
Neurogenesis
- beta-Amyloid precursor protein binds to the neurite-promoting IKVAV site of laminin
- sAPPα interupts APPL1-APPL2 dimerization, and this is how dendritic outgrowth occurs.
- Wtf are those?: Endosomal Adaptor Proteins APPL1 and APPL2 Are Novel Activators of β-Catenin/TCF-mediated Transcription
- Effectors of Rab5. Complexes with Reptin, β-catenin, HDAC1, and HDAC2.. Overexpression of either APPL protein relieves Reptin-dependent transcriptional repression and correlates with the reduced amounts of HDACs and β-catenin associated with Reptin as well as with the lower levels of Reptin and HDAC1 on the promoters of β-catenin target genes.
- Wtf are those?: Endosomal Adaptor Proteins APPL1 and APPL2 Are Novel Activators of β-Catenin/TCF-mediated Transcription
- sAPPα interupts APPL1-APPL2 dimerization, and this is how dendritic outgrowth occurs.
- Secreted amyloid precursor proteins promote proliferation and glial differentiation of adult hippocampal neural progenitor cells (Baratchi 2012)
- Soluble form of amyloid precursor protein regulates proliferation of progenitors in the adult subventricular zone (Caille 2004)
- The SVZ is major sAPP binding site, where binding occurs on EGFR-containing Progenitor Cells (not on the receptors themselves) which are the Type C cells for SVZ neurogenesis. They self-renew in the presence of EGF and differentiate into neurons and glia upon EGF removal. sAPP brinding sites are also pressent on Type A, but not B or ependymal cells.
- EGF stimulates sAPP secretion by NS cells and sAPP is required for full EGF mitogenic activity.
- Alzheimer’s shows very early odor discrimination defects! As do mice with reduced SVZ neurogenesis.
- The amyloid precursor protein controls adult hippocampal neurogenesis through GABAergic interneurons (Wang 2014)
- Selective deletion of GABAergic, but not glutamatergic (or progenitor cells) APP disrupts adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
- In case I needed reminding, this is important for maintaining excitatory-inhibitory balance of Granule Cells in the DG via these interneurons.
- Tonic GABAergic currents control network excitability in dentate gyrus: Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABA-A receptors (Farrant 2005)
- Important for Pattern Separation as well: Performance on a pattern separation task by Alzheimer’s patients shows possible links between disrupted dentate gyrus activity and apolipoprotein E ∈4 status and cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β42 levels
- GABA neurotransmission have been shown to influence key steps of hippocampal adult neurogenesis, ranging from progenitor proliferation to newborn neuron maturation and integration:
- Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology (Abrous 2005)
- GABA sets the tempo for activity-dependent adult neurogenesis (Ge 2007)
- GABAergic control of neurite outgrowth and remodeling during development and adult neurogenesis: general rules and differences in diverse systems (Sernagor 2010)
- GABAergic APP, possibly through the regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, controls a mouse’s cognitive ability to discriminate between similar contexts… this study addressed the question of in vivo actions of APP: increased proliferation of neural progenitor cells in APP−/− mice, and this is accompanied by reduced tonic GABA current recorded from granule cell.
- This view is in agreement with the recent finding that the activity of Parvalbumin+ interneurons regulates stem cell quiescence via GABA-A receptor-mediated tonic GABA signaling: Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision (Song 2012)
- In light of the reduced long-term survival of newborn neurons, it is possible that increased progenitor proliferation represents a compensatory response to diminished survival. (in APP-/- mice)
- Earlier work has shown that abolishing GABA-induced depolarization can result in defects in dendritic growth and synapse formation during adult neurogenesis:
- Amyloid Precursor Protein Regulates Cav1.2 L-type Calcium Channel Levels and Function to Influence GABAergic Short-Term Plasticity (Yang, Wang et al. 2009)
- In contrast, APP has not been shown as an essential regulator in controlling excitatory synaptic strength as a few earlier studies reported normal efficacy of excitatory hippocampal synapses both in dentate gyrus and area CA1 of APP−/− mice (Seabrook 1999, Ring 2007, Jedlicka 2012)
- Secreted forms of beta-amyloid precursor protein modulate dendrite outgrowth and calcium responses to glutamate in cultured embryonic hippocampal neurons (1994)
- Intracellular messengers in the generation and degeneration of hippocampal neuroarchitecture (1988)
- Micro levels of glutamate caused regression of dendrites but not axons. Millimolar levels caused cell death.
- Calcium ionophore and PKC activator caused regression of dendrites and axons.
- Forskolin enhanced outgrwoth rates of dendrites and axons.
- Co2+ (cobalt? wtf?) and trifluoperazine each significantly reduced glutamate-induced dendritic regression and neurotoxicity suggesting that calcium influx and/or PKC activation mediated glutamate’s actions.
- Intracellular messengers in the generation and degeneration of hippocampal neuroarchitecture (1988)
- [Amyloid precursor protein regulates differentiation of human neural stem cells (Kwak 2006)]
- sAPP binds to the surface of neural stem cells (And neuroblasts) (in the SVZ) - and regulates their proliferation and differentiation
- Activity requires soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha to promote neurite outgrowth in neural stem cell-derived neurons via activation of the MAPK pathway
- “Activity”…?
- Required active NMDAR + MAPK/ERK recruitment to induce neurite outgrowth.
- Acute depolarization led to a sharp increase in phosphorylated ERK (with fast kinetics) and such an increase was abolished by blockade of NMDAR.
- And continuous generation of sAPPα was necessary for this! Though acute sAPPα administration did not lead to ERK activation.
- This shows that basal levels of p-ERK are mostly due to endogenous activation of NMDAR and that, as in more mature neurons, also in neurons differentiating from neural stem cells ERK phosphorlation is a downstream event of NMDAR activation.
- Acute application of sAPPα did not directly affect ERK phosphorylation either in the presence or in the absence of depolarization. However, in the absence of depolarization, sAPPa enhanced the effect of APV (an NMDAR antagonist) in preventing ERK phosphorylation
- Acute depolarization led to a sharp increase in phosphorylated ERK (with fast kinetics) and such an increase was abolished by blockade of NMDAR.
- APP gene family encompasses APP and two other related proteins, amyloid precursor-like protein 1 (APLP1) and APLP2.
- “soluble amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (sAPLP2),” but not sAPLP1 is functionally redundant to sAPP in this neurite outgrowth stuff.
- The regulation of amyloid precursor protein metabolism by cholinergic mechanisms and neurotrophin receptor signaling
- Cleavage of APP to release sAPPα is enhanced by membrane depolarization andor activation of cell surfface receptors like M1 AChR/M3 AChR (Via Gq) and EGFR. BDNF→TrkA & p75 respectively increase processing and trascriptional regulation of APP.
- And indeed α-secretase activity is increased by Protein Kinase C activation - and possibly so does depolarization if it means Ca2+ influx.
- Brothers in arms: proBDNF/BDNF and sAPPα/Aβ-signaling and their common interplay with ADAM10, TrkB, p75NTR, sortilin, and sorLA in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease
-
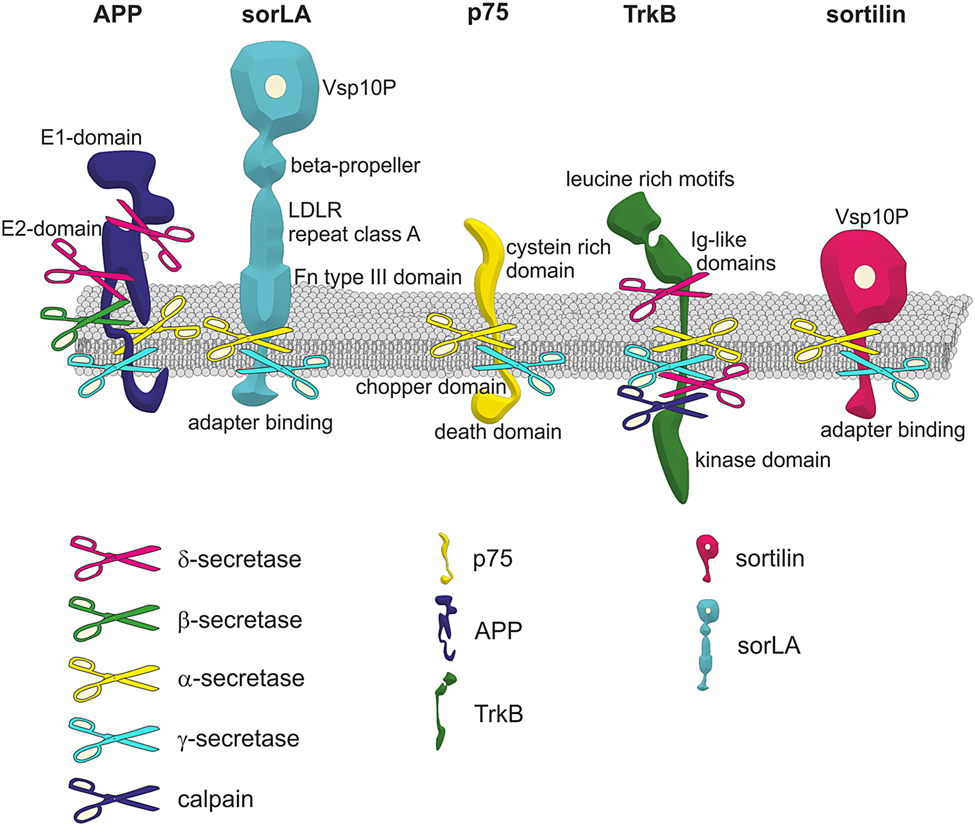 looks like BACE is restricted to APP, but interesting how ADAM10 cleaves TrkB!!
looks like BACE is restricted to APP, but interesting how ADAM10 cleaves TrkB!!
-
- Cleavage of APP to release sAPPα is enhanced by membrane depolarization andor activation of cell surfface receptors like M1 AChR/M3 AChR (Via Gq) and EGFR. BDNF→TrkA & p75 respectively increase processing and trascriptional regulation of APP.
- Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein Alpha, a Neuroprotective Protein in the Brain Has Widespread Effects on the Transcriptome and Proteome of Human Inducible Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Glutamatergic Neurons Related to Memory Mechanisms (2022) - interesting figures on protein expression changes.
- The amyloid precursor protein is a conserved Wnt receptor (Liu 2021)
- Binds WNT3a and WNT5a. Wnt3a binding promotes full-length APP (flAPP) recycling and stability. In contrast, Wnt5a promotes APP targeting to lysosomal compartments and reduces flAPP levels
- Loss of APP results in increased axonal and reduced dendritic growth of mouse embryonic primary cortical neurons.
- Regulates IGF-2: [Secreted amyloid precursor protein-α mediates neuroprotection and gene expression (Morris 2011)] - this paper is nowhere to be seen.
-
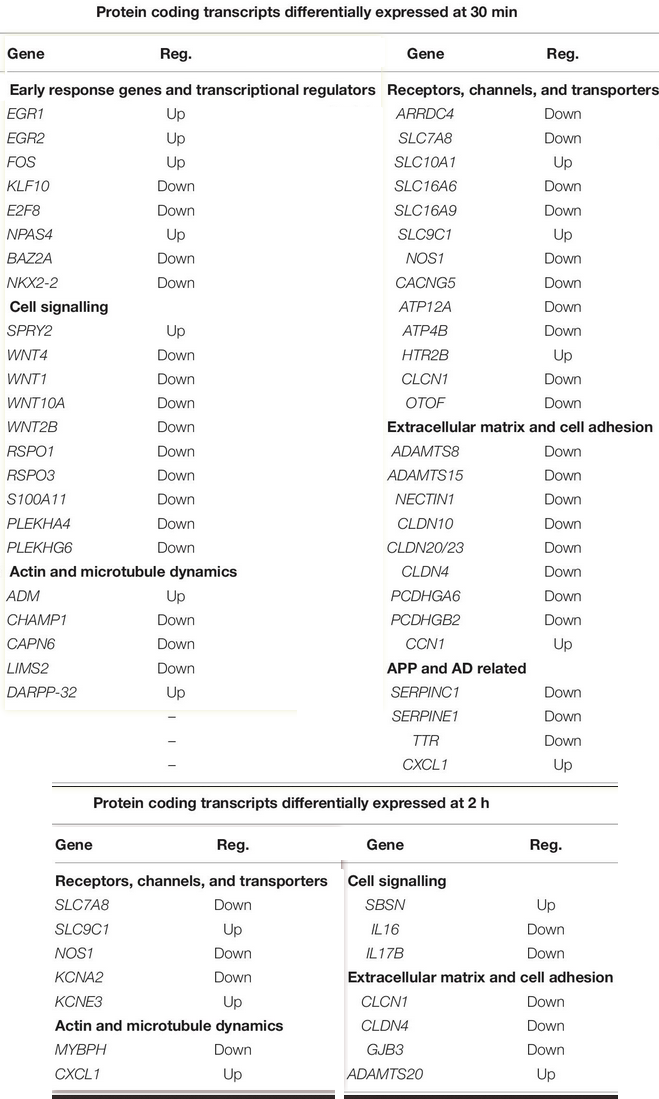
-
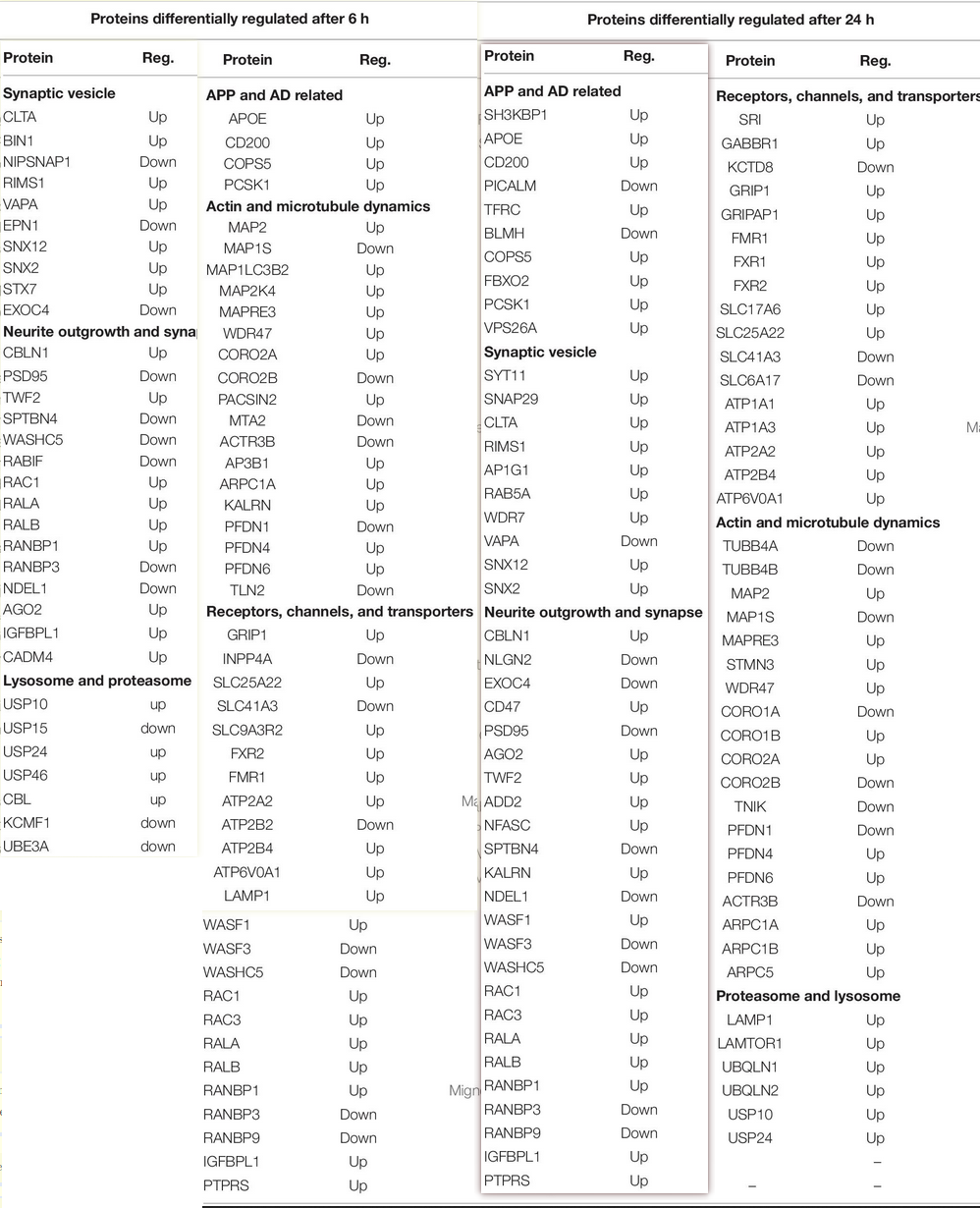
- Arp C1A (ARP 2/3 complex subunit 1A) up:
- Some of these things are a bit strange. PSD-95 down?
- The amyloid precursor protein is a conserved Wnt receptor (Liu 2021)
- Not neurogenesis, but we even see thyrocyte proliferation: Growth regulation of rat thyrocytes (FRTL-5 cells) by the secreted ectodomain of beta-amyloid precursor-like proteins
Autism
- Pax says this is something of a misunderstanding regarding the endocytosis of APP: tied to defects in mitochondrial function from cholesterol and ammonia handling issues with failure of autophagy mediated secretion of sappa to synaptic vesicles. The sappa is high but it stays in the mitochindria and never leaves the nucleus
- Autism genes and the leukocyte transcriptome in autistic toddlers relate to pathogen interactomes, infection and the immune system. A role for excess neurotrophic sAPPα and reduced antimicrobial Aβ
- There are 206 ‘Autworks’ genes (i.e. implicated in Autism) that are localized in the immune system. Many autism genes converge on APP processing, tilting this axis: in contrast to Alzheimer’s disease, levels of the antimicrobial peptide beta-amyloid are decreased and the levels of the neurotrophic/myelinotrophic soluble APP alpha are increased in autism, together with an increased activity of α-secretase.
- sAPPα induces an increase in glutamatergic and a decrease in GABA-ergic synapses creating and excitatory/inhibitory imbalance that has also been observed in autism.
-
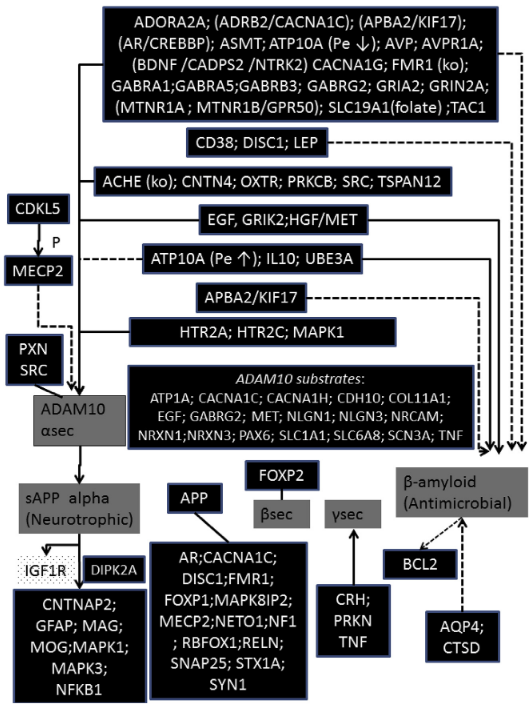
- Interesting substrates here for ADAM10…Neuroligin1/3, EAAT1
- SLC1A1:
- SLC6A8: Sodium- and chloride-dependent creatine transporter 1
- Gene expression profiling in the stress control brain region hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus reveals a novel gene network including Amyloid beta Precursor Protein
-
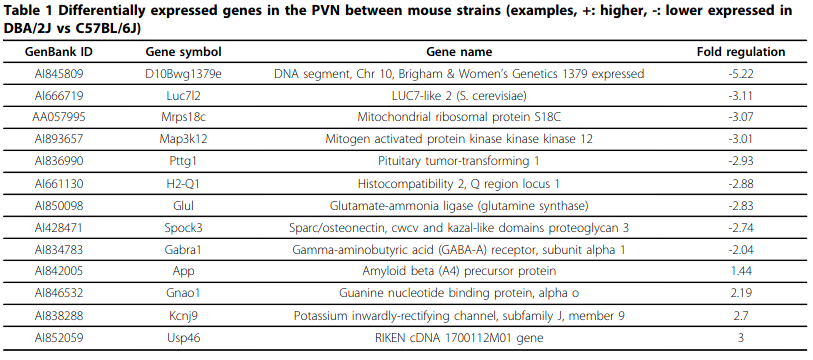
- ADAM10 is differentially down/upregulated in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice respectively. DBA/2J also expresses 1.44x APP and -2x GABA-A α subunit.
-
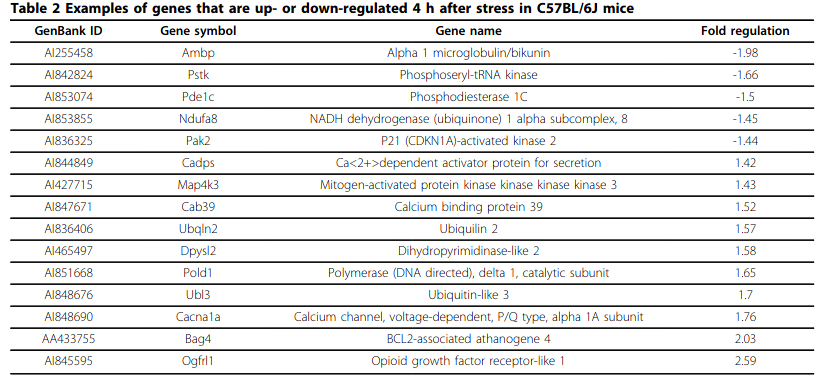
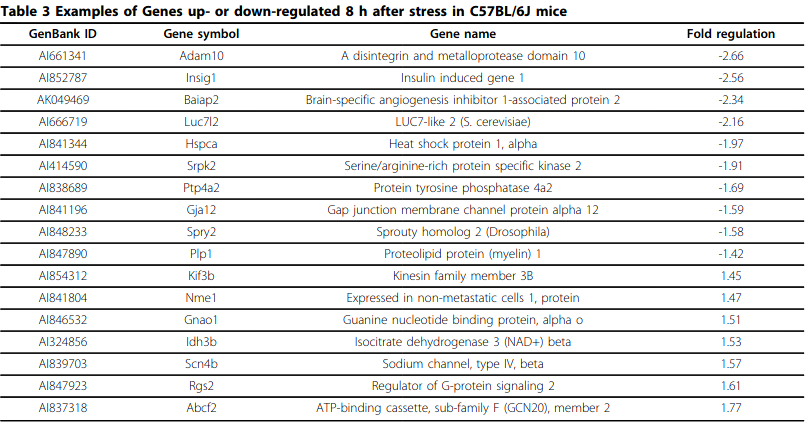
- PDE1C downregulation during stress is interesting…
-
- Autism as early neurodevelopmental disorder: evidence for an sAPPα-mediated anabolic pathway
- sAPPa simulates both neuroprotection and microglial activation - leading to neuronal overgrowth + infallatmion simultaneously.
-
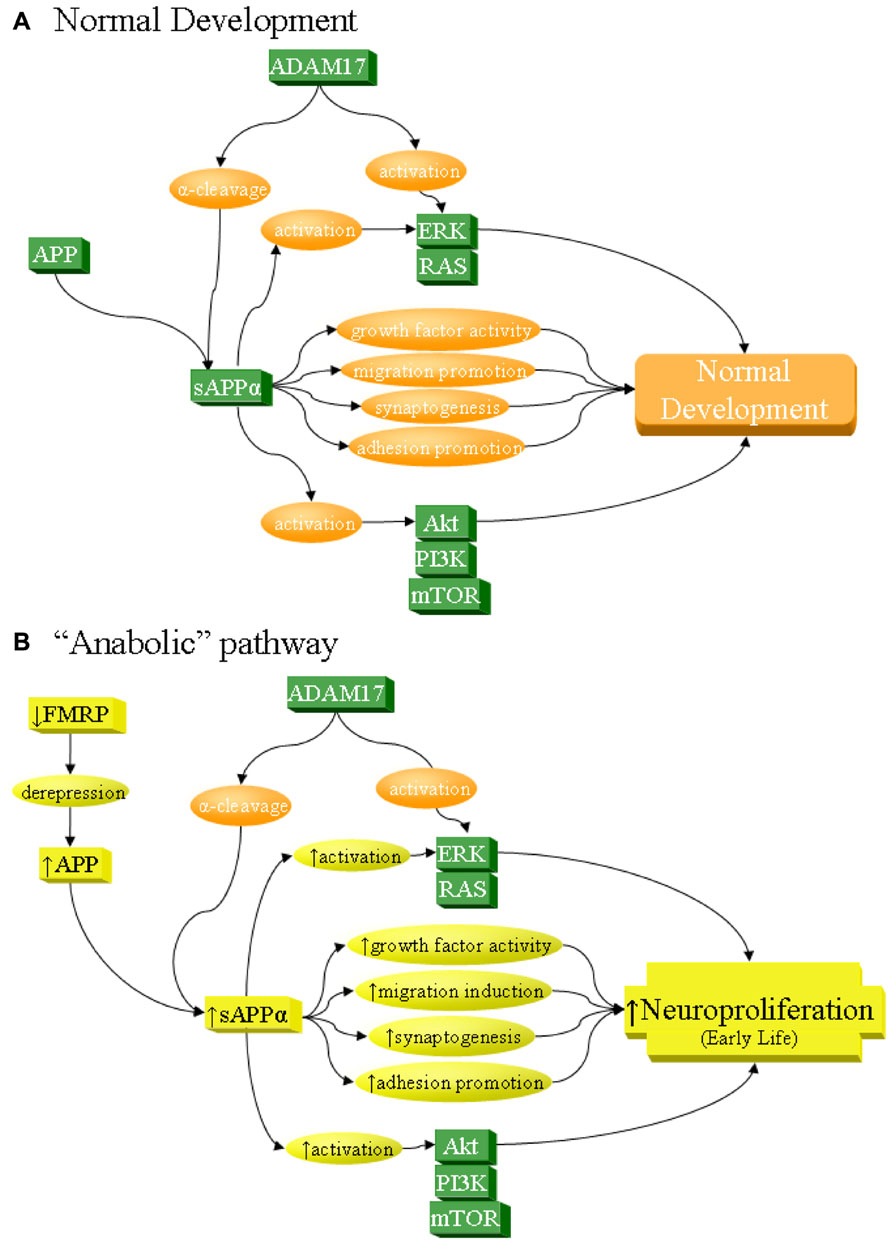
- Note FMRP downregulation leading to depression and a rise in APP->autism pipeline: Autistic behavior in children with fragile X syndrome: prevalence, stability, and the impact of FMRP 25% of boys with FXR had ’tism.
- Not to say sAPPα has an effect on FMRP. It’s all downstream.
- FMRP mediates mGluR5-dependent translation of amyloid precursor protein and indeed as the figure shows, sAPPα and sAPPβ/Aβ is elevated in autism.
- mGluR5 displaces FMRP from negatively regulating APP transcription! In the absence of FMRP (so FXS), APP synthesis is constitutively increased and nonresponsive to mGluR-mediated signaling.
- Genetic downregulation of mGluR5 signaling has reversed behavioral deficits in fmr-1 knockout mice
- Increased Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein-α (sAPPα) in Severe Autism: Proposal of a Specific, Anabolic Pathway and Putative Biomarker (2011)
FMRP
-
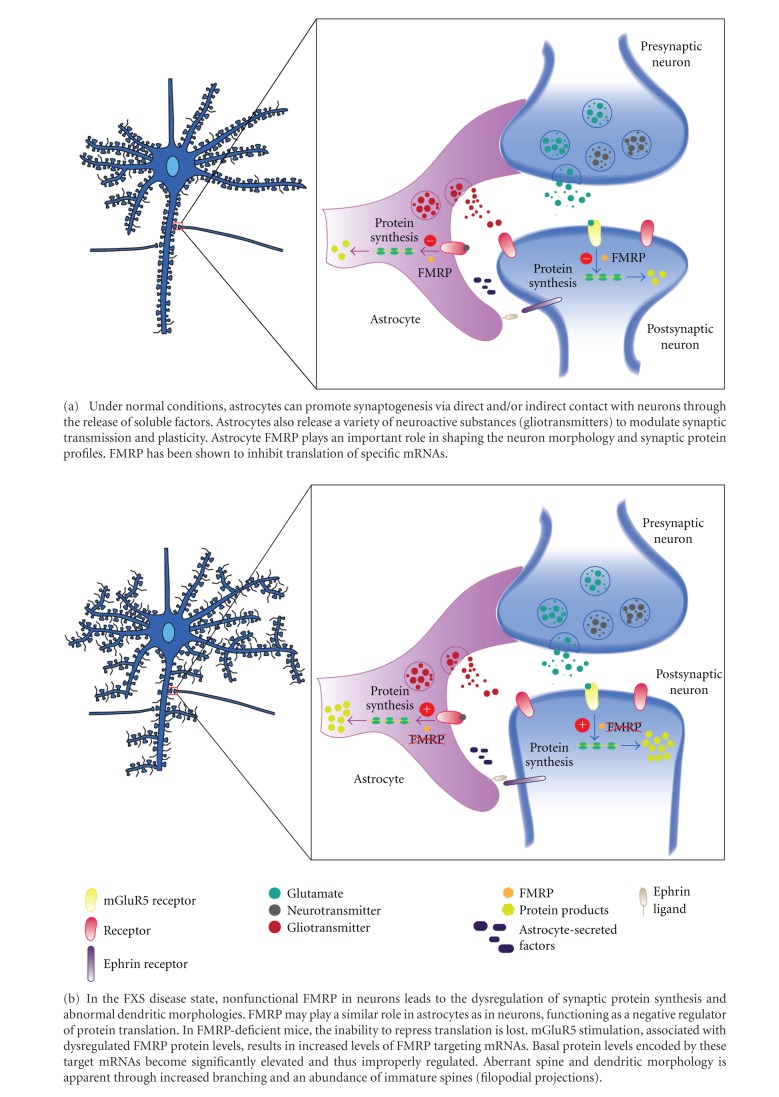
- Astrocyte FMRP plays an important role in shaping the neuron morphology and synaptic protein profiles. It inhibits excess protein synthesis, leading to increased branching and thus the abundance of immature spines (so maybe not necessarily ‘over-mature’ ones)
- Indeed it is synthesized in neurons, meaning both Gp1 mGluR are implicated. Is the transcription it not just calcium influx regulated? What’s special about mGluR?
- Roles of Calcium-Stimulated Adenylyl Cyclase and Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase IV in the Regulation of FMRP by Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (2008) this is in the ACC.
- Ca2+->CaM->AC->PKA->CAMK IV->CREB->Fmr1.
- Ca2+->CaM->CREB
- Metabotropic glutamate receptors activate FMRP in the anterior cingulate cortex through calcium-dependent signaling pathways (2007)
- FMRP Phosphorylation Reveals an Immediate-Early Signaling Pathway Triggered by Group I mGluR and Mediated by PP2A
- Rapid mGluR1 (<1 min) -> PP2A -> rapid dephosphorylation.
- Extended mGluR activation (1-5 mins) -> mTOR inhibiting PP2A, facilitating FMRP rephosphorylation.
- Roles of Calcium-Stimulated Adenylyl Cyclase and Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase IV in the Regulation of FMRP by Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (2008) this is in the ACC.
- Fragile Xsyndrome is the second most common form of mental retardation, second only to down syndrome overall.
- Gq-dependent: The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation (Gp1 = postsynaptic group 1, aka mGluR1/mGluR5.)
- FMRP is synthesized in response to mGluR5 activation. When mGluR5 upregulated (it has beentheorized that could be the case in Autism, at least in some areas. Might be more to do with sAPPα) or FMR1 is knocked out (FXS) then FMRP-mediated translation repression is overshadowed/prevented, and results in protein synthesis-dependent LTD:
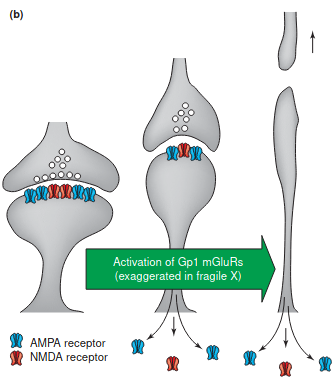
- Increased synapse loss and/or turnover, both requiring mRNA translation, and if exaggerated could account for the delay in synaptic maturation and elongated spines, i.e.:
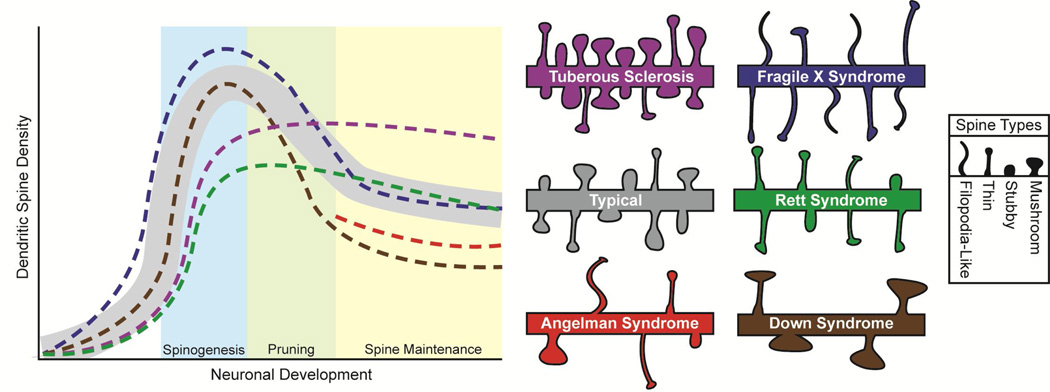
- Increased synapse loss and/or turnover, both requiring mRNA translation, and if exaggerated could account for the delay in synaptic maturation and elongated spines, i.e.:
- I am a bit confused. mGluR is just like anything else; transient activation is LTP, but prolonged agonism is LTD? They’re being weird about it.
- Just makes me wonder what these proteins are that are upregulated?? This has been hard to investigate apparently.
- What’s so special about mGluR1/5? What about other modes of Ca2+ influx?
- FMRP is synthesized in response to mGluR5 activation. When mGluR5 upregulated (it has beentheorized that could be the case in Autism, at least in some areas. Might be more to do with sAPPα) or FMR1 is knocked out (FXS) then FMRP-mediated translation repression is overshadowed/prevented, and results in protein synthesis-dependent LTD:
(Ac-)rER
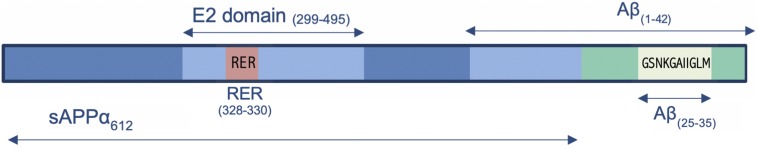
- NH2-(D-arg)-(L-glu)-(D-arg)-COOH. Ac/NAc = N-acetylated. These are AAs 328-330 of APP. Not the exact same thing as RER.
- N-terminal acylation of RER protects it against rapid degradation.
- Deacetylated, the first Arg is L, I think. But notice it is palindromic.
- It is such a small sequence, it associates with mitochondria.
- Soluble amyloid precursor protein: a novel proliferation factor of adult progenitor cells of ectodermal and mesodermal origin
- The Tripeptide RER Mimics Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein-Alpha in Upregulating LTP (Morrissey 2019)
-
- Protects ’newly formed engrams’ from interference.
- Also binds to HSC71 (heat shock cognate 71) and Syntaxin binding protein STXBP1. HSC71 hyperphosphorylation is seen in AD.
- sAPPα is too large to crossthe cell membrane.
- Defective neurite extension is caused by a mutation in amyloid beta/A4 (A beta) protein precursor found in familial Alzheimer’s disease
- Deletion of RERMS (328-332) sequencing from sAPPα removes its ability to protect against Aβ insult although this may have disrupted the structure of the coiled coil where the RER resides in the E2 domain.
-
- The peptide sequence Arg-Glu-Arg, present in the amyloid precursor protein, protects against memory loss caused by A beta and acts as a cognitive enhancer (2004) nothing special; some old references on plasticity in discussion section
- RER binding is displaced from longer peptides derived from APP’s external domain, but not Aβ. (So like sAPP and Aβ?) likely competing for binding to a putative receptor.
- The memory enhancing effect of the APP-derived tripeptide Ac-rER is mediated through CRMP2
- It is binding partners with CRMP2, Syntaxin binding protein 1, and Hsp70.
- Collapsin Response Mediator Protein-2 (CRMP2) is a Plausible Etiological Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease: Comparison and Contrast with Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau
- Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein-Alpha Enhances LTP Through the Synthesis and Trafficking of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors (Livingstone 2021)
Dosing
Orally active. 12 hour half life.
- Picogram doses - wtf.
